PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1687159

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1687159
Quinoa Seeds - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
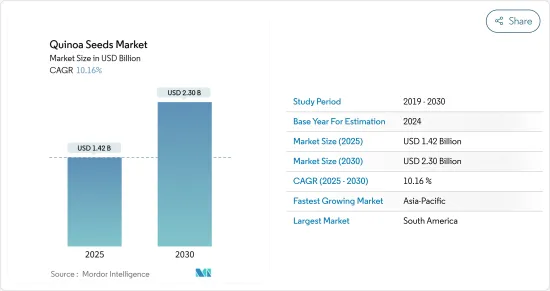
The Quinoa Seeds Market size is estimated at USD 1.42 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 2.30 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 10.16% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
The quinoa seeds market has experienced significant growth in recent years due to the increasing popularity of quinoa as a highly nutritious, gluten-free grain. Known for its exceptional nutritional profile, quinoa is rich in protein, fiber, essential amino acids, and vitamins, making it a staple in health-conscious diets worldwide.
Originally native to the Andean region of South America, quinoa is now grown in multiple countries, including the United States, Canada, and various parts of Europe and Asia. Peru and Bolivia are the leading producers of quinoa. For instance, according to FAOSTAT, quinoa production in Peru was 106,761.84 metric tons in 2021, which increased to 114,211.71 metric tons in 2022. These countries have seen significant economic benefits from quinoa exports, but the increasing global demand has also created challenges related to overproduction and price volatility. Besides, countries like Peru and Bolivia-the largest quinoa producers-have seen significant export growth, especially in North America, Europe, and Asia. The United States, in particular, has become one of the largest importers of quinoa. Likewise, the US is a major importer of quinoa and is also seeing an increase in domestic quinoa cultivation, especially in states like Colorado and Montana, where the crop has been adapted to local growing conditions.
Quinoa is increasingly being used as an ingredient in processed foods such as quinoa flour, quinoa chips, quinoa pasta, and quinoa-based protein powder. Major food companies have recognized the potential of quinoa and incorporated it into their product lines. For instance, in 2024, NIUKE Foods launched its market-first quinoa milk as part of its new lineup of vegan products. The demand for quinoa as a functional ingredient in processed and packaged foods has surged, boosting the demand for quinoa seeds. As more food manufacturers incorporate quinoa into their products, the quinoa seed market grows to meet the needs of both large-scale food producers and smaller, niche health food brands.
Quinoa Seeds Market Trends
Rising Health Consciousness is Driving the Global Production of Quinoa Seeds
The global rise in health consciousness is one of the most significant factors driving the increased production of quinoa seeds. For instance, according to FAOSTAT, global quinoa production was 157.86 thousand metric tons in 2021, which increased by 159.82 thousand metric tons in 2022. As more consumers prioritize health, wellness, and nutrition in their food choices, the demand for nutritious and sustainable food options has surged. Quinoa, often hailed as a "superfood," fits perfectly into this trend due to its exceptional nutritional profile, versatility, and environmental sustainability.
Quinoa is one of the few plant-based foods that offer a complete protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids. It is also high in fiber, vitamins (B vitamins, vitamin E), and minerals (iron, magnesium, potassium, zinc), making it an excellent choice for people looking to improve their diet. As more consumers embrace health-conscious eating habits, they are seeking nutrient-dense foods that support overall well-being. Quinoa's high protein content, along with its rich fiber and mineral profile, makes it highly appealing for those looking to improve their diet quality. This rising demand for nutrient-packed foods is driving farmers to cultivate quinoa on a larger scale, both in traditional growing regions (such as the Andes in South America) and in new regions where it can be adapted.
As gluten sensitivities and celiac disease become more recognized, and as consumers increasingly lean towards gluten-free lifestyles, the popularity of gluten-free diets surges. Quinoa, inherently gluten-free, is being championed as a nutritious substitute for wheat, barley, and other gluten-laden grains. This rising appetite for gluten-free offerings significantly propels quinoa seed production. Quinoa's adaptability, seamlessly substituting traditional grains like rice and wheat in a range of dishes from salads to baked goods, has cemented its place in gluten-free diets. Responding to the demands of health-conscious consumers shunning gluten, farmers in regions not traditionally known for quinoa, such as the US, Canada, and parts of Europe, are ramping up their quinoa cultivation efforts.
South America Dominates the Market
South America, specifically the Andean region-which includes countries like Peru, Bolivia, and Ecuador-has long been recognized as the birthplace and primary producer of quinoa. For instance, according to FAOSTAT, quinoa production in Peru was 106,761.84 metric tons in 2021, which increased to 114,211.71 metric tons in 2022. As the global demand for quinoa continues to rise due to its nutritional value and health benefits, South America maintains a dominant position in the quinoa seeds market. This dominance is shaped by historical, geographical, economic, and cultural factors that make South American countries uniquely positioned to lead global quinoa production.
Peru and Bolivia are the world's leading exporters of quinoa, with Peru accounting for approximately 40-45% of global quinoa exports and Bolivia contributing around 35%. Together, these two countries supply the majority of quinoa to international markets, including North America, Europe, and Asia. South America's dominance in quinoa exports is a significant factor in its leadership of the quinoa seeds market. These countries have established strong global trade relationships, with well-developed infrastructure for quinoa processing and export. As global demand for quinoa increases, South America continues to benefit from its central role in the supply chain.
Peru and Bolivia's governments have championed quinoa production, both at home and on the global stage. In Bolivia, initiatives have been rolled out to empower quinoa farmers, offering them enhanced access to technology, training, and market connections. Such governmental backing has not only modernized farming techniques but also boosted yields and export capabilities. Through strategic investments in marketing and trade deals, South American nations have elevated quinoa to a premier export status, solidifying their market stronghold. Moreover, international bodies and NGOs, acknowledging quinoa's promise for rural upliftment, have added momentum to production incentives.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising Health Consciousness and Nutritional Benefits
- 4.2.2 Growing Demand for Gluten-Free Products
- 4.2.3 Quinoas Sustainability and Adaptability
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Price Fluctuations and Market Volatility
- 4.3.2 Competition from Other Grains and Pseudo-Cereals
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (Production analysis (Volume), Consumption analysis (Value and Volume), Export analysis (Value and Volume), Import analysis (Value and Volume), and Price Trend Analysis)
- 5.1 Geography
- 5.1.1 North America
- 5.1.1.1 United States
- 5.1.1.2 Canada
- 5.1.2 Europe
- 5.1.2.1 Germany
- 5.1.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.1.2.3 France
- 5.1.2.4 Spain
- 5.1.2.5 Russia
- 5.1.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.1.3.1 China
- 5.1.3.2 Australia
- 5.1.3.3 India
- 5.1.4 South America
- 5.1.4.1 Brazil
- 5.1.4.2 Argentina
- 5.1.4.3 Peru
- 5.1.4.4 Bolivia
- 5.1.5 Africa
- 5.1.5.1 South Africa
- 5.1.1 North America
6 MARKET OPPORTUNITITES AND FUTURE TRENDS




