Need help finding what you are looking for?
Contact Us
PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1693546

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1693546
South America Vegetable Seed - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
PUBLISHED:
PAGES: 301 Pages
DELIVERY TIME: 2-3 business days
SELECT AN OPTION
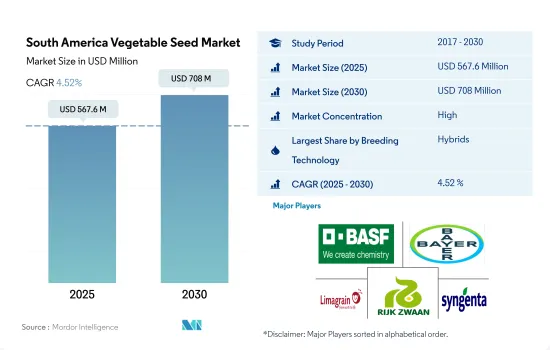
The South America Vegetable Seed Market size is estimated at 567.6 million USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 708 million USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 4.52% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Hybrids dominate the South American seed market due to their high usage in protected cultivation and their ability to produce high yields consistently
- In 2022, hybrids accounted for the major share compared to open-pollinated varieties, with a value of USD 361.4 million in 2022 in the South American vegetable seed market because the demand for hybrid seeds is high due to benefits such as drought tolerance, adaptability to the soil, and higher yield than open-pollinated seed varieties.
- The hybrids segment is estimated to register a CAGR of 9.1% during the forecast period because of the increase in the usage by farmers, companies providing new hybrid seed varieties, and benefits such as resistance to diseases, weather conditions, and pest attacks.
- The cultivation area of vegetables using hybrid seeds has increased from 627.3 thousand ha in 2017 to 695.4 thousand ha in 2022 because of the high usage of hybrids in crops such as tomatoes, garlic, and lettuce.
- In protected cultivation, the share of hybrid seeds was 100% because OPVs cannot be used in protected cultivation due to limitations such as the required insects or pests to be pollinated naturally; in protected cultivation, there is no natural pollination.
- Major companies, such as Syngenta, Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel BV, and Enza Zaden, are also focused on providing improved hybrid seed varieties that are tolerant to viral diseases and are resistant to boltings and mildews.
- Open-pollinated seed varieties are used by small-scale farmers because of the low prices of seed, helping save input costs, but the crop damage is high as pests can attack the crop. This is expected to be a restraint in the growth of open-pollinated seed varieties during the forecast period.
- Therefore, the sales of hybrid seeds are estimated to increase during the forecast period due to benefits such as higher yield and the production of high-quality vegetables.
Brazil dominated the market with a higher area under cultivation
- In 2022, South America's share in the global vegetable seed market was about 6.9% because Chile is a leading exporter of seeds, has favorable weather conditions, and has a high demand for domestic and global vegetables.
- The cultivation area for vegetables increased from 5.2 million ha in 2018 to 5.3 million ha in 2022 because of the increase in the demand for vegetables and high prices, leading to high profits. Therefore, more seeds are expected to be required for cultivation during the forecast period.
- Brazil is the major country in the region, which accounted for 35.5% of the market share in 2022. The cultivation area of vegetables in Brazil increased by 1.2% from 2019 to 2022 because of the demand for vegetables for different types of salads, high-value crops, and high return on investment. Therefore, sales of vegetable seeds in the country are projected to increase during the forecast period.
- Argentina is the second major country in the region. The cultivation area of vegetables in Argentina increased from 0.19 million ha in 2017 to 0.2 million ha in 2022. The increase in cultivation area was due to different initiatives by the government and high-value crops. Therefore, sales of vegetable seeds are estimated to increase during the forecast period.
- The Rest of South America is expected to register a CAGR of 4.07% from 2023 to 2030 because of favorable weather conditions for different vegetable crops, especially tomatoes, onions, and potatoes.
- Therefore, factors such as an increase in the cultivation area, new technological advancements, and high demand for vegetables are expected to fuel the growth of the South American vegetable seed market during the forecast period.
South America Vegetable Seed Market Trends
Chili is experiencing the fastest growth in cultivation area among vegetables in the region, driven by rising prices and consumption of chili
- South America is one of the largest producers of vegetables in the world. The area cultivated under vegetables reached 5.3 million hectares in 2022, which decreased by 1.7% between 2017 and 2022. This was due to the growing adoption of protected cultivation that offered higher yields in smaller areas. This led to a reduction in the region's overall cultivation area needed for vegetables. In South America, Brazil is the major vegetable producer. It accounted for 25.3% of the South American vegetable cultivated area, with 2.4 million hectares in 2022. The vegetable-cultivable land in the country decreased by 3.1% between 2017 and 2022 due to a shift toward protected cultivation.
- By cultivation area, roots and bulbs were the largest segments in South America. They accounted for 32.4% of the region's total vegetable area in 2022, as potatoes and other roots and bulbs are the staple food in the region. However, the total area under roots and bulbs decreased from 3.16 million ha in 2017 to 3.11 million ha in 2022 due to a shift toward other profitable crops such as cotton and soybean. Potato is one of the major vegetables cultivated in South America. The total area under potato production in South America was around 937.1 thousand ha in 2022, which decreased by 1.8% since 2017 due to increased temperatures and pest incidences in the traditional growing areas in Peru. Furthermore, other major vegetable crops cultivated in the country are onion, cabbage, peas, and chili. Between 2017 and 2022, the region's chili cultivation area increased by 14.6% due to rising prices and chili consumption.
- Therefore, the growing adoption of precision farming techniques and protected cultivation is estimated to limit South America's expansion of vegetable cultivation areas.
Disease resistant is the primary trait preferred in onion and lettuce cultivation to combat diseases such as pink root, bolting, and others.
- Lettuce is a high-value exotic vegetable that is widely consumed across the region. With the growing demand for high-quality foods, especially for exports, farmers have been cultivating lettuce using high-quality seeds that possess multiple desirable traits. Disease resistance is the most popular trait preferred in the region, including resistance to tip burn, pythium, and bolting diseases.
- Major companies like Limagrain, Rijk Zwaan, and Enza Zaden offer cultivars with these multiple traits. Other significant traits include wider adaptability, quality attributes such as a high number of leaves, soft leaves, good coloration, extended shelf life, uniformity in producing consistent heads, and early maturation varieties. Farmers are interested in cultivating such varieties to meet market demands and maximize profits.
- Similarly, onions are the leading root and bulb vegetables consumers use for seasoning and in various cuisines. Farmers in the region are cultivating onion seeds with traits that offer high yields, resistance to diseases like pink root and phytophthora, extended storage capacity, uniform bulb size, and desirable attributes such as bulb color and size. To meet market demand and increase profits, companies such as Bayer, Basf, Enza Zaden, Sakata, and Rijk Zwaan offer seed traits that help growers achieve high returns. Popular brands like BASF (Nunhems), Bayer (Seminis), and Limagrain (Vilmorin) have extensive catalogs of onion seeds that are commercially sold in the region.
- Therefore, the demand for high-quality vegetables with disease-resistant traits, quality attributes, and extended shelf life is anticipated to drive the market during the forecast period.
South America Vegetable Seed Industry Overview
The South America Vegetable Seed Market is fairly consolidated, with the top five companies occupying 87.27%. The major players in this market are BASF SE, Bayer AG, Groupe Limagrain, Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel BV and Syngenta Group (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
Product Code: 92613
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Area Under Cultivation
- 4.1.1 Vegetables
- 4.2 Most Popular Traits
- 4.2.1 Onion & Lettuce
- 4.2.2 Tomato, Pumpkin & Squash
- 4.3 Breeding Techniques
- 4.3.1 Vegetables
- 4.4 Regulatory Framework
- 4.5 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Breeding Technology
- 5.1.1 Hybrids
- 5.1.2 Open Pollinated Varieties & Hybrid Derivatives
- 5.2 Cultivation Mechanism
- 5.2.1 Open Field
- 5.2.2 Protected Cultivation
- 5.3 Crop Family
- 5.3.1 Brassicas
- 5.3.1.1 Cabbage
- 5.3.1.2 Carrot
- 5.3.1.3 Cauliflower & Broccoli
- 5.3.1.4 Other Brassicas
- 5.3.2 Cucurbits
- 5.3.2.1 Cucumber & Gherkin
- 5.3.2.2 Pumpkin & Squash
- 5.3.2.3 Other Cucurbits
- 5.3.3 Roots & Bulbs
- 5.3.3.1 Garlic
- 5.3.3.2 Onion
- 5.3.3.3 Potato
- 5.3.3.4 Other Roots & Bulbs
- 5.3.4 Solanaceae
- 5.3.4.1 Chilli
- 5.3.4.2 Eggplant
- 5.3.4.3 Tomato
- 5.3.4.4 Other Solanaceae
- 5.3.5 Unclassified Vegetables
- 5.3.5.1 Asparagus
- 5.3.5.2 Lettuce
- 5.3.5.3 Okra
- 5.3.5.4 Peas
- 5.3.5.5 Spinach
- 5.3.5.6 Other Unclassified Vegetables
- 5.3.1 Brassicas
- 5.4 Country
- 5.4.1 Argentina
- 5.4.2 Brazil
- 5.4.3 Rest of South America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles
- 6.4.1 BASF SE
- 6.4.2 Bayer AG
- 6.4.3 Bejo Zaden BV
- 6.4.4 Enza Zaden
- 6.4.5 Groupe Limagrain
- 6.4.6 KWS SAAT SE & Co. KGaA
- 6.4.7 Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel BV
- 6.4.8 Sakata Seeds Corporation
- 6.4.9 Syngenta Group
- 6.4.10 Takii and Co.,Ltd.
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SEEDS CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Global Market Size and DROs
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms
Have a question?


SELECT AN OPTION
Have a question?


Questions? Please give us a call or visit the contact form.
