PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1685806

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1685806
Rice Seed Treatment - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
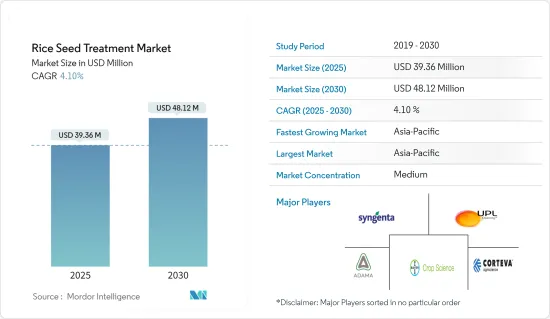
The Rice Seed Treatment Market size is estimated at USD 39.36 million in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 48.12 million by 2030, at a CAGR of 4.10% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Seed treatment protects seeds and seedlings from seed and soil-borne diseases and insect pests that affect crop emergence and growth. The global adoption of this practice among rice farmers requires effective extension strategies, including access to appropriate chemical pesticides/bio-pesticides and equipment, along with knowledge of seed treatment methods and post-treatment handling procedures. In rice cultivation, chemical seed treatment is primarily used for seed enhancement and protection.
Seed treatment is implemented globally to produce pest and disease-free seeds using products that protect against pests and diseases throughout germination and the crop cycle. According to USDA data, total rice production reached 522.7 million metric tons during MY 2023-2024. China contributed 28% of this production, followed by India at 26%, Bangladesh at 7%, Indonesia at 6%, and Vietnam at 5%.
USDA reports indicate that global rice production for MY 2024-2025 is projected to reach a record 533.7 million metric tons (milled basis), an increase of 11 million metric tons. While Argentina, Brazil, and Taiwan received upward production revisions, forecasts were reduced for Australia, Costa Rica, Cuba, the European Union, Honduras, Nepal, Panama, the Philippines, and South Korea. Global rice consumption and residual use in MY 2024-2025 is anticipated to reach 530.3 million metric tons, increasing by 6.2 million metric tons from the previous year. The rice seed treatment market growth is driven by increasing rice consumption as a staple food, higher adoption of high-quality seeds, government support in the seed industry, and technological advancements in seed treatment for reducing rice diseases and pest infestation.
Rice Seed Treatment Market Trends
Increasing Demand and Adoption of High-Quality Seeds
Farmers are increasingly acknowledging seed treatment as a mode to protect high investments made in good quality seeds. Owing to the increasing demand for high-quality seeds with desirable agronomic traits, the cost of seeds is increasing. Both companies and farmers are ready to spend extra on seed treatment solutions to save costly high-quality seeds.
The introduction of GM seeds added high value to seeds, with the cost of seeds being high and sometimes being twice as much as that of non-GM seeds. Earlier, a growth of 85% was anticipated by farmers as some seeds would rot or be destroyed by insects. With changing trends and 100% seed emergence expectations by growers even in unfavorable conditions, seed treatment has become a necessity. The key players in the market are constantly focusing on developing superior-quality seeds through modern breeding techniques, thereby increasing the cost of the seeds.
Top players in the market are focusing on the development of superior quality seeds through modern breeding techniques, thereby increasing the seed cost. Replanting seeds due to poor germination and insect attack is expensive. Moreover, the high cost of labor requirements is associated with overall cost. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization, the total crop yield of cereals accounted for 4,182.4 kg/ha in 2022, which is higher than the previous year at 4,152.2 kg/ha. Hence to meet the growing demand, farmers need quality seeds that are well-treated to enhance the yield in limited harvested areas.
