Need help finding what you are looking for?
Contact Us
PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1693510

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1693510
India Specialty Fertilizer - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
PUBLISHED:
PAGES: 192 Pages
DELIVERY TIME: 2-3 business days
SELECT AN OPTION
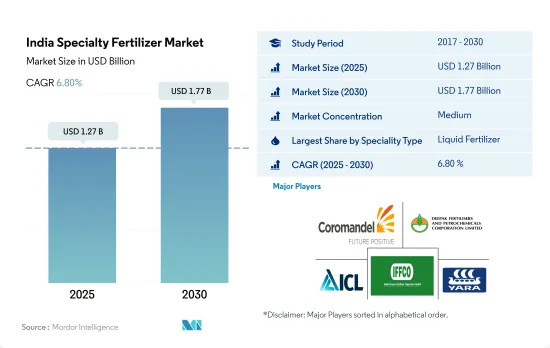
The India Specialty Fertilizer Market size is estimated at 1.27 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 1.77 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 6.80% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Sustainable farming practices and higher environmental safety are being adopted, driving the usage of specialty fertilizers
- The controlled-release fertilizer market in the country witnessed an increase in market value by 106.1%, whereas the consumption volume increased by 24.2% during 2017-2021. The main reason for this was the Government of India making it mandatory for all domestic producers of urea to produce 100% neem-coated urea and distribute it at a subsidized price to the farmers.
- Liquid fertilizers accounted for 49.7% of India's specialty fertilizer market in 2022. Complex fertilizers accounted for the maximum share in the liquid fertilizer market, i.e., 75.7%. This segment was valued at USD 206.1 million in 2017, which is anticipated to reach USD 2.12 billion by 2030. Similarly, straight fertilizers accounted for 24.3% of the liquid fertilizers market in 2022.
- Slow-release fertilizers accounted for 1.0% of the specialty fertilizer market value in 2022. Field crops and horticultural crops are the major consumers of slow-release fertilizers, accounting for 89.6% and 10.2% of the market volume in 2022. The intensive field crop and horticultural crop cultivation in the country are anticipated to drive the market for slow-release fertilizers.
- In the specialty fertilizer market, water-soluble fertilizers accounted for 46.2% of the value share in 2022. The water-soluble fertilizer market witnessed stable growth during 2017-2021, valued at USD 1.46 billion in 2022. Field crops occupied the largest share of 88.8%, followed by horticultural crops.
- The rise in demand for high-efficiency fertilizers, ease of application, adoption of sustainable farming practices, and higher environmental safety are some of the factors driving the specialty fertilizer market in India.
India Specialty Fertilizer Market Trends
manganese deficiency is a common problem in European countries, which most frequently affects sandy soils, organic soils with a pH above 6
- The area under field crop cultivation in the country increased by 3.5% during 2017-2022. The increased cultivation of cereals, pulses, and oilseeds in the country due to the rising consumer demand domestically and internationally is the major driving factor for the rising acreage.
- By crop type, rice, wheat, and soybean occupied the largest area under cultivation in the country, accounting for 47 million ha, 31.1 million ha, and 12.3 million ha in the year 2022. Rice is the most important food crop of India, covering about one-fourth of the total cropped area and providing food to about half of the Indian population. It is cultivated in almost all the states of the country, mainly in West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Punjab, and Tamil Nadu.
- Accordingly, rice consumption in the country increased from 95.8 million tons in 2016 to 107 million tons in 2022, which shows the rising demand for the crop in the country. This trend is further anticipated to drive the demand for fertilizers during 2023-2030. Similarly, wheat cultivation in the country increased from 98.5 million tons in 2017 to 107.6 million tons in the year 2020. It is cultivated majorly in Punjab, West Bengal, Haryana, and Rajasthan. Wheat is the second most important cereal crop in India and plays a vital role in the food and nutritional security of the country. Therefore, the intense cereal cultivation in the country, coupled with rising domestic and international demand, is anticipated to drive the Indian fertilizer market during 2023-2030.
Among the primary nutrients, nitrogen is the most-applied nutrient in field crops, with an average application rate of 223.5 kg per hectare
- The overall primary nutrient average application rate in 2022 was 125.1 kg/ha, with nutrients such as nitrogen with the highest average application rate of 223.5 kg/ha. Accordingly, nitrogen is the major source of nutrients for crops such as rice, which is intensively cultivated in the country, and such nutrient deficiency in soil is limiting rice productivity across the nation.
- The State of Biofertilizers and Organic Fertilizers in India marked poor status of soil health and increasing consumption of chemical fertilizers in India. Accordingly, 97.0%, 83.0%, and 71.0% of the soil tested were found to be deficient in nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium.
- By crop, wheat, rice, and corn/maize were estimated to be the crop types with the highest average nutrient application rate of 231, 156, and 149 kg/ha in 2022. Wheat and rice are important staple food domestically and globally. Multiple nutrient deficiencies are the key factors that reduce yield and profit. Wheat and rice crops require nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium, along with other micronutrients such as sulfur, boron, iron, and zinc, for their proper growth and development. The proper management of nutrients is necessary for successful crop production, which in turn is driving market growth.
- Field crops consume the maximum amount of primary nutrients, such as nitrogen fertilizer. As grains and cereals are intensively grown in the country, the soil is depleted of its nutrition, and hence they require more amount of fertilizers to supplement them, which in turn is anticipated to drive the market during 2023-2030.
India Specialty Fertilizer Industry Overview
The India Specialty Fertilizer Market is moderately consolidated, with the top five companies occupying 48.56%. The major players in this market are Coromandel International Ltd., Deepak fertilizers & Petrochemicals Corporation Ltd, ICL Group Ltd, Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative Limited and Yara International ASA (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
Product Code: 92574
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Acreage Of Major Crop Types
- 4.1.1 Field Crops
- 4.1.2 Horticultural Crops
- 4.2 Average Nutrient Application Rates
- 4.2.1 Micronutrients
- 4.2.1.1 Field Crops
- 4.2.1.2 Horticultural Crops
- 4.2.2 Primary Nutrients
- 4.2.2.1 Field Crops
- 4.2.2.2 Horticultural Crops
- 4.2.3 Secondary Macronutrients
- 4.2.3.1 Field Crops
- 4.2.3.2 Horticultural Crops
- 4.2.1 Micronutrients
- 4.3 Agricultural Land Equipped For Irrigation
- 4.4 Regulatory Framework
- 4.5 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD and Volume, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Speciality Type
- 5.1.1 CRF
- 5.1.1.1 Polymer Coated
- 5.1.1.2 Polymer-Sulfur Coated
- 5.1.1.3 Others
- 5.1.2 Liquid Fertilizer
- 5.1.3 SRF
- 5.1.4 Water Soluble
- 5.1.1 CRF
- 5.2 Application Mode
- 5.2.1 Fertigation
- 5.2.2 Foliar
- 5.2.3 Soil
- 5.3 Crop Type
- 5.3.1 Field Crops
- 5.3.2 Horticultural Crops
- 5.3.3 Turf & Ornamental
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles
- 6.4.1 Chambal Fertilizers & Chemicals Ltd
- 6.4.2 Coromandel International Ltd.
- 6.4.3 Deepak fertilizers & Petrochemicals Corporation Ltd
- 6.4.4 Grupa Azoty S.A. (Compo Expert)
- 6.4.5 Haifa Group
- 6.4.6 ICL Group Ltd
- 6.4.7 Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative Limited
- 6.4.8 Mangalore Chemicals & Fertilizers Ltd.
- 6.4.9 Sociedad Quimica y Minera de Chile SA
- 6.4.10 Yara International ASA
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR FERTILIZER CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms
Have a question?


SELECT AN OPTION
Have a question?


Questions? Please give us a call or visit the contact form.
