PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1693915

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1693915
Japan Diabetes Drugs And Devices - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
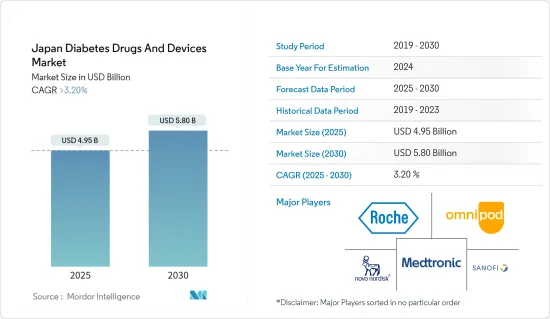
The Japan Diabetes Drugs And Devices Market size is estimated at USD 4.95 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 5.80 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of greater than 3.2% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Japan's diabetes drugs and devices market is poised for significant growth through the forecast period, driven by a rising prevalence of diabetes and proactive initiatives from companies, including product development and expanding production capacities.
Diabetes drugs and devices are crucial in monitoring and managing blood glucose levels. With Japan's diabetic population on the rise, companies are set to see an expanding user base. According to the IDF Diabetes Atlas, Japan is projected to have around 10,542.7 thousand individuals with diabetes by 2030; the number is expected to reach 10,117.9 thousand by 2045.
Recognizing the widening gap between the demand and supply of diabetic drugs, several companies are seizing the opportunity. For instance, in June 2024, Eli Lilly and Company made significant investments to boost its production capacity for drugs targeting obesity and diabetes. This move came as the company lifted restrictions on shipping its flagship diabetes drug, Manjaro, in Japan. By enhancing its production capabilities, Eli Lilly aims to meet the escalating demand for diabetes drugs, especially in light of limited supplies at the national level.
In May 2024, the Japan Diabetes Society published guidelines emphasizing the safe use of diabetes drugs, particularly Incretin-Related Drugs. This initiative was prompted by the rising adoption of GLP-1 receptor agonists, known for their efficacy in blood sugar management and weight reduction. These drugs have also shown promising results in addressing diabetes-related kidney and cardiovascular diseases, further bolstered by the introduction of orally administered formulations.
The diabetes drugs and devices market in Japan is on a robust growth trajectory. The increasing prevalence of diabetes, coupled with strategic initiatives by companies and regulatory support, is expected to drive market expansion. This dynamic environment presents significant opportunities for stakeholders in the diabetes care sector.
Japan Diabetes Drugs and Devices Market Trends
The Continuous Glucose Monitoring Segment is Expected to Witness Significant Growth Over the Forecast Period
The continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) market in Japan is expected to experience significant growth over the forecast period. This growth can be attributed to technological advancements and the increasing adoption of CGM devices among diabetes patients.
Continuous glucose monitoring sensors rely on glucose oxidase to gauge blood sugar levels. This enzyme converts glucose to hydrogen peroxide, which generates an electrical signal transmitted to a receiver upon reacting with platinum in the sensor. The sensor is pivotal in any continuous blood glucose monitoring apparatus. Researchers are actively exploring alternatives to electrochemical glucose sensors, aiming to render CGM sensors more cost-effective, less invasive, and user-friendly. Optical measurement is a promising avenue for glucose assessment.
Various techniques, such as spectroscopy, fluorescence, and holography, show significant potential for continuous glucose monitoring. For instance, Eversense, a fluorescence-based CGM sensor from Sensonics Company, boasts a notably longer lifespan than its electrochemical counterparts. With ongoing technological enhancements to boost sensor precision, the segment is primed for substantial growth.
Japan's expanding CGM landscape is set to fuel segmental expansion. In March 2024, Abbott unveiled its FreeStyle Libre 2 Continuous Glucose Monitoring Device, offering real-time, minute-to-minute glucose monitoring and customizable alerts for diabetes management. In a similar move, Abbott introduced an official LINE account in 2023, specifically for its "FreeStyle Libre Care" support program, streamlining registration for FreeStyle Libre Care through the LINE platform.
Highlighting the rising adoption of CGM, in March 2024, the Japan Diabetes Society released updated versions of its Guidelines for Real-time CGM Use and its stance on Intermittent Scanning Continuous Glucose Monitors (isCGM), specifically referencing FreeStyle Libre. These guidelines are expected to play a significant role in enhancing patients' blood sugar management, detailing the patient profiles for whom these tools are recommended, especially in conjunction with SMBG.
Hence, the growth of the segment is driven by technological innovations and increasing market offerings. These advancements are expected to significantly improve diabetes management and patient outcomes over the forecast period.
Rising Diabetes Prevalence is Expected to Drive the Market
Diabetes remains a critical health issue globally, and Japan is no exception. The increasing prevalence of diabetes in the country is a cause for concern, necessitating immediate attention and action from healthcare authorities and stakeholders.
The Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare in Japan has identified diabetes as a pressing health concern. Type 2 diabetes, in particular, poses a substantial economic burden, especially for patients with comorbidities such as hypertension and hyperlipidemia or those who develop complications.
Japan is witnessing a surge in diabetes across all age groups, attributed to a rising obese population, poor dietary habits, and sedentary lifestyles. The International Diabetes Federation (IDF) projects Japan's diabetic population to reach 10,542.7 thousand by 2030 and 10,117.9 thousand by 2045.
With the diabetic population on the rise, Japan is seeing more frequent product developments and guideline updates. For instance, in May 2024, during the 67th Annual Meeting of the Japan Diabetes Society, Light Touch Technology (based in Joto-ku, Osaka) unveiled a non-invasive blood glucose sensor. This innovative sensor, which is in the mass production prototype stage, uses a mid-infrared laser to measure glucose concentration in capillaries. Additionally, it only requires the user to hold their finger over the sensor for five seconds. The company aims to release the sensor in the coming years.
Given the escalating diabetes prevalence and the country's proactive responses, the diabetes segment is poised for robust growth over the forecast period.
Hence, Japan's increasing diabetes prevalence presents significant challenges and opportunities. The country's commitment to addressing this health crisis through innovative solutions and updated guidelines will be crucial in managing the economic and health impacts of diabetes in the coming years.
Japan Diabetes Drugs and Devices Industry Overview
The Japanese diabetes drugs and devices market is semi-consolidated with the presence of key players such as Novo Nordisk A/S, Medtronic, Insulet Corporation, Sanofi, and Eli Lilly and Company.
Large companies such as Abbott and Medtronic have made numerous mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships to gain market dominance while adhering to organic growth strategies. The manufacturers of insulin delivery devices are spending a huge amount on the R&D of the devices.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Dynamics
- 4.2.1 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1.1 Rising Diabetes Prevalence In The Country
- 4.2.1.2 Growing Strategic Initiatives By The Government
- 4.2.2 Market Restraints
- 4.2.2.1 Limited Availability of Affordable Drug Delivery Devices In The Country
- 4.2.1 Market Drivers
- 4.3 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.3.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.3.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.3.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.3.4 Threat of Substitute Products and Services
- 4.3.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (Market Size by Value - USD)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Devices
- 5.1.1.1 Monitoring Devices
- 5.1.1.1.1 Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Devices
- 5.1.1.1.2 Continuous Blood Glucose Monitoring
- 5.1.1.2 Management Devices
- 5.1.1.2.1 Insulin Pump
- 5.1.1.2.2 Insulin Syringes
- 5.1.1.2.3 Disposable Pens
- 5.1.1.2.4 Others
- 5.1.2 Drugs
- 5.1.2.1 Oral Anti-diabetes Drugs
- 5.1.2.2 Insulin Drugs
- 5.1.2.3 Others
- 5.1.1 Devices
6 Market Indicators
- 6.1 Type-1 Diabetes Population (2021-2029)
- 6.2 Type-2 Diabetes Population (2021-2029)
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Company Profiles
- 7.1.1 Novo Nordisk A/S
- 7.1.2 Medtronic
- 7.1.3 Insulet Corporation
- 7.1.4 Tandem Diabetes Care
- 7.1.5 Ypsomed
- 7.1.6 Novartis AG
- 7.1.7 Sanofi
- 7.1.8 Eli Lilly and Company
- 7.1.9 Abbottt
- 7.1.10 Astrazeneca
- 7.1.11 Dexcom Inc.
8 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS




