PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1521620

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1521620
Germany Dangerous Goods Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029)
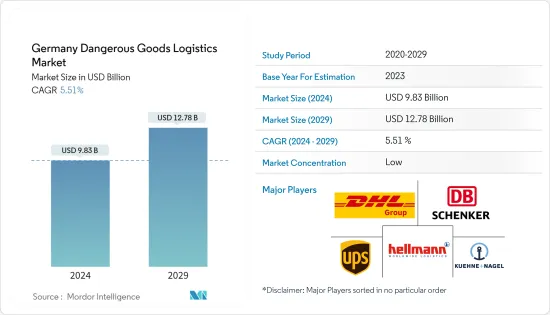
The Germany Dangerous Goods Logistics Market size is estimated at USD 9.83 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 12.78 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 5.51% during the forecast period (2024-2029).
Germany has a well-developed and highly regulated logistics market for dangerous goods. It plays a crucial role in ensuring the safe transportation, handling, and storage of hazardous materials within the country and across borders.
In Germany, pharmaceuticals and new fine and specialty chemicals are the main focus. The dangerous goods logistics market in Germany accounts for nearly a fifth of the European market.
In Germany, the Energiewende is the process of transitioning from a hydrocarbon and nuclear-dominated economy to a low-carbon and nuclear-free economy based on renewable energy sources.
Germany has set a target of 80% of its energy supply coming from renewable sources by 2030. The 2% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions across all industrial sectors in 2022 was not enough to reach the country's 2030 climate target of reducing emissions by 55% from 1990.
The Russian energy crisis caused by the war in Ukraine increased the use of dirty coal electricity. Germany missed its 2022 GHG reduction targets for both the transportation sector and the real estate sector. To reach its 2030 target, Germany would need to triple its annual GHG reduction from 2% to 6% from 2023.
Germany relies heavily on oil and gas for electricity supply, and imports almost all of its energy. This dependency has created two sources of instability: first, global price movements have a significant impact on Germany's energy imports and end users, and second, market trends are heavily influenced by Germany's relations with some countries.
At the same time, the planned phase-out of nuclear and coal power will increase the country's reliance on gas, so it is becoming increasingly important to diversify its gas supply, including by importing more LNG.
Germany's share of electricity generated from renewable energy fed into its grid has been steadily increasing, and there have not been any notable incidents of power outages. This means that both commercial and private customers can count on a reliable and consistent energy supply, as Germany has among the lowest power outage rates in the world.
Germany Dangerous Goods Logistics Market Trends
Decrease in Cross-border Transportation of Oil
Following the entry into force of the second phase of the oil embargo, only the remaining volumes of crude oil that had been exported to the EU from Russia before the turn of the year were imported into Germany in January 2023 (3,500 tonnes), according to the Federal Statistical Office (Destatis).
The volume of imports in January 2022 was 2.8 million tonnes. The total volume of imports of crude oil from Russia in January 2023 decreased by almost 90%, and the arithmetical volume decreased by 99.9%.
The share of Russia in the total crude oil imports of Germany decreased from 36.5% in January 2022 to just 0.1% in January 2023. In total, 6.2 million tons of crude oil worth EUR 3.8 billion (USD 4.10 billion) were imported into Germany in January 2022, which decreased by 20.5% in volume terms and by 9.6% in value terms compared to the same month last year.
Increasing Demand for Gas in Germany
In 2022, natural gas accounted for slightly less than 25% of Germany's primary energy use, making it its second most important resource. Germany is one of the largest importers of natural gas in the world, with about 95% of gas consumption being imported, according to BGR.
Germany produced about 5.7 bcm of natural gas in 2021, but geologists believe the fields are close to exhaustion. Domestic production of natural gas has been declining since 2004 and is expected to reach the end of its life in the next few years. Although the war in Ukraine has brought the topic of unconventional fracking back into the spotlight, legal constraints, popular and government opposition, and the country's goal of becoming carbon neutral by 2045 make its use highly unlikely.
In 2021, Germany imported 5,009 PJs of natural gas, according to data from the Federal Office for Economic Affairs and Export Control (BAFA). The share of imports from different countries was not clear for several years. In 2016, BAFA ceased to publish import volumes by country due to data privacy regulations.
The economy and climate ministry reported in 2022 that before the invasion of Ukraine by Russia, 55% of gas imports were from Russia, 30% from Norway and 13% from the Netherlands. According to the energy industry association BDEW, early estimates showed that about 20% of natural gas used in Germany in 2022 came from Russia.
BDEW noted that in some cases, it is hard to determine the origin of gas that crosses the border into Germany. For instance, pipelines from Austria and Switzerland can contain Russian gas (via Ukraine), Algerian natural gas (via Algeria), or LNG (via Italian LNG terminals).
Germany Dangerous Goods Logistics Industry Overview
The German dangerous goods logistics market is highly competitive, with several key players vying for business in the specialized sector. Some of the major players in the market include DHL, DB Schenker, Kuehne + Nagel, Hellmann Worldwide Logistics, UPS, etc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definitions
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 Analysis Methodology
- 2.2 Research Phases
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Current Market Scenario
- 4.3 Technological Trends in the Industry
- 4.4 Government Initiatives and Regulations
- 4.5 Insights into the Ecommerce
- 4.6 Value Chain/Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.7 Demand and Supply Analysis
- 4.8 Impact of COVID-19 on the Market
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Drivers
- 5.1.1 Industrial Growth Supporting the Market
- 5.1.2 Global Trade Driving the Market
- 5.2 Restraints
- 5.2.1 Compliance Challenges Affecting the Market
- 5.2.2 Limited Infrastructure Inhibiting the Market
- 5.3 Opportunitites
- 5.3.1 Technological Advancements Driving the Market
- 5.3.2 Sustainable Practices Driving the Market
- 5.4 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 5.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 5.4.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers/Buyers
- 5.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 5.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 5.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Service
- 6.1.1 Transportation
- 6.1.2 Warehousing and Distribution
- 6.1.3 Value-added services
- 6.2 By Destination
- 6.2.1 Domestic
- 6.2.2 International
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Overview (Market Concentration and Major Players)
- 7.2 Company Profiles
- 7.2.1 DHL
- 7.2.2 DB Schenker
- 7.2.3 Kuehne + Nagel
- 7.2.4 Hellmann Worldwide Logistics
- 7.2.5 UPS
- 7.2.6 DACHSER
- 7.2.7 Gebruder Weiss
- 7.2.8 Rhenus Logistics
- 7.2.9 Panalpina
- 7.2.10 Agility Logistics*
- 7.3 Other Companies
8 FUTURE OF THE MARKET
9 APPENDIX




