PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906902

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906902
Food Allergen Testing - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
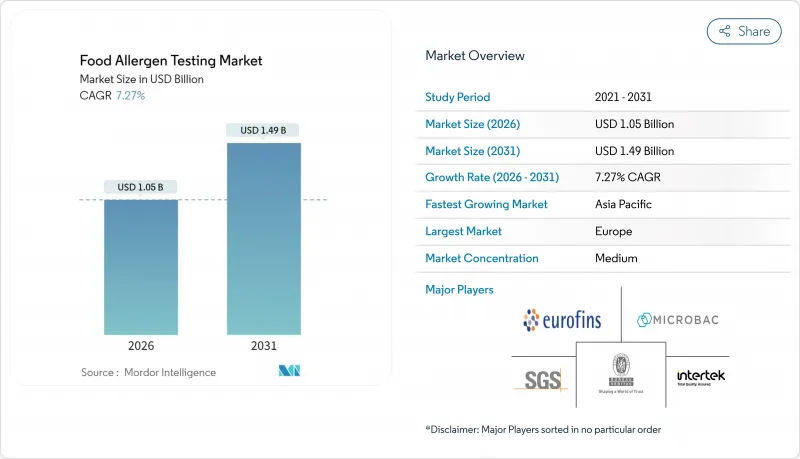
The food allergen testing market was valued at USD 0.98 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 1.05 billion in 2026 to reach USD 1.49 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 7.27% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
Intensifying regulatory scrutiny, rising recall costs, and the push for harmonized reference-dose rules are the foremost forces accelerating growth. Heightened cross-border trade in processed foods, coupled with consumer demand for clean-label products, is broadening the testing footprint across every supply-chain tier. Technology adoption is shifting toward multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction and mass-spectrometry platforms as laboratories seek lower limits of quantification, while artificial-intelligence tools shorten turnaround times and reduce false positives. At the same time, high instrument costs and the complexity of multi-allergen protocols restrain penetration among smaller manufacturers, creating white-space opportunities for contract laboratories and rapid test-kit vendors.
Global Food Allergen Testing Market Trends and Insights
Surge in food recalls and brand-risk costs
The increasing frequency and financial impact of allergen-related food recalls is transforming risk management priorities across the food industry, as undeclared allergens remain the primary cause of recalls globally. United Kingdom food safety data showed 53 cases of undeclared allergen recalls in 2024, a 10% increase that highlights the ongoing challenge of cross-contamination control. The FDA's implementation of Food Safety Modernization Act Section 204 traceability requirements, taking effect in January 2026, requires digital tracking systems that will increase the visibility of allergen control failures and associated liability exposure. This regulatory change is driving manufacturers to invest in preventive testing protocols instead of reactive recall management, generating consistent demand for rapid allergen screening technologies. Risk mitigation and regulatory compliance concerns are especially significant in the foodservice sector, where restaurants experience the second-highest incidence of allergic reactions after home consumption, creating market opportunities for point-of-use testing solutions.
Tightening allergen labeling laws and enforcement
Regulatory harmonization across major markets is creating unprecedented standardization pressure that extends beyond traditional labeling requirements to encompass manufacturing processes and supply chain verification protocols. The FDA's release of Edition 5 guidance for allergen controls in 2024 introduced enhanced validation requirements for cleaning procedures and environmental monitoring, while the United States Department of Agriculture's Food Safety and Inspection Service launched a comprehensive allergen verification program targeting meat and poultry processors. The Dutch Food and Consumer Product Safety Authority's updated cross-contact prevention guidelines exemplify the trend toward prescriptive manufacturing standards that mandate specific testing frequencies and analytical methods. These regulatory developments are particularly impactful for multinational food companies that must navigate varying enforcement intensities across jurisdictions, with European markets maintaining the most stringent compliance frameworks. The regulatory influence extends to emerging markets where export-oriented manufacturers must adopt international testing standards to access premium markets, creating a multiplier effect that amplifies demand for accredited testing services.
High cost of testing technologies
The high capital requirements for advanced allergen testing platforms create significant barriers to market entry, particularly affecting small and medium-sized food manufacturers that constitute the majority of global food production capacity. LC-MS/MS systems for confirmatory allergen analysis require initial investments exceeding USD 500,000, with annual maintenance and consumable costs reaching USD 100,000 per instrument. The financial burden extends beyond equipment costs to include specialized personnel training, method validation, and regulatory compliance documentation, which can collectively exceed USD 1 million for comprehensive allergen testing capabilities. This cost structure has created a divided market where large multinational corporations maintain in-house testing facilities while smaller manufacturers depend on contract testing services, potentially causing delays during peak demand periods. The cost barrier is especially significant in emerging markets, where local laboratories often lack the financial resources for advanced analytical platforms, resulting in dependence on international testing providers and longer turnaround times for safety assessments.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Expansion of global processed-food trade
- Harmonised reference-dose rules lowering LOQs
- Complexity of multi-allergen testing
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Immunoassay-based technologies hold a dominant 57.62% market share in 2025, due to their reliability, cost-effectiveness, and acceptance within global food safety regulations. PCR-based methods are growing at an 8.12% CAGR through 2031, driven by their high specificity and ability to test multiple allergens simultaneously. Mass-spectrometry methods are increasing in confirmatory testing applications, particularly for processed foods where protein modifications can affect immunoassay performance. Spectroscopy and imaging technologies serve specific rapid screening applications, while nanobiosensor platforms are advancing point-of-use testing through smartphone integration and AI analysis.
The market is moving toward hybrid platforms that integrate multiple detection methods to address technical limitations while maintaining cost efficiency for routine testing. Advanced biosensor technologies using gold nanoparticles and graphene-based transducers achieve femtomolar detection limits, exceeding traditional ELISA sensitivity and enabling the detection of previously undetectable trace allergen contamination. However, regulatory validation remains a significant challenge for new technologies, as ISO 16140-2 compliance requires extensive validation studies that typically add 2-3 years to market entry timelines.
The Food Allergen Testing Market Report Segments the Industry Into Technology (Immunoassay-Based, PCR-Based, Mass-Spectrometry-Based, Spectroscopy and Imaging, Others), Application (Bakery and Confectionery, Dairy Products, Seafood and Meat Products, Beverages, Baby Food and Infant Formula, Others), and Geography (North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Europe holds a dominant market share of 34.21% in 2025, supported by comprehensive regulatory frameworks and well-established testing infrastructure across government laboratories and commercial service providers. The European Food Safety Authority's regular updates to allergen assessment guidelines and the Dutch Food and Consumer Product Safety Authority's standards for cross-contact prevention demonstrate the region's stringent regulatory environment that sustains testing demand. Asia-Pacific registers the highest growth rate at 9.86% CAGR through 2031, with this growth stemming from evolving regulations in China and India as they align with international standards to enhance food exports. Japan's doubled food allergy prevalence highlights demographic shifts driving market growth, while South Korea and Australia serve as key testing hubs for multinational food companies.
North America operates under established FDA and USDA regulatory frameworks, with market growth primarily driven by technological advancements rather than regulatory expansion. The region maintains sophisticated testing protocols and infrastructure, while continuing to adapt to emerging allergen detection technologies and methodologies. The established regulatory environment provides a stable foundation for market operations, though the focus has shifted towards optimization and efficiency improvements rather than fundamental regulatory changes.
South America and Middle East and Africa present growth opportunities through developing regulations and export market requirements. However, limited local analytical capabilities and reliance on international testing providers restrict market development. The market distribution reflects the relationship between regulatory advancement and market growth, as regions invest in testing capabilities to enhance domestic food safety and international trade competitiveness. These emerging markets demonstrate increasing awareness of food safety standards and are gradually developing their testing infrastructure to meet international requirements.
- Eurofins Scientific SE
- SGS SA
- Intertek Group PLC
- Bureau Veritas SA
- ALS Limited
- Merieux NutriSciences
- Neogen Corporation
- Microbac Laboratories Inc.
- Crystal Chem Inc.
- Romer Labs Division GmbH
- R-Biopharm AG
- Hygiena LLC
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- PerkinElmer Inc.
- Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc.
- Charm Sciences Inc.
- Danaher Corp. (Cepheid / SCIEX)
- Agilent Technologies Inc.
- QIAGEN N.V.
- AsureQuality Ltd.
- TUV SUD AG
- TUV Nord AG
- TUV Rheinland Group
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Surge in food recalls and brand-risk costs
- 4.2.2 Tightening allergen labeling laws and enforcement
- 4.2.3 Expansion of global processed-food trade
- 4.2.4 Harmonised reference-dose rules lowering LOQs
- 4.2.5 Consumer demand for clean-Label and allergen-free foods
- 4.2.6 Accredited labs and audit readiness standardize test protocols
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High cost of testing technologies
- 4.3.2 Complexity of multi-allergen testing
- 4.3.3 Limited shelf-life of rapid test kits
- 4.3.4 Lack of harmonized global methods
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory and Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECAST (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Technology
- 5.1.1 Immunoassay-Based
- 5.1.2 PCR-Based
- 5.1.3 Mass-Spectrometry-Based
- 5.1.4 Spectroscopy and Imaging
- 5.1.5 Others
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Bakery and Confectionery
- 5.2.2 Dairy Products
- 5.2.3 Seafood and Meat Products
- 5.2.4 Beverages
- 5.2.5 Baby Food and Infant Formula
- 5.2.6 Others
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 North America
- 5.3.1.1 United States
- 5.3.1.2 Canada
- 5.3.1.3 Mexico
- 5.3.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.3.2 Europe
- 5.3.2.1 Germany
- 5.3.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.3.2.3 France
- 5.3.2.4 Italy
- 5.3.2.5 Spain
- 5.3.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.3.1 China
- 5.3.3.2 Japan
- 5.3.3.3 India
- 5.3.3.4 South Korea
- 5.3.3.5 Australia
- 5.3.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.4 South America
- 5.3.4.1 Brazil
- 5.3.4.2 Argentina
- 5.3.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.3.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.3.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.3.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.3.5.3 South Africa
- 5.3.5.4 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.3.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Most Active Companies
- 6.2 Market Positioning Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles {(includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)}
- 6.3.1 Eurofins Scientific SE
- 6.3.2 SGS SA
- 6.3.3 Intertek Group PLC
- 6.3.4 Bureau Veritas SA
- 6.3.5 ALS Limited
- 6.3.6 Merieux NutriSciences
- 6.3.7 Neogen Corporation
- 6.3.8 Microbac Laboratories Inc.
- 6.3.9 Crystal Chem Inc.
- 6.3.10 Romer Labs Division GmbH
- 6.3.11 R-Biopharm AG
- 6.3.12 Hygiena LLC
- 6.3.13 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- 6.3.14 PerkinElmer Inc.
- 6.3.15 Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc.
- 6.3.16 Charm Sciences Inc.
- 6.3.17 Danaher Corp. (Cepheid / SCIEX)
- 6.3.18 Agilent Technologies Inc.
- 6.3.19 QIAGEN N.V.
- 6.3.20 AsureQuality Ltd.
- 6.3.21 TUV SUD AG
- 6.3.22 TUV Nord AG
- 6.3.23 TUV Rheinland Group
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK




