PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1445797

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1445797
Latin America Biguanide - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029)
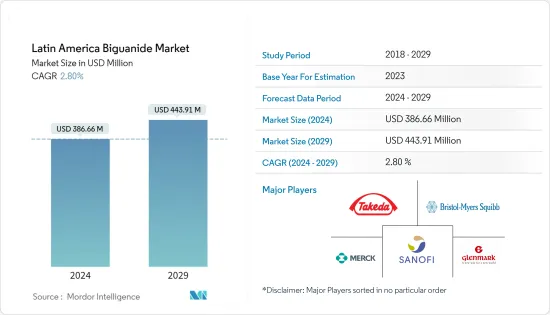
The Latin America Biguanide Market size is estimated at USD 386.66 million in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 443.91 million by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 2.80% during the forecast period (2024-2029).
The market is estimated to reach a value of about USD 420 million by 2027.
The COVID-19 pandemic positively impacted the Latin America Biguanide Market. Diabetes and uncontrolled hyperglycemia are risk factors for poor outcomes in patients with COVID-19 including an increased risk of severe illness or death. People with diabetes have a weaker immune system, the COVID-19 complication aggravates the condition, and the immune system gets weaker very fast. People with diabetes have more chances to get into serious complications rather than normal people. The COVID-19 pandemic has been testing the capacity to respond and adapt to populations, governments, and health systems worldwide. Brazil presented the first suspected and the first confirmed case in the Latin America region. Most Latin American countries failed to implement timely measures to protect individuals with diabetes, which severely impacted individuals, health systems, and economies.
Biguanides are a class of medications used to treat type 2 diabetes. They work by reducing the production of glucose that occurs during digestion. Metformin is the only biguanide currently available in most countries for treating diabetes. Glucophage (metformin) and Glucophage XR (metformin extended release) are well-known brand names for these drugs. Others include Fortamet, Glumetza, and Riomet. Metformin is also available in combination with several other types of diabetes medications, such as sulfonylureas.
As Type 2 diabetes is associated with both poorer clinical outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic and an increased risk of death in such hospitalized patients, the role of glucose control has been emphasized to improve the prognosis. Metformin is the first-line choice for the management of hyperglycemia in T2DM. Besides being an important glucose-lowering agent, metformin also has significant anti-inflammatory. Therefore, metformin has been a potential candidate for treating patients affected by COVID-19 infection, with type 2 diabetes, as well as an excellent antidiabetic (glucose-lowering) agent during COVID-19 pandemic times.
Therefore, owing to the aforementioned factors the studied market is anticipated to witness growth over the analysis period.
Latin America Biguanide Market Trends
Rising diabetes prevalence
The diabetes population in the Latin American region is expected to rise by more than 3% over the forecast period.
According to the IDF Diabetes Atlas 2021, 15.7 million adults, or 10.5%, were living with diabetes in Brazil. The cost of diabetes-related health expenditures in Brazil was the third highest in the world, at 42.9 billion USD. In addition, 18 million adults (around 11.9%) have impaired glucose tolerance, which places them at high risk of developing type-2 diabetes. Additional data on glycemic control in Brazil show that only 25% met the therapeutic goal of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) less than 7% before the pandemic, as recommended by the Brazilian Diabetes Society (SBD).
Diabetes reduces lifespan, and people with the disease are likely to experience blindness and be hospitalized for amputations, kidney failure, heart attacks, strokes, and heart failure. The first-line therapy used in patients with type-2 diabetes is metformin monotherapy. When metformin is contraindicated or not tolerated, or when treatment goals are not achieved after three months of use at the maximum tolerated dose, other options need to be considered. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors, and glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists are generally used to supplement treatment with metformin.
When diabetes is undetected or inadequately treated, people with diabetes are at risk of serious and life-threatening complications, such as heart attack, stroke, kidney failure, blindness, and lower-limb amputation. These result in reduced quality of life and higher healthcare costs, which lead to a greater need for access to care. Brazil has implemented a set of reforms over the past decade to improve the distribution of doctors, develop new forms of service organization, introduce new financing models, and implement a range of quality improvement initiatives and policy frameworks to overcome risk factors such as obesity and emerging pandemic threats.
Owing to the rising rate of obesity, the growing genetic factors for type-2 diabetes, and the increasing prevalence, the market will likely continue to grow.
Mexico holds the highest market share in the Latin America Biguanide Market in the current year
Mexico holds the highest market share of about 46.4% in the Latin American biguanide market in the current year.
According to the IDF Diabetes Atlas 2021, the prevalence of diabetes in Mexico reached 16.9%, or one in six adults. Additionally, 11 million adults in the country have impaired glucose tolerance, which places them at high risk of developing type-2 diabetes. Diabetes-related health expenditure in Mexico has put it in the top ten countries or territories with the highest total health expenditure. Under half of the people living with diabetes in the country are undiagnosed. Metformin is typically the first medication used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes due to its wide range of efficacy, safety, and mechanisms of action. Metformin and other anti-diabetic drug combinations have a low risk of hypoglycemia, provide beta cell protection, offer cardio-renal benefits, and are safe for patients with kidney or liver conditions and senior citizens.
Lack of health insurance deprives the poor of access to services and puts them at risk of financial hardship. To protect the people against excessive health expenditures, many countries like Mexico have implemented mechanisms such as community-based health insurance, national health insurance, and targeted public health insurance. Mexico has multiple health insurance providers. The Instituto de Seguridad y Servicios Sociales de los Trabajadores del Estado (State Employee's Social Security and Social Services Institute, ISSSTE) provides coverage for government employees, and the Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social (Mexican Social Security Institute, IMSS) covers private-sector employees. The Seguro Popular (People's Insurance) was launched to protect the working-age population against steep healthcare costs. Enrollment in the Seguro Popular is independent of health status or pre-existing illness; there is no co-payment in accordance with the type of health care received; and family contributions are determined solely by the ability to pay. The Government of Mexico partnered with numerous private companies to utilize their supply chain (manufacturing, distribution, and retailers) to ensure low prices for drugs.
The aforementioned factors are expected to drive the market's growth.
Latin America Biguanide Industry Overview
The Latin American biguanide market is fragmented, with manufacturers like Takeda, Merck, Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, etc. having a global market presence, and the market is highly competitive due to generic drug manufacturers' presence.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.4 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products and Services
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Biguanide
- 5.2 Geography
- 5.2.1 Mexico
- 5.2.2 Brazil
- 5.2.3 Rest of Latin America
6 MARKET INDICATORS
- 6.1 Type-1 Diabetes Population
- 6.2 Type-2 Diabetes Population
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Company Profiles
- 7.1.1 Merck
- 7.1.2 Takeda
- 7.1.3 GlaxoSmithKline
- 7.1.4 Sanofi
- 7.1.5 Boehringer Ingelheim
- 7.1.6 Glenmark
- 7.1.7 Bristol-Myers Squibb
- 7.2 Company Share Analysis
- 7.2.1 Merck
- 7.2.2 Takeda
- 7.2.3 Sanofi
- 7.2.4 Other Company Share Analyses
8 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS




