PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1639440

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1639440
GCC Construction - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
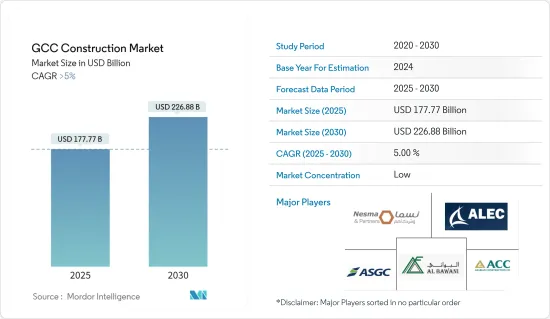
The GCC Construction Market size is estimated at USD 177.77 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 226.88 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of greater than 5% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
The GCC projects market has faced various challenges in recent years, including the global pandemic, inflation, and geopolitical issues. These challenges have tested contractors, suppliers, and engineering firms as they try to adapt to the rapidly changing market conditions.
In 2020, the market experienced a low, with contract awards totaling just over USD 71 billion due to the impact of COVID-19. However, in 2021, the market rebounded strongly to almost USD 116 billion, thanks to higher oil prices and the resumption of delayed projects. At the beginning of 2022, there was optimism for continued recovery, but the market did not perform as expected. In total, about USD 94 billion worth of contracts were awarded in 2022, which was a decline of over USD 20 billion compared to the previous year. This contraction in 2022 can be largely attributed to a 25% decline in new contracts in the UAE and a 44% decline in Qatar. Qatar has reduced its capital expenditure in preparation for the FIFA World Cup, while the UAE continues to face challenges in its real estate sector.
The only positive aspect is Saudi Arabia, which has seen contract awards worth just under USD 54 billion, making its projects market larger than the combined markets of the other five GCC states.
GCC Construction Market Trends
Rising Investments in the Infrastructure Construction Market
While the global economy remains uncertain, the GCC region is currently experiencing strong economic growth, moderate inflation, and fiscal surpluses. To further diversify and expand their economies, governments in Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates are making significant investments in infrastructure. However, without effective policies for planning and managing these public investments, there is a risk that the projects may not achieve their intended goals.
Effective public investment management (PIM) involves carefully selecting the right investments and ensuring their proper implementation. This includes assessing the need for new infrastructure, aligning investment projects with national and sectoral strategies, promoting effective coordination between government entities, and managing risks appropriately.
According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), inefficiencies in PIM processes result in an average loss of about 30% of returns on investments for countries. In the GCC, these inefficiencies include non-standardized evaluation processes for proposed investments, mismatched funding and budget allocations, limited coordination between agencies, inadequate evaluations after investments are made, and insufficient performance data and reporting.
One way to evaluate the efficiency of public investments is by comparing the quality of infrastructure to a country's per capita capital stock. Although GCC countries have a high level of capital stock per capita and rank in the top quartile globally, this does not necessarily mean that the quality of their infrastructure matches the amount invested. There is still room for improvement in the region to catch up with countries that are closest to the "efficiency frontier," which represents the highest level of attainable efficiency according to the IMF's methodology.
Saudi Arabia Leading the GCC Construction Sector
In 2022, Saudi Arabia remained the largest market for projects in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), with contracts worth USD 54.2 billion awarded. This was slightly higher than the USD 53.9 billion awarded in 2021. However, other GCC countries experienced a decline in project awards due to global economic challenges.
The total value of contracts awarded in the GCC dropped by 18.7% to USD 93.6 billion, the lowest since 2005, excluding the decline caused by the pandemic in 2020. This decline was attributed to high inflation and supply chain issues, primarily caused by intermittent COVID-19 restrictions in China, which have now been lifted. Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Qatar accounted for 93.6% of the total value of contracts awarded in the GCC. Kuwait saw a decrease in project awards from USD 5.2 billion in 2021 to USD 2.8 billion in 2022. Similarly, Oman witnessed a 27.1% drop in new project awards to USD 2.2 billion, while Bahrain's contract awards reached USD 96 million in 2022 compared to USD 2.7 billion in 2021.
The construction industry received the majority of new contract awards, with a total value of USD 34.3 billion in 2022, an increase of USD 3.2 billion from the previous year. The growth in the GCC construction sector was mainly driven by the increase in contract awards in Saudi Arabia's construction sector.
GCC Construction Industry Overview
The construction market in GCC countries is fragmented, with a lot of players having scope for growth. The developers are trying to bring new and lower-cost products to meet the current demand. Evolving technological advancements such as new proptech solutions are driving the market in terms of increased transactions and better management of real estate assets. Some of the major players in the GCC construction market include Nesma & Partners Contracting, Albawani Group, ALEC Engineering and Contracting, Arabian Construction Company, and ASGC Construction.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Current Economic and Construction Market Scenario
- 4.2 Technological Innovations in the Construction Market
- 4.3 Review and Commentary on the Extent of Government Infrastructure Development Schemes
- 4.4 Comparison of Key Industry Metrics in GCC
- 4.5 Comparison of Construction Cost Metrics in GCC
- 4.6 Impact of Government Regulations and Initiatives in the Construction Industry
- 4.7 Real Estate Prices (sales and leasing) by Asset Classes (residential, commercial, retail)
- 4.8 Industry Value Chain/Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.9 Impact of COVID-19 on the Market
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Green And Sustainable Buildings Initiatives
- 5.1.2 Urbanisation and Tousrism Growth
- 5.2 Market Restraints
- 5.2.1 Decliing Crude Oil Prices
- 5.3 Market Opportunities
- 5.3.1 Business Tourism
- 5.4 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 5.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 5.4.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 5.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 5.4.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 5.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Sector
- 6.1.1 Commercial Construction
- 6.1.2 Residential Construction
- 6.1.3 Industrial Construction
- 6.1.4 Infrastructure (Transportation) Construction
- 6.1.5 Energy and Utilities Construction
- 6.2 By Country
- 6.2.1 United Arab Emirates
- 6.2.2 Saudi Arabia
- 6.2.3 Oman
- 6.2.4 Qatar
- 6.2.5 Kuwait
- 6.2.6 Bahrain
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Company profiles
- 7.1.1 Nesma & Partners Contracting
- 7.1.2 Albawani Group
- 7.1.3 ALEC Engineering and Contracting
- 7.1.4 Arabian Construction Company
- 7.1.5 ASGC Construction
- 7.1.6 Al Naboodah Construction
- 7.1.7 Almabani General Contractors
- 7.1.8 Airolink
- 7.1.9 UCC Holding
- 7.1.10 Khansaheb*
8 FUTURE OF THE MARKET
9 APPENDIX
10 DISCLAIMER




