PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1640605

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1640605
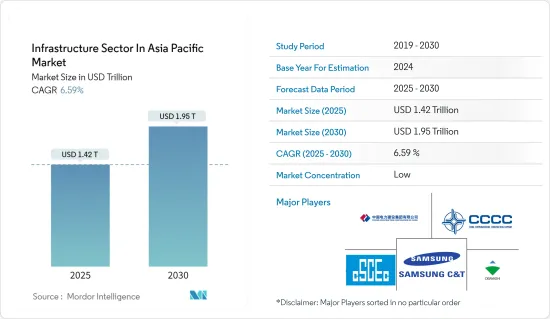
Infrastructure Sector In Asia Pacific - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Infrastructure Sector In Asia Pacific Market size is estimated at USD 1.42 trillion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 1.95 trillion by 2030, at a CAGR of 6.59% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Southeast Asia is experiencing a boom in infrastructure, with major projects in Vietnam, Thailand, the Philippines, Malaysia, and Indonesia accepted. Those were supported in many cases by loans and other assistance provided by Japan and China. The distinction between Japan and China's one-year investment in Southeast Asia represents just part of the story. China's investments in ASEAN infrastructure have risen rapidly in recent years.
The backbone of the Indian economy, the infrastructure sector, is essential to improving the nation's overall development. Other industry sub-segments include telephony, power, roads, ports, etc. India has to enhance its infrastructure to reach its 2025 economic growth target of USD 5 trillion. The National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP), along with other initiatives like "Make in India" and the production-linked incentives (PLI) program, was launched by the government to promote the expansion of the infrastructure industry. Under the PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan (NMP), 44 Central Ministries and 36 States/UTs have come on board, integrating a total of 1,614 data layers. To uphold data accuracy, key infrastructure ministries have established Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) within a three-tier system. SOPs have been officially notified for 8 infrastructure ministries and 15 social sector ministries, while development efforts are ongoing for additional ministries and States/UTs.
Japan's Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transportation (MLIT) plays a pivotal role in managing the nation's infrastructure. According to MLIT, proactively detecting and addressing at-risk infrastructure can prevent severe incidents and cut maintenance and renewal costs by an impressive 47%, translating to a potential savings of USD 46 billion by 2048. In light of this, MLIT has been championing Digital Transformation (DX) for infrastructure since 2021, urging municipalities, the entities responsible for managing infrastructure, to adopt and implement advanced inspection technologies. In 2023, over 730,000 bridges, 11,000 tunnels, 10,000 water gates, 470,000 meters of sewage pipes, and 5,000 harbor quays have surpassed the 50-year mark. The challenges posed by this aging infrastructure, coupled with related accidents, have garnered heightened scrutiny from both the government and the public.
Overall, the prospects for regional infrastructure investment are highly promising. While COVID-19 has had a considerable influence on infrastructure development and finance throughout the area, part of that change is beneficial to project lenders and investors. The epidemic has hastened investment in low-carbon, climate-resilient infrastructure, as well as initiatives that improve internet connection and public health. The two areas-ESG and digitalization-will continue to dominate the infrastructure sector for the foreseeable future.
APAC Infrastructure Market Trends
Increasing Investments in Transport Infrastructure Sector
Japan, renowned for its cutting-edge transportation infrastructure, is making bold moves to secure financing for its long-term infrastructure needs. The nation boasts an extensive high-speed railway network, the Shinkansen, alongside well-maintained roads and efficient airports. Ongoing investments aim to expand and modernize these systems. Tokyo's Haneda and Narita airports are undergoing significant expansions and renovations to better accommodate rising air traffic and tourism. Enhancements focus on upgrading passenger facilities and boosting runway capacity. To tackle a truck driver shortage, Japan plans to build an automated cargo transport corridor, dubbed the "conveyor belt road," stretching from Tokyo to Osaka. Set to begin trial runs soon, the corridor anticipates full operations by the mid-2030s. This state-of-the-art corridor will feature unmanned, automated transport systems, seamlessly linking airports, railways, and ports.
Under the "Parvatmala Pariyojana" National Ropeways Development Programme, the Government of India has announced more than 200 projects, with a total allocation of INR 1.25 lakh crore (USD 14.77 billion) for the upcoming five years. In 2024, the Union Cabinet has approved INR 4,406 crore (USD 0.52 billion) initiative aimed at constructing 2,280 km of roads in the border areas of Punjab and Rajasthan. In India, roads & highways dominate the transport sector, followed closely by railways and urban public transport. The government has set ambitious targets for the transport sector, including the development of a 2 lakh-km national highway network by 2025 and expanding the number of airports to 220. Additionally, plans include operationalizing 23 waterways by 2030 and developing 35 Multi-Modal Logistics Parks (MMLPs). The total budgetary outlay for infrastructure-related ministries increased from around INR 3.7 lakh crore (USD 43.74 billion) in FY23 to INR 5 lakh crore (USD 59.11 billion) in FY24, presenting investment opportunities for the private sector across various transport sub-segments.
China Infrastructure is Witnessing Significant Growth
As 2023 concluded, rural roads in China spanned a total of 4.6 million kilometers. Of these, paved roads stretched across 4.22 million kilometers, making up 91.8% of the total rural road network. This marks a significant rise of 27.2% over the last decade. Furthermore, paved roads have been established in approximately 30,000 towns and townships, as well as in over 500,000 administrative villages, underscoring the growing accessibility in rural regions.
China's latest renewable energy initiative sets bold consumption targets for 2025 and 2030. Departing from earlier plans that centered on merely installing capacity, this new approach prioritizes enhancing the utilization of renewable energy. This will be achieved through upgrading infrastructure and integrating renewables across various sectors, such as transportation, agriculture, and manufacturing. As a result of this strategic pivot, significant business prospects are anticipated in green technologies, grid modernization, and the broader clean energy arena
However, in 2024, China scaled back infrastructure spending in 12 regions grappling with heightened debt-servicing challenges. The central government is prioritizing the containment of local-government debt risks. Earlier this year, the central government directed these 12 regions to either delay or halt specific government-led infrastructure initiatives, aiming to mitigate their escalating debt challenges.
APAC Infrastructure Industry Overview
The market is fragmented, as many new entrants focus on bagging projects to strengthen their positions among the market's key players and are expected to grow during the forecast period due to private and venture capital investment.
Key players in the market are China State Construction Engineering, China Communications Construction Company, Power Construction Corporation of China, Samsung C&T, and Obayashi Corporation.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Deliverables
- 1.2 Study Assumptions
- 1.3 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Industry Policies and Regulations
- 4.3 Government Regulations and Initiatives
- 4.4 Supply Chain/Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Insights into Technological Innovation in the APAC Infrastructure Sector
- 4.6 Impact of Geopolitics and Pandemic on the Market
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Strong investment inflow from governments
- 5.1.2 Rising population of APAC nations
- 5.2 Market Restraints
- 5.2.1 Limited public budget and difficulty in attracting private investment
- 5.2.2 Delay in land acquisition
- 5.3 Market Opportunities
- 5.3.1 Rapid growth of mobile and internet usage
- 5.3.2 Strong pipeline of urbanization projects
- 5.4 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 5.4.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 5.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 5.4.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 5.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 5.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 Social Infrastructure
- 6.1.1 Schools
- 6.1.2 Hospitals
- 6.1.3 Defence
- 6.1.4 Other social infrastructures
- 6.2 Transportation Infrastructure
- 6.2.1 Railways
- 6.2.2 Roadways
- 6.2.3 Airports
- 6.2.4 Waterways
- 6.3 Extraction Infrastructure
- 6.3.1 Power Generation
- 6.3.2 Electricity Transmission & Distribution
- 6.3.3 Water
- 6.3.4 Gas
- 6.3.5 Telecoms
- 6.4 Manufacturing Infrastructure
- 6.4.1 Metal and Ore Production
- 6.4.2 Petroleum Refining
- 6.4.3 Chemical Manufacturing
- 6.4.4 Industrial Parks and Clusters
- 6.4.5 Other manufacturing infrastructures
- 6.5 Country
- 6.5.1 China
- 6.5.2 India
- 6.5.3 Philippines
- 6.5.4 Japan
- 6.5.5 South Korea
- 6.5.6 Rest of Asia Pacific
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Market Concentration Overview
- 7.2 Company Profiles
- 7.2.1 China State Construction Engineering
- 7.2.2 China Communications Construction Company
- 7.2.3 Power Construction Corporation of China
- 7.2.4 Samsung C&T
- 7.2.5 Obayashi Corporation
- 7.2.6 Shanghai Construction Group
- 7.2.7 Hyundai E&C
- 7.2.8 China Petroleum Engineering Corporation
- 7.2.9 L&T
- 7.2.10 China Metallurgical Group*
- 7.3 Other Companies
8 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS
9 APPENDIX
- 9.1 Macroeconomic Indicators (GDP Distribution, by Activity)
- 9.2 Economic Statistics - Transport and Storage Sector Contribution to the Economy
- 9.3 External Trade Statistics - Export and Import, by Product




