Need help finding what you are looking for?
Contact Us
PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1550244

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1550244
India Semiconductor - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029)
PUBLISHED:
PAGES: 100 Pages
DELIVERY TIME: 2-3 business days
SELECT AN OPTION
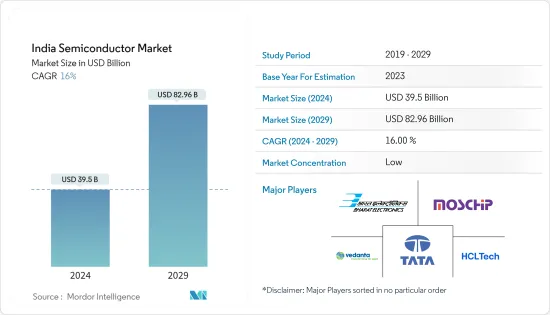
The India Semiconductor Market size is estimated at USD 39.5 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 82.96 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 16% during the forecast period (2024-2029).
Key Highlights
- Semiconductors like silicon are essential for creating transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits, forming the foundation of modern electronics. They are crucial for managing electrical signals and facilitating the advancement of various electronic technologies. As the demand for data-driven applications grows, there is a noticeable trend toward using solid-state drives (SSDs) instead of traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). The adoption of non-volatile memory express (NVMe) technology is rapidly increasing, improving data transfer speeds.
- Furthermore, there is a noticeable trend in consumer electronics in India toward embracing advanced technologies and digitalization. This includes a growing preference for smart home devices such as IoT-enabled products like smart TVs, speakers, and appliances. The smartphone market is also seeing a shift toward affordable yet feature-packed models, leading to an increase in smartphone usage.
- The use of smartphones and digitalization efforts are also driving the demand for high-capacity RAM modules. The gaming industry's growth is also sparking interest in faster and more efficient memory solutions. An example of this is the upcoming production of India's first domestically made memory chip in Gujarat due to a lucrative deal with South Korea's Simmtech.
- Mumbai and Pune are becoming important hubs for semiconductor design and manufacturing, with a strong emphasis on innovation, research, and development. The regions are experiencing growth in startups and collaborations, leading to a thriving ecosystem. The increasing use of cutting-edge technologies like AI, IoT, and 5G is fueling the need for advanced semiconductor products.
- India has the potential to greatly enhance its participation in global semiconductor value chains if the government continues to support investment policies, fosters a favorable regulatory and business environment, and refrains from implementing measures that may cause uncertainty. Over the next five years, India could potentially increase its presence in the semiconductor assembly, test, and packaging (ATP) sector by establishing up to five facilities and attracting fabs that manufacture older-generation semiconductors at 28 nm or higher.
- In addition, India and the United States announced a collaborative initiative on Critical and Emerging Technology (CET) aimed at expanding strategic technology partnerships and defense industrial cooperation between businesses, academic institutions, and government agencies of both nations. In 2023, the Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) in the United States and the India Electronics and Semiconductor Association (IESA) agreed to work together on a "readiness assessment" to identify industry opportunities and promote the strategic development of their semiconductor ecosystem.
- India is also currently experiencing a significant moment and opportunity. The aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, along with global efforts to adjust supply chains, rising costs in China, advancements in technologies like AI and EVs, demographic changes, and various other factors have prompted multinational companies to reevaluate their global value chain structures in search of improved diversification, resilience, sustainability, and cost efficiency.
- In addition to this, India is currently actively seeking foreign investments to support its domestic semiconductor industry for the advancement and design of fabs, ATMP, and other related technologies. One example of this is the Government of Assam's efforts to fast-track the establishment of a semiconductor unit in Morigaon, achieved through a 60-year lease agreement with the Tata Group for more than 170 acres of land and an investment of INR 270 billion (USD 3.22 billion). Furthermore, approval has been granted for Tata's semiconductor chip fabrication unit in Gujarat with a budget of nearly INR 500 billion (USD 5.97 billion)
- India is fortunate to have a significant number of design engineers. However, there is a noticeable shortage of semiconductor engineers with expertise in device physics and process technology, which is crucial for chip fabrication and manufacturing and is significantly hindering market growth. It is anticipated that the semiconductor industry in India will encounter a deficit of 250,000 to 300,000 professionals in various sectors, such as research and development, manufacturing, design, and advanced packaging, by 2027.
India Semiconductor Market Trends
The Sensors and Actuators Segment is Expected to Witness Significant Growth
- The increasing use of sensors in the Indian market has prompted vendors and users to make significant investments in the growth of this market. The automotive and consumer electronics industries are also playing a key role in driving demand for sensors in India. The expansion of the sensor market can also be linked to the overall growth of the industrial sector, as well as the introduction of micro electro mechanical systems (MEMS) sensors.
- The increasing demand for automation and the widespread use of devices such as tablets, PCs, smartphones, and smartwatches, along with the growing automotive sales and advancements in consumer electronics technology, are expected to be the main factors driving the Indian sensors market.
- Furthermore, the manufacturing industry in India has been experiencing significant growth due to the country's expanding population. Investments in the sector are increasing, and initiatives like 'Make in India' are aimed at positioning India as a global manufacturing hub. The manufacturing industry saw a 4.7% annual production growth rate in the fiscal year 2023. Numerous organizations and institutions are actively involved in this initiative, with notable achievements such as the development of the first "Make in India" human breath sensor by researchers at IIT Jodhpur in February 2024. This sensor is based on metal oxides and nano silicon and operates at room temperature.
- The advancement of factory automation and the adoption of Industry 4.0 are greatly dependent on the use of industrial sensors. These sensors, such as motion, environmental, and vibration sensors, play a crucial role in the process. India's industrial sectors are set for economic and demographic growth, supporting both local businesses and export prospects, which are expected to see substantial development.
- In the field of industrial automation, process control, robotics, and equipment, sensors are essential. India has also been making significant investments in the advancement of the Internet of Things (IoT) technology and smart city projects. According to a NASSCOM report, the Indian IoT market is expected to reach a value of USD 15 billion by 2025. Various industries, including agriculture, healthcare, manufacturing, and smart cities, are experiencing positive changes driven by IoT innovations.
Growing Automotive Industry and EV Demand Across India to Propel the Market
- India's automotive and EV industry is poised for a transformative journey that has the potential to greatly impact the nation's transportation landscape. This industry has the ability to drive change, create a more sustainable future for India, and contribute to global initiatives to combat climate change and improve the quality of urban living. According to CII, India has set ambitious goals to increase the percentage of EV sales in various vehicle categories by 2030.
- According to information provided by IBEF, it is projected that India has the potential to emerge as the leading electric vehicle (EV) market by 2030, presenting a significant investment opportunity of over USD 200 billion within the next 8-10 years. There is also a growing need for automation in key industries like food and beverage, manufacturing, and pharmaceuticals, driven by workforce constraints and the necessity for remote monitoring and operations. Consequently, there is a rising demand for a variety of sensors to cater to this increase in automation requirements.
- In line with the 'Make in India' initiative, the Indian government is placing emphasis on the growth of automobile manufacturing. The Auto Mission Plan (AMP) 2016-26 forecasts a significant increase in the passenger car market to 9.4 million units by 2026, resulting in a higher demand for sensors in the region.
- The success of EVs can be attributed to a variety of factors, such as government initiatives at both the central and state levels, a strong focus from the industry, and the increasing acceptance of electric vehicles by the public. Programs like FAME India, the PLI scheme for the Auto and Auto Component, and the PLI scheme for manufacturing ACC batteries have played a crucial role in promoting local production and encouraging the adoption of EVs.
- India is becoming a prominent destination for sourcing auto components on a global scale, with the industry exporting more than 25% of its production each year. For instance, Hyundai Motor expressed its intention to invest USD 2.45 billion in Tamil Nadu over the next 10 years to further develop its electric vehicle initiatives in India. The company is also looking to assemble EV battery packs and establish 100 charging stations for electric vehicles.
- Furthermore, the NITI Aayog and Rocky Mountain Institute (RMI) have forecasted that India's electric vehicle (EV) finance sector is projected to reach INR 3.7 lakh crore (USD 50 billion) by 2030. Leading automakers have already started making significant investments across different segments of the industry to cater to the increasing demand. For example, in March 2023, Foxconn, a tech company based in Taiwan, revealed its plans to invest in the development of semiconductors and EVs in India.
India Semiconductor Industry Overview
The Indian semiconductor market is fragmented with the presence of several players like Tata Group, HCL Technologies, Bharat Electronics Limited, MosChip Technologies, and various other global players such as AMD, Foxconn, and NXP Semiconductors. The companies aim to continuously invest in strategic partnerships and product developments to gain substantial market share.
- May 2024: Lam Research announced its expansion of the global semiconductor fabrication equipment supply chain to India. The Ministry of Electronics and IT's efforts to develop a downstream ecosystem have been instrumental in this decision. Lam Research is evaluating capabilities in different supply chain segments and has expressed its interest in collaborating with India-based suppliers to meet the demand for precision components and other necessary supplies.
- March 2024: Tata Group announced that it was aiming to commence commercial production from India's first semiconductor fabrication unit by 2026, with the goal of achieving self-reliance in chips that are essential for powering a wide range of technologies, from smartphones to defense systems. The plant, owned by Tata Electronics Pvt. Ltd, located in Assam, will initially focus on producing semiconductor chips starting at 28 nm. It is anticipated that production at the plant will begin by late 2025 or early 2026, catering to various sectors, such as automotive, power, electronics, consumer goods, and medical devices.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
Product Code: 50002849
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.2.1 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.2.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.2.4 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.3 Assessment of the Impact of COVID-19 and Macroeconomic Factors on the Market
- 4.4 Semiconductor Industry Value Chain Analysis
- 4.4.1 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.4.2 Focus Areas in the Value Chain and Type of Projects Currently Encouraged by India
- 4.5 Global Semiconductor Industry Analysis
- 4.6 Largest Semiconductor Clusters in India and Expected Largest Manufacturing Hubs
- 4.7 Analysis of Government Regulations and Incentive Programs
- 4.7.1 Government Initiatives/Schemes in India and Ways to Access the Schemes
- 4.8 Eligibility Criteria and Fiscal Support for Various Categories (Silicon Semiconductor Fab, Display Fab, Compound Semiconductor/SiPh/Sensors Fab and OSAT/Assembly/Testing)
- 4.9 SWOT Analysis of Semiconductor IC Industry in India (IC Design, IC Fabrication, and Assembly/Test/Packaging)
- 4.10 Workforce Analysis for the Indian Semiconductor Industry
- 4.11 Semiconductor Component Sourcing Analysis
- 4.12 Semiconductor Design Market Analysis
- 4.13 List of Key Stakeholders and Their Role in Shaping the Semiconductor Industry in India
- 4.14 Challenges in Setting up a Semiconductor Manufacturing Plant in India
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Growing Automotive Industry and EV Demand
- 5.1.2 Smartphone and Consumer Electronics Demand Growth
- 5.1.3 Growing Telecom Infrastructure Augmented by 5G and Fixed Internet Connections
- 5.2 Market Restraints
- 5.2.1 Limited Presence in the Design Space and Lack of Homegrown Vendors
- 5.2.2 Foundry Capacity and Investment Compared to Other Countries such as Taiwan, Japan, and China
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Semiconductor Device Type
- 6.1.1 Discrete Semiconductor
- 6.1.2 Optoelectronics
- 6.1.3 Sensors and Actuators
- 6.1.4 Integrated Circuits
- 6.1.4.1 Analog
- 6.1.4.2 Micro
- 6.1.4.3 Logic
- 6.1.4.4 Memory
- 6.2 By End-user Industry
- 6.2.1 Computer
- 6.2.2 Communication (Includes Wireline and Wireless)
- 6.2.3 Automotive
- 6.2.4 Consumer
- 6.2.5 Other End-user Industries (Industrial, Government, etc.)
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Company Profiles
- 7.1.1 Tata Group
- 7.1.2 Bharat Electronics Limited
- 7.1.3 Moschip Semiconductor Technologies
- 7.1.4 Vedanta Semiconductors Private Limited (VSPL)
- 7.1.5 HCL Technologies
- 7.1.6 ASM Technologies Ltd
- 7.1.7 Applied Materials India Pvt. Ltd
- 7.1.8 Hon Hai Technology Group (Foxconn)
- 7.1.9 Broadcom Inc.
- 7.1.10 NXP Semiconductors
- 7.1.11 ROHM Semiconductor
- 7.1.12 Infineon Technologies
- 7.1.13 Renesas Electronics
- 7.1.14 STMicroelectronics
- 7.1.15 Powerchip Semiconductor Manufacturing Corp (PSMC)
- 7.1.16 AMD Group
- 7.1.17 Intel Corporation
- 7.1.18 Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd
- 7.1.19 Qualcomm Incorporated
- 7.1.20 Micron Technology Inc.
- 7.1.21 Texas Instruments Incorporated
- 7.1.22 Mediatek Inc.
8 INVESTMENT ANALYSIS
9 FUTURE OF THE MARKET
Have a question?


SELECT AN OPTION
Have a question?


Questions? Please give us a call or visit the contact form.