African countries do not produce enough rice and are reliant on imports. One such country is Sierra Leone. Hence, to become self-sufficient, the country's government is adopting a few strategies. A promising solution is the dissemination of high-yielding rice varieties, such as the New Rice of Africa (NERICA), which have become known as the miracle crop for African rice farmers because they combine the genetic qualities of Asian rice (high yielding) and African rice (high resistance to drought and disease). However, current estimates suggest only 2% of farmers in the country use NERICAs. This is due to the cost of improved varieties that cost 40-100% more than traditional ones, representing a significant barrier to adoption among poor farmers. Hence, due to the high cost of these hybrid varieties, there is an opportunity for paddy farmers to use treated seeds at an affordable cost. This, in turn, is anticipated to lead to the positive growth of the rice seed treatment market in the coming years.
Asia-Pacific Dominates the Market
The Asia-Pacific region held the largest market share in the rice seed treatment sector in 2023, driven by rice being the primary staple food and most cultivated crop. China emerged as the region's largest and fastest-growing market, followed by India and Japan. China represents the world's second-largest seed market after the United States, with an annual seed planting volume of 12 million metric tons and a market value of USD 19 billion in 2021. According to USDA data, global hybrid rice seed production reached 168,000 metric tons in 2022, with an average yield of 2,160 kg/ha.
The Chinese Ministry of Agriculture reports that the rice seed industry is prioritizing differentiated commercial varieties to address the limitations of current high-yield, low-resistance varieties, particularly regarding rice blast resistance. China's emphasis on seed value enhancement has resulted in increased hybrid rice variety development. Rice remains China's primary crop, with FAO data showing production of 210 million metric tons in 2022 across 29.7 million hectares. The country's expanding rice production and growing food demand continue to drive the rice seed treatment market growth.
India maintains its position as the world's second-largest producer and primary rice exporter. The country's diverse altitude and climatic conditions support widespread rice cultivation. ITC Trade Map data indicates that India exported 10.5 million metric tons of rice in 2023, accounting for 32.5% of global export volume and ranking as the world's leading rice exporter. The country's favorable climate and agricultural practices have increased rice production, strengthening the demand for rice seed treatment chemicals. The regional rice seed treatment market is projected to maintain steady growth, supported by increasing food demand and ongoing research and development efforts to develop innovative products.
Rice Seed Treatment Industry Overview
The rice seed treatment market is consolidated, with a few major players dominating the market share in 2023. Bayer AG, Syngenta International AG, UPL Limited, Adama Agricultural Solutions Ltd, and Corteva Agriscience are the key companies operating in the market. These companies primarily focus on new product launches, partnerships, and acquisitions. Investment in research and development and the development of innovative product portfolios remain essential strategies for market growth.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increasing Demand And Adoption Of High-Quality Seeds
- 4.2.2 Technological Developments In The Crop Protection Industry
- 4.2.3 Rising Government Support For Seed Treatment
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Rising Environmental Concerns
- 4.3.2 Limitations Across Farm-Level Seed Treatment
- 4.4 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Application
- 5.1.1 Chemical
- 5.1.2 Non-chemical/Biological
- 5.2 Function
- 5.2.1 Seed Protection
- 5.2.2 Seed Enhancement
- 5.2.3 Other Functions
- 5.3 Application Techniques
- 5.3.1 Seed Coating
- 5.3.2 Seed Pelleting
- 5.3.3 Seed Dressing
- 5.3.4 Other Application Techniques
- 5.4 Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 Spain
- 5.4.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.3 France
- 5.4.2.4 Germany
- 5.4.2.5 Russia
- 5.4.2.6 Italy
- 5.4.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 Japan
- 5.4.3.3 India
- 5.4.3.4 Australia
- 5.4.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Africa
- 5.4.5.1 South Africa
- 5.4.5.2 Rest of and Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Most Adopted Strategies
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 Adama Agricultural Solutions Ltd
- 6.3.2 Yara International ASA
- 6.3.3 Bayer AG
- 6.3.4 Indofill Industries Limited
- 6.3.5 Dhanuka Agritech Limited
- 6.3.6 Corteva Agriscience
- 6.3.7 Croda International (INCOTEC)
- 6.3.8 Crystal Crop Protection Limited
- 6.3.9 UPL Limited
- 6.3.10 Nufarm Limited
- 6.3.11 Syngenta AG
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS




