PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1636163

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1636163
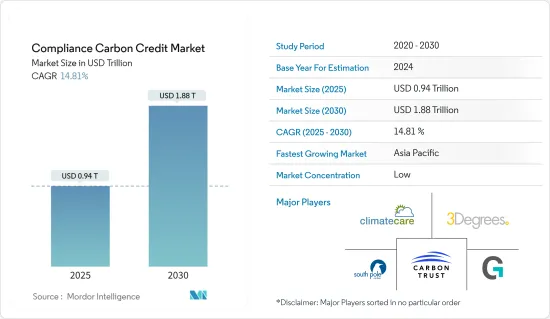
Compliance Carbon Credit - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Compliance Carbon Credit Market size is estimated at USD 0.94 trillion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 1.88 trillion by 2030, at a CAGR of 14.81% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
The compliance carbon credit market operates under regulatory frameworks that limit greenhouse gas emissions, such as emissions trading schemes (ETS) or cap-and-trade systems. Its primary function is to provide a mechanism for entities subject to emissions regulations, such as industries, power plants, and transportation sectors, to meet compliance obligations by purchasing carbon credits.
Compliance carbon markets operate within a diverse regulatory landscape, with different jurisdictions implementing emissions trading schemes and regulatory frameworks. Major compliance markets include the European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS), the California Cap-and-Trade Program, the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI), and various national schemes in China, South Korea, and New Zealand.
Compliance carbon credits are generated from various emission reduction projects, including renewable energy installations (e.g., wind, solar), energy efficiency initiatives, forestry and land-use projects (e.g., afforestation, reforestation), and industrial process improvements.
Compliance Carbon Credit Market Trends
Charting the Course of Carbon Pricing: UK-ETS Post-Brexit
- After leaving the European Union in 2020, the United Kingdom implemented its carbon pricing mechanism, the UK-ETS, which replaced its participation in the EU-ETS. This transition allowed the United Kingdom to establish its emissions trading system and set its carbon pricing policies independent of the European Union.
- The price of emissions allowances (UKAs) traded on the United Kingdom's Emissions Trading System (UK-ETS) has experienced notable fluctuations since its inception in January 2021. According to industry experts, the price reached a high of GBP 97.75 per metric ton on August 19, 2022, indicating strong demand or regulatory factors driving the price. However, by May 31, 2023, the price dropped to GBP 51.04 per metric ton, marking the lowest price before January 2022. Various factors, including changes in market conditions, regulatory adjustments, or shifts in supply and demand dynamics, could have influenced this decline in price.
- In 2022, the UK-ETS generated significant revenue, totaling GBP 4.3. This revenue represents the financial impact of carbon pricing on regulated entities within the United Kingdom, including industrial facilities, power plants, and other sectors covered by the emissions trading system. The revenue generated from carbon allowances reflects the cost of compliance for these entities and contributes to government funds dedicated to climate-related initiatives and investments.
Renewable Energy Investments and Technological Innovations Driving Carbon Credit Generation
- Many energy companies invest in renewable power sources, including wind, hydroelectric, and solar power, to reduce their carbon footprint. This shift toward cleaner energy production creates opportunities for generating compliance carbon credits from renewable energy projects.
- For instance, in February 2024, Chile embarked on a European hunt for investors in solar, wind, and green hydrogen technologies to decarbonize copper mines and other industries reliant on fossil fuels. During renegotiations of the EU Chile Trade and Investment Agreement, Marcos Kulka, president of H2Chile, a hydrogen association representing 102 publicly and privately owned companies, went to Europe to present his government's energy strategy.
- Further, Industry experts believe blockchain technology can enhance carbon credit validation in the carbon market by integrating with MRV (Digital Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification) systems. MRV systems collect data from various sources, including satellite images, IoT sensors, and monitoring systems. The digital MRV data is hashed and uploaded to the blockchain to verify carbon credits. Smart contracts automate the verification process by ensuring carbon credits are issued only to projects that fulfill specific criteria. Using decentralized oracles, off-chain information feeds can be added to the validation process, allowing for real-time carbon credit validation.
Compliance Carbon Credit Industry Overview
Various certification bodies and standards organizations certify emission reduction projects and issue carbon credits based on predefined criteria and methodologies. Competition may exist among certification bodies to attract project developers seeking certification services, with differences in certification fees, timelines, and reputation influencing their choice of certifier. Carbon credit prices and market dynamics can vary significantly over time and across different markets, leading to pricing, liquidity, and market behavior fragmentation. This variability can make it challenging for market participants to predict and navigate market conditions effectively. Some of the compliant carbon credit market players are Carbon Trust, ClimateCare, and 3Degrees.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Deliverables
- 1.2 Study Assumptions
- 1.3 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Technological Trends
- 4.3 Industry Value Chain Analysis
- 4.4 Government Regulations and Initiatives
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Drivers
- 5.1.1 Regulatory Mandates and Policies
- 5.1.2 Growing Corporate Sustainability Initiatives
- 5.2 Restraints
- 5.2.1 Market Complexity and Uncertainty
- 5.3 Opportunities
- 5.3.1 Innovation and Technology Advancements
- 5.4 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 5.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 5.4.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers / Buyers
- 5.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 5.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 5.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Type of Credits
- 6.1.1 Renewable Energy Projects
- 6.1.2 Forestry and Land Use
- 6.1.3 Energy Efficiency
- 6.1.4 Industrial Process Improvements
- 6.2 By Sector
- 6.2.1 Energy Sector
- 6.2.2 Transportation
- 6.2.3 Industrial Sector
- 6.2.4 Agriculture and Forestry
- 6.3 By Geography
- 6.3.1 North America
- 6.3.1.1 United States
- 6.3.1.2 Canada
- 6.3.2 Europe
- 6.3.2.1 United Kingdom
- 6.3.2.2 Germany
- 6.3.2.3 France
- 6.3.2.4 Rest of Europe
- 6.3.3 Asia-Pacific
- 6.3.3.1 China
- 6.3.3.2 Japan
- 6.3.3.3 India
- 6.3.3.4 South Korea
- 6.3.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 6.3.4 Middle East and Africa
- 6.3.5 Latin America
- 6.3.1 North America
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Overview (Market Concentration and Major Players)
- 7.2 Company Profiles
- 7.2.1 Carbon Trust
- 7.2.2 ClimateCare
- 7.2.3 3Degrees
- 7.2.4 South Pole
- 7.2.5 Gold Standard
- 7.2.6 Natural Capital Partners
- 7.2.7 Shell New Energies
- 7.2.8 Sustainable Travel International
- 7.2.9 Forest Carbon
- 7.2.10 Atmosfair*
- 7.3 Other Companies
8 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS
9 APPENDIX




