PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851940

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851940
GCC Fruit And Vegetable - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
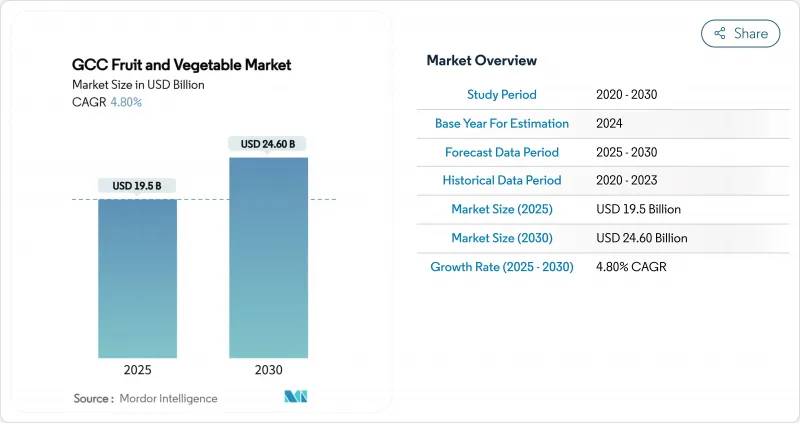
The GCC fruit and vegetable market size reached USD 19.5 billion in 2025 and is anticipated to grow to USD 24.6 billion by 2030, registering a CAGR of 4.8% during the forecast period.
Gulf governments are shifting their food policies toward domestic production technologies to reduce import dependence and strengthen their balance of payments. Saudi Arabia's USD 2 billion agriculture fund and the United Arab Emirates's Food Tech Valley are investing in controlled-environment farming facilities that produce pesticide-free crops while optimizing water usage. The implementation of hydroponic and drip irrigation systems has decreased water consumption per unit and enabled year-round production, reducing reliance on imports. Cold-chain infrastructure developments, such as RSA Cold Chain's 40,000-pallet facility in Dubai, are reducing post-harvest losses and creating new re-export opportunities to Asian and European markets. The market is fragmented, with major stakeholders such as Pure Harvest Smart Farms integrating agricultural technology to achieve market consolidation, vertical integration, and technological differentiation.
GCC Fruit And Vegetable Market Trends and Insights
Widespread Adoption of Drip and Hydroponic Systems Across GCC Farms
Hydroponic adoption at scale is transforming resource efficiency in the GCC fruit and vegetable market. Bustanica's 30,658 m2 vertical farming facility produces 1 million kg of leafy greens annually while saving 250 million liters of water, reducing water usage by 95% compared to conventional farming. Saudi Arabia's Dava Agricultural Co. demonstrates similar progress through its 107-hectare greenhouse complex, which exports tomatoes to Europe, establishing the commercial feasibility of desert-grown fresh produce exports. The integration of AI-driven nutrient dosing, automated climate control, and cloud analytics helps reduce production costs to compete with imports. Government policies support this transition through water conservation subsidies and, integration of hydroponics into national food security strategies.
Government-Backed Agri-Parks and Food-Security Funds
Saudi Arabia allocated USD 2 billion for agriculture in 2025, representing a 67% budget increase focused on precision greenhouses, variable-rate irrigation, and agricultural robotics. The United Arab Emirates's Food Tech Valley has generated over 300 products through its integrated framework of startups, investors, and research institutes. Oman aims to improve food self-sufficiency by implementing AI-based crop planning and satellite imagery to transform individual farms into connected agricultural clusters. These integrated approaches minimize investment risks and facilitate technology adoption among medium-sized farms, supporting growth in the GCC fruit and vegetable market.
Saline-Ground-Water and Limited Arable Land
The Gulf region's renewable water resources primarily support agriculture, limiting the capacity to mitigate increasing salinity levels. Bahrain's limited land mass and brackish aquifers necessitate substantial food imports. Kuwait's agricultural studies demonstrate that salinity constrains crop selection, even though certain varieties achieve efficient water usage. While moisture-retention technologies such as stearic-acid-coated sand show promise, they have not reached commercial viability. The GCC fruit and vegetable market growth remains constrained by saline intrusion into farmland, a challenge that will persist unless desalination becomes more cost-effective.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Expansion of Cold-Chain Logistics Reducing Post-Harvest Losses
- Rapid Growth of Controlled-Environment Agriculture (CEA) Greenhouses
- Price Volatility in Global Spot Markets
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The GCC Fruit and Vegetable Market Report is Segmented by Geography (United Arab Emirates, Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, and Saudi Arabia). The Report Includes Production Analysis (Volume), Consumption Analysis (Value and Volume), Export Analysis (Value and Volume), Import Analysis (Value and Volume), and Price Trend Analysis. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Metric Tons).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Market Overview
- Market Drivers
- Market Restraints
- Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- Regulatory Landscape
- Technological Outlook
- PESTLE Analysis
- List of Stakeholders
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Widespread Adoption of Drip and Hydroponic Systems Across GCC Farms
- 4.2.2 Government-Backed Agri-Parks and Food-Security Funds
- 4.2.3 Expansion of Cold-Chain Logistics Reducing Post-Harvest Losses
- 4.2.4 Rapid Growth of Controlled-Environment Agriculture (CEA) Greenhouses
- 4.2.5 Surge in Institutional Buyers Sourcing Locally
- 4.2.6 Carbon-Border-Adjustment Pressures Favoring Regional Produce
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Saline-Ground-Water and Limited Arable Land
- 4.3.2 High Energy Cost of Desalinated Irrigation Water
- 4.3.3 Price Volatility in Global Spot Markets
- 4.3.4 Fragmented Smallholder Farm Structure Limiting Economies of Scale and Bargaining Power
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 PESTLE Analysis
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value and Volume)
- 5.1 By Geography (Production Analysis (Volume), Consumption Analysis (Volume and Value), Import Analysis (Volume and Value), Export Analysis (Volume and Value), and Price Trend Analysis)
- 5.1.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.1.1.1 Fruits
- 5.1.1.2 Vegetables
- 5.1.2 Bahrain
- 5.1.2.1 Fruits
- 5.1.2.2 Vegetables
- 5.1.3 Kuwait
- 5.1.3.1 Fruits
- 5.1.3.2 Vegetables
- 5.1.4 Oman
- 5.1.4.1 Fruits
- 5.1.4.2 Vegetables
- 5.1.5 Qatar
- 5.1.5.1 Fruits
- 5.1.5.2 Vegetables
- 5.1.6 Saudi Arabia
- 5.1.6.1 Fruits
- 5.1.6.2 Vegetables
- 5.1.1 United Arab Emirates
6 International Trade and Price Scenarios
- 6.1 Onion
- 6.2 Potato
- 6.3 Tomatoes
- 6.4 Garlic
- 6.5 Cauliflower
- 6.6 Beans
- 6.7 Eggplant
- 6.8 Lemons
- 6.9 Apples
- 6.10 Bananas
- 6.11 Grapefruit
- 6.12 Dates
- 6.13 Cabbage
- 6.14 Watermelon
- 6.15 Mango
- 6.16 Chilies
- 6.17 Strawberries
7 Competitive Landscape
- 7.1 List of Stakeholders
8 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook




