PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1640455

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1640455
Malaysia Renewable Energy - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
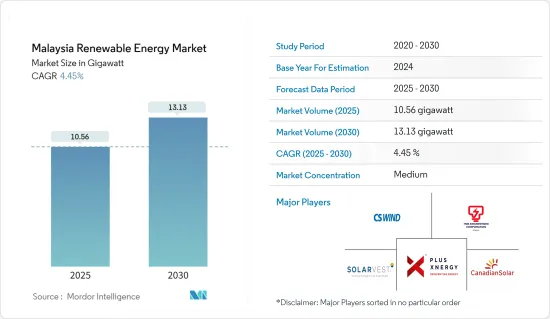
The Malaysia Renewable Energy Market size is estimated at 10.56 gigawatt in 2025, and is expected to reach 13.13 gigawatt by 2030, at a CAGR of 4.45% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
The spread of COVID-19 hurt the market because investments dropped and some regions had to close down.Currently, the market has rebounded from pre-pandemic levels.
Key Highlights
- During the period covered by the forecast, the market is likely to be driven by things like more investments and the country's efforts to switch from fossil fuels to renewable energy as a source of power.The government of Malaysia has also put in place policies and incentives to help solar energy grow, which is expected to drive the market even more.
- However, on the other hand, factors such as the rising adoption of alternate clean power sources, such as gas-fired power plants and nuclear energy projects, are likely to hinder the market's growth during the study period.
- Malaysia is aiming to install 9 GW of solar energy capacity by 2050. Therefore, the country's ambitious solar energy targets and business models such as solar leasing are expected to create significant opportunities in the near future.
Malaysia Renewable Energy Market Trends
Solar Photovoltaic (PV) to Dominate the Market
- Solar PV is poised to dominate the renewable energy landscape in Malaysia due to several key factors. First and foremost, Malaysia enjoys abundant solar resources due to its location near the equator and high levels of sunlight throughout the year. This natural advantage provides a strong foundation for solar PV installations, making it a highly viable renewable energy option. The declining costs of solar PV technology have significantly improved its cost competitiveness, making it increasingly attractive for investors and energy consumers.
- The Malaysian government has implemented supportive policies and incentives to foster solar energy development. Programs like Net Energy Metering (NEM) allow consumers to install solar PV systems and sell excess electricity back to the grid. At the same time, feed-in tariffs and tax incentives encourage investment in solar PV projects.
- For instance, in October 2022, the Malaysian government decided to extend the duration of power purchase agreements for large-scale photovoltaic (PV) projects under the fourth LSS4 tender. The original period of 21 years was increased to 25 years. The LSS4 program successfully allocated a total capacity of 823.06 MW across 30 projects. Overall, the program has awarded 2,457 MW of capacity, but as of June 2022, only 1,160 MW of that capacity was operational.
- Technological advancements have also played a crucial role in the prominence of solar PV. The industry has witnessed significant improvements in solar panel efficiency and overall performance, driving down costs and enhancing power generation capabilities.
- According to the International Renewable Energy Agency, the installed capacity of solar photovoltaics in the country increased by more than 8% between 2021 and 2022, signifying the increasing adoption of solar photovoltaics in the country.
- Therefore, based on the factors above, the utility sector is expected to dominate the Malaysian renewable energy market during the forecast period.
Supportive Government Policies to Drive the Market
- Government policies play a pivotal role in driving the renewable energy market in Malaysia. The government has implemented various policy measures to stimulate the growth of renewable energy, including the establishment of feed-in tariffs and power purchase agreements that provide stable and long-term contracts for renewable energy producers, encouraging investment in the sector. Setting ambitious renewable energy targets provides a clear direction and incentive for investors to participate in the market.
- Malaysia has set a target to derive 20% of its energy from renewable sources by 2025. The country will require an investment of approximately USD 8 billion in its renewable energy sector to achieve this goal. The expected investments are anticipated to come from a combination of government funding, public-private partnerships, and private financing.
- The government intends to encourage private financing and enhance private participation in the renewable energy sector. In addition to the ongoing government incentives like the Green Technology Financing Scheme, the Green Investment Tax Allowance, and the Green Income Tax Exemption, the emphasis will be on implementing institutional reforms to support the growth of renewable energy further.
- According to the International Renewable Energy Agency, the installed capacity of renewable energy in the country increased significantly between 2018 and 2022. The growth rate during this period was recorded at more than 20%, signifying healthy growth of renewables in the region.
- A supportive regulatory framework with streamlined permitting processes has also reduced barriers and bureaucratic hurdles for developers, facilitating the development of renewable energy projects.
- For instance, in March 2023, the 10 MWAC Solar Project in Labuan, Sabah, Malaysia, achieved financial close through Solar PV Power Sdn Bhd (SPP). SPP is a joint venture between Jetama Energy Sdn Bhd (Jetama) and Symbior Solar Limited (Symbior).
- Therefore, supportive government policies and initiatives are expected to drive the share of solar and renewable energy.
Malaysia Renewable Energy Industry Overview
The Malaysian renewable energy market is moderately fragmented. Some of the major players in the market (in no particular order) include JA Solar Technology Co. Ltd, Solarvest Holdings Berhad, TNB Engineering Corporation Sdn Bhd, CS Wind Malaysia, and Plus Xnergy Holding Sdn Bhd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Scope of the Study
- 1.2 Market Definition
- 1.3 Study Assumptions
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Renewable Energy Mix, Malaysia, 2022
- 4.3 Renewable Energy Installed Capacity and Forecast in MW, till 2028
- 4.4 Government Policies and Regulations
- 4.5 Recent Trends and Developments
- 4.6 Market Dynamics
- 4.6.1 Drivers
- 4.6.1.1 Supportive Government Policies and Incentives
- 4.6.1.2 Increasing Investments in Renewable Energy Projects
- 4.6.2 Restraints
- 4.6.2.1 Grid Integration Challenges
- 4.6.1 Drivers
- 4.7 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.8 PESTLE Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION - BY TYPE
- 5.1 Solar
- 5.2 Hydro
- 5.3 Bio-energy
- 5.4 Other types
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Mergers and Acquisitions, Joint Ventures, Collaborations, and Agreements
- 6.2 Strategies Adopted by Leading Players
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 First Solar Inc.
- 6.3.2 Canadian Solar Inc.
- 6.3.3 Plus Xnergy Holding Sdn Bhd
- 6.3.4 TNB Engineering Corporation Sdn Bhd
- 6.3.5 Solarvest Holdings Berhad
- 6.3.6 JA SOLAR Technology Co. Ltd
- 6.3.7 SunPower Corporation
- 6.3.8 Trina Solar Co. Ltd
- 6.3.9 CS Wind Malaysia
- 6.3.10 TS Solartech Sdn Bhd
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS
- 7.1 Improving Energy Efficiency Across Various Sectors




