PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851140

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851140
Autonomous Ships - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
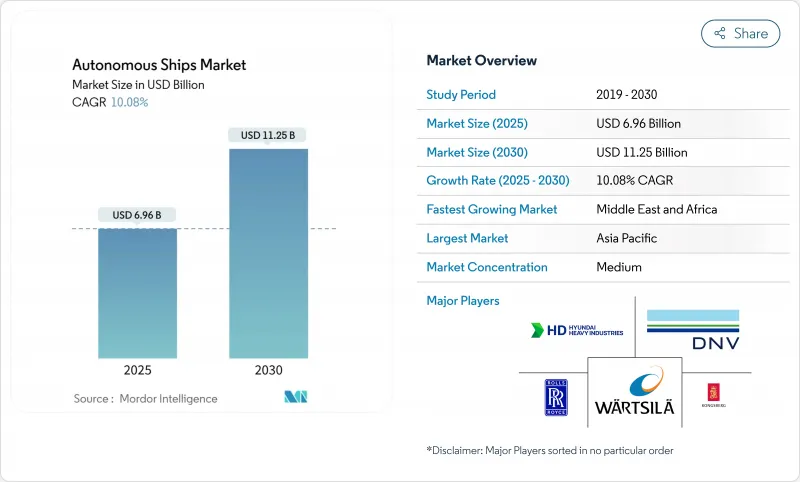
The autonomous ships market size was recorded at USD 6.96 billion in 2025 and is forecasted to rise to USD 11.25 billion by 2030, reflecting a 10.08% CAGR over 2025-2030.
Operator pressure to cut crew-related expenses, tightening emissions rules, and rapid gains in artificial intelligence propel commercial fleets toward progressively higher automation levels. The IMO's upcoming Maritime Autonomous Surface Ships (MASS) Code, national defense spending on unmanned surface vessels, and reliable 5G/LEO satellite links collectively shorten the adoption timetable for ocean-going and littoral vessels. Asia-Pacific remains the principal beneficiary as South Korean, Chinese, and Japanese yards launch technology-laden prototypes. At the same time, the Middle East leverages liberal test corridors and smart-port investments to attract foreign pilots. Competitive activity centers on integrated navigation suites that pair sensor fusion with edge processing, creating attractive retrofit packages for operators unwilling to invest in purpose-built platforms at the outset.
Global Autonomous Ships Market Trends and Insights
Data-driven fleet optimisation and remote operations
Operators now link Artificial Intelligence (AI) voyage-planning engines with shore control centers to fine-tune speed profiles, schedule maintenance, and redeploy crews more efficiently. After rolling out predictive routing analytics, Stena Line trimmed fuel costs and improved on-time performance. Samsung Heavy Industries' 1,500 km transoceanic run without an onboard crew strengthened industry confidence that remote-supervised passages can be executed safely. Multi-sensor fusion-radar, LiDAR, optical, and acoustic-delivers a richer operational picture than a human bridge watch, allowing algorithms to dodge congested sea lanes and inclement weather in real time.
Decarbonisation and fuel efficiency
Autonomous control logic harmonises speed, load, and optimal battery dispatch, a synergy that unlocks true zero-emission potential on short-sea and shuttle services. Norway's battery-only ferries scheduled for 2026 rely on algorithmic energy budgeting to meet duty cycles without range-anxiety penalties. Wartsila documented 15-25% fuel savings on hybrid retrofits, gains that rise further when autonomous modes trim unnecessary throttle oscillations. The Yara Birkeland's 7 MWh pack slashed operating expense by 90% versus a comparable diesel feeder.
Cyber-security vulnerabilities of remote navigation stacks
The malware incidents that sidelined Maersk and COSCO illustrate the stakes. Astaara doubled its dedicated maritime cyber-risk cover to USD 25 million and broadened clauses to include terror-linked attacks, a sign that insurers view ransomware as a systemic threat. Autonomous assets multiply entry points-shore centers, VSAT beams, edge processors-forcing owners to deploy layered defences and continuous penetration tests.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Demand for advanced situational-awareness suites
- Development of next-generation autonomous vessels
- Regulatory fragmentation and flag-state variance
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Partially autonomous systems claimed 74.35% of revenue in 2024, evidence that shipowners prefer step-wise enhancements allowing bridge crews to oversee automated collision avoidance and dynamic positioning. Fully autonomous craft, while representing only a sliver of today's autonomous ships market, are pacing the expansion with a 19.58% CAGR. DARPA's crewless Defiant backdrop confirms that eliminating accommodation blocks frees payload and cuts OpEx. The IMO's four-stage taxonomy guides retrofits as operators move from on-board support to remote supervision and finally to unmanned routes. Growing regulatory clarity and falling sensor costs indicate an inflection point where fully autonomous voyages transition from pilot projects to liner schedules.
Autonomous technology providers bundle shore control, encrypted links, and digital fleet twins into subscription packages that offset upfront hardware expense. Remote operator training curricula are emerging, creating new maritime career paths. Insurance underwriters increasingly separate partial and full autonomy risk pools, reinforcing the capex case for fuller automation in predictable trades. As more autonomous ships market participants collect operational data, confidence in long-haul unmanned passages will mount, gradually shifting the majority share toward higher autonomy tiers by the late 2020s.
Hardware still anchors 62.78% of 2024 spend because radar arrays, integrated bridges, and propulsion controls remain compulsory for safe operations. Yet software revenues are growing almost three times faster as machine-learning models ingest terabytes of hydro-meteorological data to deliver route recommendations at the edge. Companies such as L3Harris ship AMORPHOUS C2 suites that orchestrate entire flotillas from a single console, an efficiency play that captivates fleet managers. Hardware OEMs now publish application programming interfaces so third parties can update perception or path-planning modules without replacing sensors, lowering operator lifecycle costs.
Standardized open-architecture kits encourage retrofit business, a segment that could eclipse newbuild packages once the autonomous ships market size for upgrades passes the USD 3 billion mark after 2028. Meanwhile, venture-backed firms exploit cloud-based simulation to shorten validation time. As fleets convert raw logs into structured training sets, software developers can iterate on behaviour trees with minimal sea trials, accelerating performance improvements and cementing code as the main value driver.
The Autonomous Ships Market Report is Segmented by Autonomy Level (Partially Autonomous, Remotely Controlled, and More), Component (Hardware and Software), Ship Type (Cargo, Passenger, Defense, and More), End User (Commercial, Government and Military), Propulsion (Fully Electric, Hybrid, and Conventional), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific posted 38.98% revenue share in 2024, thanks to manufacturing depth, coordinated government grants, and success stories such as Samsung Heavy Industries' unmanned 1,500 km voyage. China's Jin Dou Yun 0 Hao saved 20% on construction and 15% on fuel burn versus conventional peers, validating cost-benefit assumptions. Japan's MEGURI2040 coalition demonstrates the region's systemic approach, aligning yards, telecoms, and software start-ups under common test corridors.
The Middle East and Africa segment is expanding at the fastest 14.01% CAGR. The UAE green-lit Fugro's Pegasus, the first over-the-horizon USV on its registry, and Abu Dhabi ports pilot smart-tug operations. Dubai's bespoke controls for remotely piloted craft reduce bureaucratic friction, making the Gulf an attractive sandbox for global vendors.
Due to Norway's trailblazing battery ferries and proactive class-society engagement, Europe retains a notable slice of the autonomous ships market. The EU's concurrent AI and maritime safety rules aim to anchor global standards. North America-underpinned by US Navy outlays, Canadian Arctic logistics and Silicon Valley's connectivity ecosystems-remains influential. The convergence of defense and civil deployments in these regions provides a reinforcing feedback loop: defense funds prime early R&D, and commercial operators adopt matured components at lower unit costs.
- ABB Ltd.
- BAE Systems plc
- DNV AS
- Fugro NV
- Hanwha Corporation
- HD Hyundai Heavy Industries Co. Ltd.
- Kongsberg Gruppen ASA
- L3Harris Technologies, Inc.
- Marine AI Ltd.
- MITSUI E&S Group
- Praxis Automation Technology B.V.
- Rolls-Royce plc
- Sea Machines Robotics, Inc.
- Samsung Heavy Industries Co., Ltd.
- Wartsila Corporation
- Vigor Industrial LLC
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Data-driven fleet optimization and remote operations
- 4.2.2 Decarbonization and fuel efficiency
- 4.2.3 Demand for advanced situational-awareness suites
- 4.2.4 Development of next-generation autonomous vessels
- 4.2.5 Defense push for unmanned surface vessels in navies
- 4.2.6 Edge-AI and 5G/LEO connectivity breakthroughs enabling real-time vessel autonomy
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Cyber-security vulnerabilities of remote navigation stacks
- 4.3.2 Regulatory fragmentation and flag-state variance
- 4.3.3 High retrofit capital outlay
- 4.3.4 Marine-insurance and liability uncertainties
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Autonomy Level
- 5.1.1 Partially Autonomous
- 5.1.2 Remotely Controlled
- 5.1.3 Fully Autonomous
- 5.2 By Component
- 5.2.1 Hardware
- 5.2.2 Software
- 5.3 By Ship Type
- 5.3.1 Cargo
- 5.3.2 Passenger
- 5.3.3 Offshore Support and Energy
- 5.3.4 Defense
- 5.3.5 Special Purpose
- 5.4 By End User
- 5.4.1 Commercial
- 5.4.2 Government and Military
- 5.5 By Propulsion
- 5.5.1 Fully Electric
- 5.5.2 Hybrid
- 5.5.3 Conventional
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 Europe
- 5.6.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.6.2.2 Germany
- 5.6.2.3 France
- 5.6.2.4 Italy
- 5.6.2.5 Russia
- 5.6.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.3.1 China
- 5.6.3.2 India
- 5.6.3.3 Japan
- 5.6.3.4 South Korea
- 5.6.3.5 Australia
- 5.6.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4 South America
- 5.6.4.1 Brazil
- 5.6.4.2 Rest of South America
- 5.6.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5.1 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.5.1.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.5.2 Africa
- 5.6.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.6.5.2.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 ABB Ltd.
- 6.4.2 BAE Systems plc
- 6.4.3 DNV AS
- 6.4.4 Fugro NV
- 6.4.5 Hanwha Corporation
- 6.4.6 HD Hyundai Heavy Industries Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.7 Kongsberg Gruppen ASA
- 6.4.8 L3Harris Technologies, Inc.
- 6.4.9 Marine AI Ltd.
- 6.4.10 MITSUI E&S Group
- 6.4.11 Praxis Automation Technology B.V.
- 6.4.12 Rolls-Royce plc
- 6.4.13 Sea Machines Robotics, Inc.
- 6.4.14 Samsung Heavy Industries Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.15 Wartsila Corporation
- 6.4.16 Vigor Industrial LLC
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




