Need help finding what you are looking for?
Contact Us
PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1693437

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1693437
Asia-Pacific Vegetable Seed - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
PUBLISHED:
PAGES: 398 Pages
DELIVERY TIME: 2-3 business days
SELECT AN OPTION
The Asia-Pacific Vegetable Seed Market size is estimated at 2.89 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 3.67 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 4.90% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
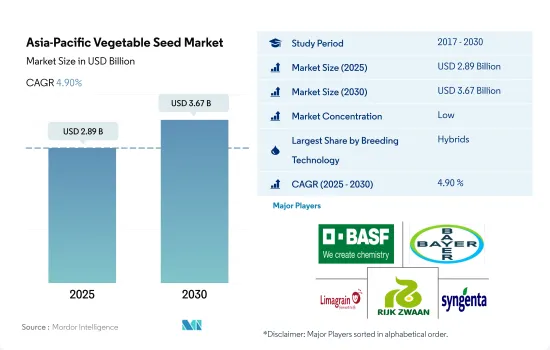
The increasing adoption of hybrid vegetable seeds and their benefits, such as higher yield, are anticipated to drive the hybrid seed market
- In Asia-Pacific, the hybrid seed segment dominated the market in terms of volume and value, which held 75.4% of the vegetable seed market value in 2022. The hybrid vegetable seed market grew by 32.4% between 2017 and 2022. This was mainly due to the high adoption of hybrid seed varieties in large countries such as China, India, and Bangladesh.
- Solanaceae and cucurbits dominated the Asia-Pacific hybrid vegetable seed market, collectively accounting for about 45.2% in 2022. This large market share of solanaceous and cucurbits seeds is mainly attributed to their significant demand in the region. Moreover, there has been an increase in seed replacement rate and rising awareness about the high-yielding varieties in the region.
- China and India were the region's major countries, collectively accounting for 61.3% of the hybrid vegetable market in 2022. This was mainly due to the presence of highly cultivatable areas, high consumer demand, and high usage of commercial hybrids.
- The open-pollinated varieties and hybrid derivatives held a market share of 24.6% in 2022. The low share was mainly due to an increased preference for high-yielding and disease-resistant hybrids.
- Among Asia-Pacific countries, China and India accounted for 63.2% of the open-pollinated variety market in 2022. Open-pollinated varieties require fewer inputs, such as fertilizers and pesticides, and are less expensive for low-income farmers. They also reduce the reliance on hybrid seed imports, thus boosting the market in the region.
- Therefore, with increasing food demand and the implementation of commercial hybrid varieties, hybrid breeding technology is likely to dominate the market during the forecast period.
An increase in the cultivation area, new technological advancements, and high global demand for vegetables are driving vegetable seed sales in the region
- The Asia-Pacific region is one of the largest producers and consumers of vegetables in the global market. In 2022, Asia-Pacific's market share was 32.4% in 2022. China is a leading vegetable producer globally due to the presence of favorable weather conditions and high demand for vegetables globally and in the country.
- In Asia-Pacific, China dominated the vegetable seed market, accounting for 32.3% in 2022, followed by India with 23.5%, Japan with 8.5%, and Indonesia with 7.4%. Furthermore, China had the highest vegetable production, amounting to 596.0 million metric ton in 2021 and accounting for 51.9% of the global output.
- In India, the share of vegetable seeds is expected to increase during the forecast period due to the increasing demand for vegetables and growing awareness about their health benefit.
- Australia has a diverse agricultural sector, where vegetable farming is an important food source of income. It accounted for 4.6% of the Asia-Pacific vegetable seed market in 2022. The major vegetable crops grown in the country are onion, peas, pumpkin, squash, and tomato.
- In Japan, urban agriculture is developing as a new trend in agriculture. As agricultural land faces constraints, urban agriculture, such as greenhouse, has been expanding in the country. For instance, about 74% of tomatoes and 61% of cucumbers and gherkins in 2022 were cultivated under protected cultivation.
- Factors such as an increase in the cultivation area, new technological advancements, and high global demand are expected to fuel the growth of the vegetable seed market in the region during the forecast period.
Asia-Pacific Vegetable Seed Market Trends
High consumption demand of salad, and leading vegetable-producing countries such as India and China are driving the increase in the area of cultivation
- The area under cultivation for vegetables in Asia-Pacific is lower than that of row crops. In 2022, 5.5% of the area was cultivated as vegetables, which are more vulnerable to adverse weather, leading to a higher risk of failure. The inefficiency in meeting the supply and demand in different countries and the lack of good quality infrastructure for storage also restrain the growers from cultivating more vegetables than grains such as rice and corn.
- Roots and bulbs had the largest share in the area used to cultivate vegetables. The segment had a share of 51% in 2022 as the region is one of the major producers of onion and potato. Consumers in the region prefer onions for seasoning and high export potential, and potato is used in Indian cuisines such as aloo tikki, paranthas, and others, which lead to a high area under onion and potato cultivation. For instance, the area under onion cultivation in Asia-Pacific was 36.3 million ha, of which India and China accounted for 69% in 2022.
- India and China are the primary producers of tomatoes. The area under tomato cultivation in India increased from 797,000 ha in 2017 to 857,321.1 ha in 2022 and from 1.0 million ha to 1.1 million ha during the same period in China. Increased cultivation area will increase demand for tomato seeds in the region. Moreover, other unclassified vegetables such as lettuce, spinach, and other green leafy vegetables witnessed a growth of 3.1% in the area cultivated from 2017 to 2022 due to an increase in the demand for these vegetables as they have high nutritional value and increase in the consumption of salads. Therefore, the rising demand for vegetables, with the region being a major producer of roots and bulbs, is increasing the area of vegetable cultivation in the region during the forecast period.
Cabbage and lettuce seeds with wider adaptability and suitable for protected cultivation are gaining popularity among farmers who are adopting new cultivation practices
- Asia-Pacific is one of the leading global cabbage and lettuce producers. There is a high demand from growers for seed varieties with traits such as disease resistance, bolting tolerance, and wider adaptability to gain higher profits. The major players in the market, such as Bayer AG, BASF SE, and Syngenta, are providing seed products with traits that resist early rots and leaf diseases, along with higher productivity. These seed varieties are witnessing high demand to prevent crop losses from diseases and increase yield and quality. The other traits, such as leaf color, size, and heat resistance, are widely adopted by lettuce and cabbage growers to produce crops for salads and high nutritional values.
- The demand for seeds with broader adaptability traits is expected to increase across the region due to the change in yields caused by increasing temperature and shifts in rainfall patterns in the growing seasons that affect crop productivity. Companies such as Syngenta AG, BASF SE, and Bayer AG provide seeds with these traits to grow in adverse weather conditions.
- Lettuce is a cool-season vegetable crop. Due to the increasing demand for lettuce in the off-season, farmers are using protected cultivation for the crop. High summer temperatures in a greenhouse can cause lettuce to bolt prematurely. Therefore, the demand for bolting-resistant varieties is expected to grow to prevent bolting and increase lettuce cultivation in the summer. Furthermore, the seed companies provide products with disease-resistant traits to resist downy mildew and big veins.
- The prevalence of different diseases, changes in weather conditions, and new cultivation methods are increasing the demand for new seed varieties during the forecast period.
Asia-Pacific Vegetable Seed Industry Overview
The Asia-Pacific Vegetable Seed Market is fragmented, with the top five companies occupying 29.11%. The major players in this market are BASF SE, Bayer AG, Groupe Limagrain, Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel BV and Syngenta Group (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
Product Code: 92499
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Area Under Cultivation
- 4.1.1 Vegetables
- 4.2 Most Popular Traits
- 4.2.1 Cabbage & Lettuce
- 4.2.2 Tomato & Chilli
- 4.3 Breeding Techniques
- 4.3.1 Vegetables
- 4.4 Regulatory Framework
- 4.5 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Breeding Technology
- 5.1.1 Hybrids
- 5.1.2 Open Pollinated Varieties & Hybrid Derivatives
- 5.2 Cultivation Mechanism
- 5.2.1 Open Field
- 5.2.2 Protected Cultivation
- 5.3 Crop Family
- 5.3.1 Brassicas
- 5.3.1.1 Cabbage
- 5.3.1.2 Carrot
- 5.3.1.3 Cauliflower & Broccoli
- 5.3.1.4 Other Brassicas
- 5.3.2 Cucurbits
- 5.3.2.1 Cucumber & Gherkin
- 5.3.2.2 Pumpkin & Squash
- 5.3.2.3 Other Cucurbits
- 5.3.3 Roots & Bulbs
- 5.3.3.1 Garlic
- 5.3.3.2 Onion
- 5.3.3.3 Potato
- 5.3.3.4 Other Roots & Bulbs
- 5.3.4 Solanaceae
- 5.3.4.1 Chilli
- 5.3.4.2 Eggplant
- 5.3.4.3 Tomato
- 5.3.4.4 Other Solanaceae
- 5.3.5 Unclassified Vegetables
- 5.3.5.1 Asparagus
- 5.3.5.2 Lettuce
- 5.3.5.3 Okra
- 5.3.5.4 Peas
- 5.3.5.5 Spinach
- 5.3.5.6 Other Unclassified Vegetables
- 5.3.1 Brassicas
- 5.4 Country
- 5.4.1 Australia
- 5.4.2 Bangladesh
- 5.4.3 China
- 5.4.4 India
- 5.4.5 Indonesia
- 5.4.6 Japan
- 5.4.7 Myanmar
- 5.4.8 Pakistan
- 5.4.9 Philippines
- 5.4.10 Thailand
- 5.4.11 Vietnam
- 5.4.12 Rest of Asia-Pacific
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles
- 6.4.1 Advanta Seeds - UPL
- 6.4.2 BASF SE
- 6.4.3 Bayer AG
- 6.4.4 Bejo Zaden BV
- 6.4.5 East-West Seed
- 6.4.6 Groupe Limagrain
- 6.4.7 Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel BV
- 6.4.8 Sakata Seeds Corporation
- 6.4.9 Syngenta Group
- 6.4.10 Yuan Longping High-Tech Agriculture Co. Ltd
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SEEDS CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Global Market Size and DROs
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms
Have a question?


SELECT AN OPTION
Have a question?


Questions? Please give us a call or visit the contact form.
