PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1692128

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1692128
Rare Disease Treatment - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
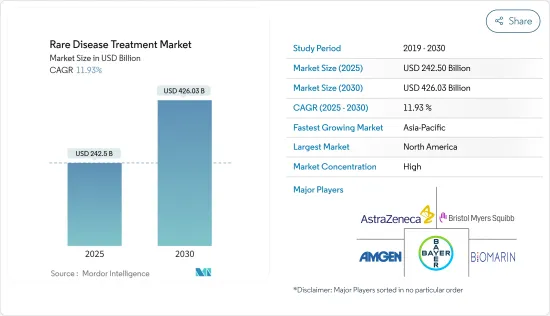
The Rare Disease Treatment Market size is estimated at USD 242.50 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 426.03 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 11.93% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Megatrends Shaping the Market: The Rare Disease Treatment Market is experiencing robust growth, driven by two primary megatrends: the rising global prevalence of rare diseases and the intensifying focus on research and development (R&D) for novel therapeutics. These megatrends are supported by increasing awareness, favorable government policies, and a surge in new drug launches. Collectively, these factors are propelling the market forward and shaping the future of the rare disease treatment landscape.
Increase in the Number of Rare Disease Cases: A key driver for market expansion is the growing prevalence of rare diseases worldwide. According to GlobalGenes, more than 400 million people are affected by rare diseases globally, with approximately 7,000 known conditions. This substantial patient population drives demand for specialized treatments, especially since 80% of these diseases have genetic origins. The discovery of 250 to 280 new rare diseases annually further emphasizes the expanding market scope and the need for continuous innovation in treatment approaches.
Rising R&D Activities for Novel Therapeutics and Drugs: R&D is at the heart of growth in the rare disease treatment market. Increased funding and strategic public-private initiatives are catalyzing innovation. For example, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has committed over USD 38 million in funding over four years to support clinical trials and research tools for rare diseases. Such investments are critical in addressing the unmet medical needs of rare disease patients, fostering significant market growth.
Increase in the Number of New Drug Launches: The number of FDA-approved drugs for rare diseases, many of which are classified as orphan drugs, is growing rapidly. Recent approvals like Xenpozyme, designed for treating Acid Sphingomyelinase Deficiency (ASMD), highlight the sector's focus on rare disease drug development. These new treatments not only offer hope to patients but also contribute to market expansion by providing more options to address the specific needs of those affected by rare diseases.
Favorable Government Policies: Government initiatives play a crucial role in accelerating market growth. Countries like India and the United States are introducing policies that support rare disease research and treatment. For instance, in August 2024, India added 63 rare diseases to its National Policy for Rare Diseases, following recommendations from the Central Technical Committee for Rare Diseases (CTCRD). Similarly, the U.S. FDA's Accelerating Rare Disease Cures (ARC) Program is designed to fast-track the development of treatment options for rare diseases, creating a favorable environment for market players.
Strategic Initiatives by Market Players: Strategic collaborations, mergers, and acquisitions are shaping the competitive landscape. Companies like AstraZeneca and CanSino Biologics Inc. are partnering to enhance rare disease diagnosis and treatment access in China. Such initiatives are expected to drive innovation, expand market reach, and further stimulate market growth in the years ahead.
Rare Disease Treatment Market Trends
Biologics: Driving Innovation in Rare Disease Treatment
Segment Overview: Biologics are transforming the rare disease treatment market, accounting for 58% of the current market share. These complex therapies, including proteins, antibodies, and peptides, offer a targeted approach to treating genetic and chronic conditions previously considered untreatable.
Growth Drivers: Several factors are driving the growth of biologics. Advances in genetic research, alongside developments in personalized medicine, have enabled the creation of highly targeted therapies. The increasing prevalence of rare diseases, combined with greater understanding of their molecular mechanisms, is fueling research in this area. Additionally, regulatory incentives for orphan drug development are encouraging companies to invest in biologics, resulting in a strong pipeline of innovative treatments.
Competitive Landscape: The biologics market is characterized by intense competition, with companies focusing on innovation and collaboration. Pharmaceutical firms are investing heavily in R&D to develop biological therapies that tackle the root causes of rare diseases. Collaborations between pharmaceutical companies and research institutions are becoming more common, facilitating the development of novel biologics. The use of advanced technologies, such as gene editing and cell therapies, is expected to disrupt existing treatment paradigms and drive future growth in the biologics segment.
Asia-Pacific: Emerging Powerhouse in Rare Disease Treatment
Regional Dynamics: The Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a key growth market for rare disease treatments, with a projected Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of over 12% from 2024 to 2029. The region's rapid market expansion highlights its potential in the global rare disease treatment landscape.
Growth Catalysts: Several factors are propelling growth in Asia-Pacific. Increased awareness of rare diseases, spearheaded by government initiatives, patient advocacy, and healthcare providers, is improving diagnosis rates and increasing demand for treatments. Governments across the region are introducing policies to enhance rare disease management. Singapore's Rare Disease Fund and Malaysia's healthcare investments are notable examples of supportive efforts. Furthermore, the region's expanding healthcare infrastructure is improving access to advanced diagnostics and treatments, particularly in emerging economies.
Strategic Imperatives: Companies seeking to capitalize on Asia-Pacific's rapid growth are focusing on treatments targeting rare diseases prevalent in the region, recognizing its unique genetic diversity. Collaborations between international pharmaceutical firms and local healthcare providers are on the rise, aimed at improving clinical trial capabilities and expanding research on rare diseases in Asian populations. Companies are also leveraging digital health technologies, such as telemedicine and patient monitoring platforms, to support rare disease management.
Future Outlook: The Asia-Pacific market is expected to attract increased investment and innovation due to its robust growth. Strategic partnerships, technological advancements, and regulatory support will be key to addressing the challenges and opportunities in this dynamic market. Companies that navigate the diverse regulatory environments and healthcare systems in the region while leveraging emerging technologies are well-positioned for success.
Rare Disease Treatment Industry Overview
Market Dominance: Global Conglomerates Lead
The Rare Disease Treatment Market is dominated by global pharmaceutical conglomerates, with companies like Pfizer, Novartis, Roche, and Sanofi controlling a significant portion of the market. Their strong market positions are due to extensive R&D capabilities and global reach. Rare disease portfolios play an increasingly important role in these companies' overall revenue, with ample opportunities for further expansion due to the growing total addressable market (TAM).
Key Players: Innovation and Specialization Drive Success
Top players, such as Pfizer, Novartis, Roche, and Sanofi, share a focus on innovation and specialization. Their leadership in the market is bolstered by substantial investments in R&D, particularly in biologics and gene therapies. Breakthrough treatments like Novartis' Zolgensma for spinal muscular atrophy and Roche's Hemlibra for hemophilia A showcase the companies' ability to develop pioneering treatments. Their global presence and financial resources allow them to navigate the complexities of rare disease drug development, positioning them as leaders in this specialized market.
Strategies for Market Success: R&D and Collaboration
Future success in the rare disease treatment market will depend on intensified R&D efforts, strategic collaborations, and the adoption of emerging technologies. Companies are increasingly focusing on gene therapies and personalized medicine, as demonstrated by the approval of treatments like Zolgensma. Partnerships with research institutions and patient advocacy groups are vital in identifying unmet needs and accelerating drug development. For instance, BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc. and the Allen Institute's collaboration on gene therapies for rare central nervous system diseases is a prime example of the innovative partnerships shaping the market. Additionally, the use of AI and big data for drug discovery and optimizing clinical trials is becoming a key strategy for enhancing competitive advantage.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increase in the Number of Rare Disease Cases
- 4.2.2 Rising R&D Activities for Novel Therapeutics and Drugs and Increase in the Number of New Drug Launches and Favorable Government Policies
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Lack of Awareness Regarding Rare Disease Treatment
- 4.3.2 High Cost of Treatment
- 4.4 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.4.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (Market Size by Value - in USD)
- 5.1 By Drug Type
- 5.1.1 Biologics
- 5.1.2 Non-biologics
- 5.2 By Therapeutic Area
- 5.2.1 Genetic Diseases
- 5.2.2 Neurological Diseases
- 5.2.3 Oncology
- 5.2.4 Infectious Diseases
- 5.2.5 Cardiovascular Diseases
- 5.2.6 Other Therapeutic Area
- 5.3 By Mode of Administration
- 5.3.1 Oral
- 5.3.2 Injection
- 5.3.3 Other Modes of Administration
- 5.4 Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 Germany
- 5.4.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.3 France
- 5.4.2.4 Italy
- 5.4.2.5 Spain
- 5.4.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 Japan
- 5.4.3.3 India
- 5.4.3.4 Australia
- 5.4.3.5 South Korea
- 5.4.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.4.1 GCC
- 5.4.4.2 South Africa
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5 South America
- 5.4.5.1 Brazil
- 5.4.5.2 Argentina
- 5.4.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Company Profiles
- 6.1.1 AbbVie Inc.
- 6.1.2 AstraZeneca (Alexion Pharmaceuticals Inc.)
- 6.1.3 Amgen Inc.
- 6.1.4 Baxter
- 6.1.5 Bayer AG
- 6.1.6 Biomarin Pharmaceuticals
- 6.1.7 Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
- 6.1.8 Eisai Co. Ltd
- 6.1.9 Eli Lilly and Company
- 6.1.10 F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd
- 6.1.11 Novartis AG
- 6.1.12 Pfizer Inc.
- 6.1.13 Sanofi
- 6.1.14 Teva Pharmaceuticals
- 6.1.15 Vertex Pharmaceuticals
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS




