PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1445785

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1445785
Japan Diabetes Drugs - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029)
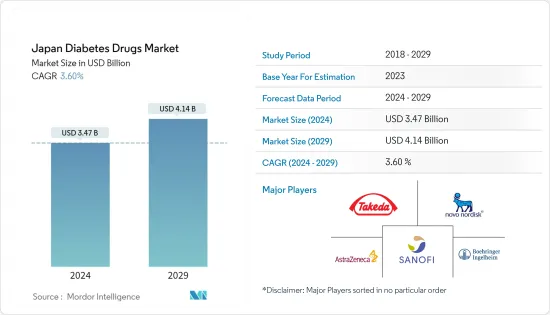
The Japan Diabetes Drugs Market size is estimated at USD 3.47 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 4.14 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 3.60% during the forecast period (2024-2029).
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a substantial impact on the diabetes drugs market. The prevalence of diabetes in people hospitalized with COVID-19 infection and the recognition that improved glycemic control might improve outcomes and reduce the length of stay in patients with SARS-CoV-2 have underlined the importance of diabetes care devices. A retrospective analysis was presented at the virtual 81st Scientific Sessions of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) which showed diabetes was the main risk factor for the accelerated advancement to a severe state in Japanese COVID-19 patients.
Throughout the pandemic, diabetes has persisted as a significant risk factor for COVID-19. In hospitalized patients with diabetes and COVID-19, one in 10 people died within seven days of admission.
The pandemic also highlighted opportunities for continuing and expanding innovations in the delivery of diabetes drugs, through virtual consultations between healthcare providers and people with diabetes, and the use of diabetes technology. Crisis management has created unprecedented interest in remote care from both patients and providers and removed many long-standing regulatory barriers. Thus, the COVID-19 outbreak increased the Japanese diabetes drugs market's growth.
While Type 1 diabetes is caused by an immune system malfunction, Type 2 diabetes is linked to leading a sedentary lifestyle, which results in the development of inherent resistance to insulin. Hence, Type 1 diabetes can be characterized as insulin-requiring, while Type 2 diabetes can be characterized as insulin-dependent diabetes. Japan has one of the largest elderly populations in the world which is more susceptible to the onset of type 2 diabetes. As Japan's population continues to age, the prevalence of diabetes increases as well. The monitoring and management of blood glucose levels are on the rise, to avoid negative consequences, such as cardiovascular diseases, kidney disorders, and many other conditions.
Therefore, owing to the aforementioned factors the studied market is anticipated to witness growth over the analysis period.
Japan Diabetes Drugs Market Trends
The oral anti-diabetic drugs segment holds the highest market share in the Japan Diabetes Drugs Market in the current year
The oral anti-diabetic drugs segment holds the highest market share of about 69% in the Japan Diabetes Drugs Market in the current year.
Oral Anti-Diabetic Drugs are available internationally and are recommended for use when escalation of treatment for type 2 diabetes is required along with lifestyle management. Oral agents are typically the first medications used in treating type 2 diabetes due to their wide range of efficacy, safety, and mechanisms of action. Anti-diabetic drugs help diabetes patients control their condition and lower the risk of diabetes complications. People with diabetes may need to take anti-diabetic drugs for their whole lives to control their blood glucose levels and avoid hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. Oral anti-diabetic agents present the advantages of easier management and lower cost. So they became an attractive alternative to insulin with better acceptance, which enhances adherence to the treatment.
The prevalence of diabetes is growing among all ages in Japan, which can be attributed to the growing obese population, unhealthy diets, and sedentary lifestyles. Diabetes mellitus is of wide concern with its high prevalence, resulting in increased financial burdens for clinical systems, individuals, and governments. The Japanese healthcare system includes a few disease management programs conducted by the Japan Association for Diabetes Education and Care. Japan is one of the regional leaders in Asia-Pacific in terms of diabetic public health policies. The country promotes public awareness and embraces preventive policies focusing on lifestyle and dietary adjustments, which can lessen the likelihood of adult-onset diabetes.
Owing to the above factors, the market will likely continue to grow.
Sodium-glucose cotransport -2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor segment is expected to register the highest CAGR in the Japan Diabetes Drugs Market over the forecast period
Sodium-glucose cotransport -2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor segment is expected to register the highest CAGR of about 8% in the Japan Diabetes Drugs Market over the forecast period.
SGLT-2 inhibitors, also called gliflozins, are a medicine class used to lower high blood glucose levels in people with type 2 diabetes. SGLT-2 inhibitors act independently of beta-cell function in the pancreas. SGLT-2 drugs significantly manage cardiovascular risk factors, including blood pressure, cardiac function, and antiinflammatory activity.SGLT-2 inhibitors are effective at lowering hemoglobin A1c levels and improving weight loss. They include a low risk of hypoglycemia and are usually well tolerated.
Technological advancements increased over the period leading to several modifications in the SGLT-2 inhibitors or the formulations being developed. Diabetes emerged as a global epidemic. Japan contains around 11 million people with diabetes, according to IDF 2021 data. Diabetes is identified as a healthcare priority by the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare. The high prevalence of type 2 diabetes is associated with a significant economic burden. The costs of diabetes are increased in patients with co-morbidities such as hypertension and hyperlipidemia and in patients who develop complications. Costs increase with an increasing number of complications. Well-organized medical insurance systems cover all medical fees for diabetes mellitus, and people with diabetes can visit doctors freely in Japan. Such advantages helped the increased adoption of these products in the Japanese market.
Japan Diabetes Drugs Industry Overview
The Japan Diabetes Drugs Market is moderately consolidated, with major manufacturers, namely Eli Lilly, Sanofi, Novo Nordisk, AstraZeneca, and other generic players, holding a presence in the region. A major share of the market is held by manufacturers concomitant with strategy-based M&A operations and constantly entering the market to generate new revenue streams and boost existing ones.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.4 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products and Services
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Insulins
- 5.1.1 Basal or Long Acting Insulins
- 5.1.1.1 Lantus (Insulin Glargine)
- 5.1.1.2 Levemir (Insulin Detemir)
- 5.1.1.3 Toujeo (Insulin Glargine)
- 5.1.1.4 Tresiba (Insulin Degludec)
- 5.1.1.5 Basaglar (Insulin Glargine)
- 5.1.2 Bolus or Fast Acting Insulins
- 5.1.2.1 NovoRapid/Novolog (Insulin Aspart)
- 5.1.2.2 Humalog (Insulin Lispro)
- 5.1.2.3 Apidra (Insulin Glulisine)
- 5.1.3 Traditional Human Insulins
- 5.1.3.1 Novolin/Actrapid/Insulatard
- 5.1.3.2 Humulin
- 5.1.3.3 Insuman
- 5.1.4 Biosimilar Insulins
- 5.1.4.1 Insulin Glargine Biosimilars
- 5.1.4.2 Human Insulin Biosimilars
- 5.1.1 Basal or Long Acting Insulins
- 5.2 Oral Anti-diabetic drugs
- 5.2.1 Biguanides
- 5.2.1.1 Metformin
- 5.2.2 Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors
- 5.2.2.1 Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors
- 5.2.3 Dopamine D2 receptor agonist
- 5.2.3.1 Bromocriptin
- 5.2.4 SGLT-2 inhibitors
- 5.2.4.1 Invokana (Canagliflozin)
- 5.2.4.2 Jardiance (Empagliflozin)
- 5.2.4.3 Farxiga/Forxiga (Dapagliflozin)
- 5.2.4.4 Suglat (Ipragliflozin)
- 5.2.5 DPP-4 inhibitors
- 5.2.5.1 Onglyza (Saxagliptin)
- 5.2.5.2 Tradjenta (Linagliptin)
- 5.2.5.3 Vipidia/Nesina(Alogliptin)
- 5.2.5.4 Galvus (Vildagliptin)
- 5.2.6 Sulfonylureas
- 5.2.6.1 Sulfonylureas
- 5.2.7 Meglitinides
- 5.2.7.1 Meglitinides
- 5.2.1 Biguanides
- 5.3 Non-Insulin Injectable drugs
- 5.3.1 GLP-1 receptor agonists
- 5.3.1.1 Victoza (Liraglutide)
- 5.3.1.2 Byetta (Exenatide)
- 5.3.1.3 Bydureon (Exenatide)
- 5.3.1.4 Trulicity (Dulaglutide)
- 5.3.1.5 Lyxumia (Lixisenatide)
- 5.3.2 Amylin Analogue
- 5.3.2.1 Symlin (Pramlintide)
- 5.3.1 GLP-1 receptor agonists
- 5.4 Combination drugs
- 5.4.1 Insulin combinations
- 5.4.1.1 NovoMix (Biphasic Insulin Aspart)
- 5.4.1.2 Ryzodeg (Insulin Degludec and Insulin Aspart)
- 5.4.1.3 Xultophy (Insulin Degludec and Liraglutide)
- 5.4.2 Oral Combinations
- 5.4.2.1 Janumet (Sitagliptin and Metformin)
- 5.4.1 Insulin combinations
6 MARKET INDICATORS
- 6.1 Type-1 Diabetic Population
- 6.2 Type-2 Diabetic Population
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 COMPANY PROFILES
- 7.1.1 Novo Nordisk A/S
- 7.1.2 Takeda
- 7.1.3 Pfizer
- 7.1.4 Eli Lilly
- 7.1.5 Janssen Pharmaceuticals
- 7.1.6 Astellas
- 7.1.7 Boehringer Ingelheim
- 7.1.8 Merck And Co.
- 7.1.9 AstraZeneca
- 7.1.10 Bristol Myers Squibb
- 7.1.11 Novartis
- 7.1.12 Sanofi Aventis
- 7.2 COMPANY SHARE ANALYSIS
- 7.2.1 Novo Nordisk A/S
- 7.2.2 Sanofi Aventis
- 7.2.3 Eli Lilly
- 7.2.4 Merck And Co.
- 7.2.5 Others
8 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS




