PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1685686

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1685686
Agricultural Chelates - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
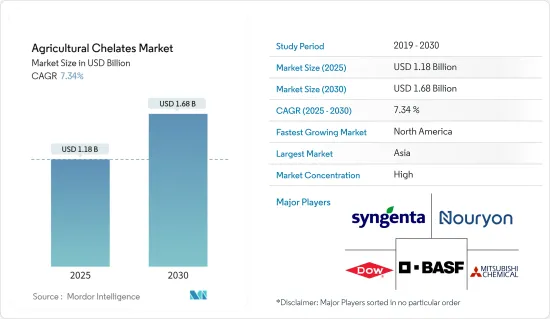
The Agricultural Chelates Market size is estimated at USD 1.18 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 1.68 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 7.34% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Key Highlights
- Concerns over food security are rising due to changing climate conditions, diminishing arable land, and a swiftly expanding global population. The 2022 Census of Agriculture, conducted by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), revealed that the number of farms in the United States (U.S.) has dipped below 2 million. Specifically, in 2022, the U.S. counted 1.9 Million farms, marking a 7% decrease from the figures in the 2017 Census. Additionally, the Census highlighted a 2.2% reduction in total U.S. farmland, bringing it down to 880 million acres in 2022. Given these developments, boosting productivity through appropriate agricultural inputs has become imperative. Consequently, there's been a notable surge in the adoption of chelating agents in agriculture, to enhance crop yields to satisfy global food requirements. Chelating agents facilitate plants' uptake of nutrients, making certain nutrients more accessible. This leads to improved plant growth and development, ultimately enhancing crop yield and quality.
- Independent laboratory analyses highlight troubling trends, includes wheat crops in the UK are experiencing a 10% nitrogen deficiency and a 25% phosphorus deficiency, as evidenced by thousands of soil samples. Chelation serves as a protective mechanism, shielding micronutrients from unwanted reactions in both solutions and soil. By boosting the bioavailability of micronutrients like Fe, Cu, Mn, and Zn, chelated fertilizers play a pivotal role in enhancing the productivity and profitability of commercial crop production. Notably, in soils with a pH exceeding 6.5 or those under low-micronutrient stress, chelated fertilizers have demonstrated a superior capacity to boost commercial yields compared to standard micronutrients.
- With the rising momentum of sustainable farming and growing awareness about the environmental repercussions of synthetic chelating agents, there's a marked pivot towards exploring biodegradable alternatives. In light of this, companies are strategically positioning themselves to meet this evolving demand, thereby strengthening their market presence.
Agricultural Chelates Market Trends
Increasing Preference for EDTA in Agriculture
- Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) has emerged as the premier synthetic chelating agent in agriculture, widely employed for both soil and foliar nutrient applications. At soil pH levels around 6.0, EDTA demonstrates its efficacy in open-field fertigation. This adaptability plays a pivotal role in cementing EDTA's leading market position.
- EDTA chelates are preferred over conventional inorganic sources due to their superior efficiency in transferring essential trace elements such as iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), copper (Cu), and zinc (Zn)-from the soil directly to plant roots. The Indian Institute of Soil Science highlights a concerning trend of micronutrient deficiencies are widespread, with average deficiencies in Indian soils being 43.0% for Zinc, 12.1% for Iron, 5.4% for Copper, 5.6% for Manganese, and 18.3% for Boron. Alarmingly, the combined deficiency of Zn and B in acidic soils, and Zn and Fe in semi-arid regions, signals potential challenges for future cropping systems. Zinc, a crucial micronutrient, is essential for maintaining plant hormone balance and fostering growth. Organic chelated zinc sources, particularly Zn-EDTA (which contains 12% Zn), are frequently regarded as superior to their inorganic alternatives. For instance, when treating crops like corn and beans, the application of Zn-EDTA chelate fertilizer allows farmers to use only half the quantity compared to traditional zinc sulfate (ZnSO4). Additionally, EDTA chelates not only come at a lower price point but also boast greater accessibility than numerous other commercial agricultural chelates available today.
- Prominent players in the market showcase a wide array of EDTA products tailored for agricultural use. Corteva, for instance, offers its EDTA chelating agents under the brand names Versenol and Crop Max, both of which are in high demand within the agricultural community. Beyond its nutrient application, EDTA's ability to detoxify soils contaminated with heavy metals like mercury, cadmium, and lead further fuels its market expansion. However, EDTA isn't without its challenges. Like many synthetic agents, it grapples with issues such as high costs, limited biodegradability, and potential secondary pollution risks. These challenges could hinder the segment's growth trajectory.
Asia-Pacific Dominates the Market
- In the Asia-Pacific region, China, India, Japan, and Australia lead in market demand for agricultural chelates. According to the Australian Government, alkaline soils account for about 24% of Australia's land, particularly in the western regions, where pH levels range from 4 to 8.5. As a result, Australia is experiencing an increasing demand for chelating agents, driven by trace element deficiencies that impede agricultural productivity growth.
- China, home to the world's largest population, also hosts some of the most expansive agricultural facilities. With its population surging and food demand rising, Chinese farmers are under pressure to achieve higher crop yields. Yet, various regions in China grapple with micronutrient deficiencies in their calcareous soils. To address these challenges, China is undertaking a comprehensive soil census, led by a nonprofit environmental organization from Beijing, with an anticipated completion in 2025. Insights from this soil survey are poised to illuminate soil deficiencies, potentially boosting chelate sales in the nation.
- Micronutrient deficiencies are currently undermining productivity in rice-growing nations, notably Thailand. An independent study identified key micronutrients (Fe, Mn, Zn, and Cu) as pivotal, revealing their deficiency could slash rice grain yields by a staggering 24.12%-46.46%. However, with the application of DTPA, these yields can be significantly bolstered through the addition of these micronutrients.
Agricultural Chelates Industry Overview
The global agricultural chelates market is consolidated, with the major players in the market including BASF SE, Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation, Syngenta Ag, Dow Inc, Nouryon Chemicals Holding B.V, etc holding a significant share of the market. The significant market share of these players can be attributed to a highly diversified product portfolio and acquisitions and partnerships during the review period. These players also focus on R&D and product innovations to widen their geographical presence.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Demand For Higher Crop Yields
- 4.2.2 Application of Chelates in Micronutrient Intoxication
- 4.2.3 Micronutrient Deficiency In Soil
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Poor Product Offering in Biodegradable Chelates
- 4.3.2 Rising Regulation on Use of Synthetic Chelating Agents
- 4.4 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Type
- 5.1.1 Synthetic
- 5.1.1.1 EDTA
- 5.1.1.2 EDDHA
- 5.1.1.3 DTPA
- 5.1.1.4 IDHA
- 5.1.1.5 Other Synthetic Types
- 5.1.2 Organic
- 5.1.2.1 LingoSulphates
- 5.1.2.2 Aminoacids
- 5.1.2.3 Heptagluconates
- 5.1.2.4 Other Organic Types
- 5.1.1 Synthetic
- 5.2 Application
- 5.2.1 Soil
- 5.2.2 Foliar
- 5.2.3 Fertigation
- 5.2.4 Other Applications
- 5.3 Crop Type
- 5.3.1 Grains and Cereals
- 5.3.2 Pulses and Oilseeds
- 5.3.3 Commercial Crops
- 5.3.4 Fruits and Vegetables
- 5.3.5 Turf and Ornamentals
- 5.4 Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 Spain
- 5.4.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.3 France
- 5.4.2.4 Germany
- 5.4.2.5 Russia
- 5.4.2.6 Italy
- 5.4.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 Japan
- 5.4.3.3 India
- 5.4.3.4 Australia
- 5.4.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Africa
- 5.4.5.1 South Africa
- 5.4.5.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Most Adopted Strategies
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 Nouryon Chemicals Holding B.V
- 6.3.2 Shandong Iro Chelating Chemical Co. Ltd
- 6.3.3 Ava Chemicals Private Limited
- 6.3.4 Protex International
- 6.3.5 Innospec Inc.
- 6.3.6 Syngenta Ag
- 6.3.7 Mitsubishi Group (Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation)
- 6.3.8 Dow Inc
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS




