PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850267

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850267
Exosomes - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The exosomes market is valued at USD 0.71 billion in 2025 and is forecast to climb to USD 2.21 billion by 2030, tracking a 25.5% CAGR during 2025-2030.
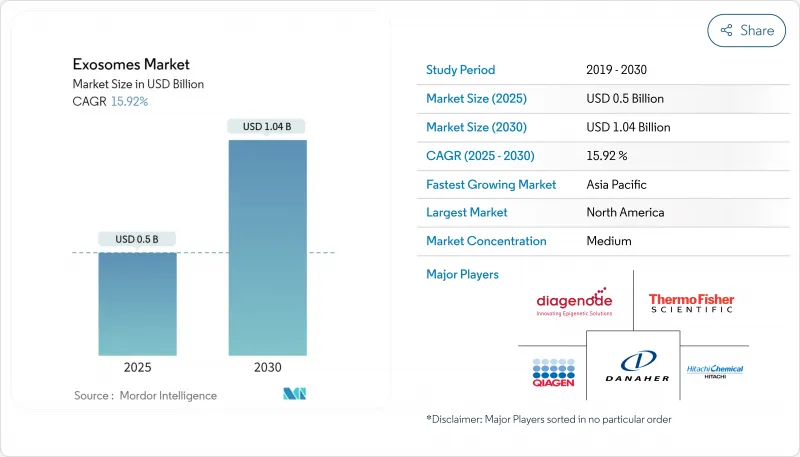
Strong momentum stems from the ability of nano-sized vesicles to cross biological barriers and deliver cargo with low immunogenicity, positioning exosomes as a preferred platform for next-generation diagnostics and targeted therapeutics. North America leads adoption, propelled by a supportive regulatory environment and heavy R&D funding, while Asia-Pacific is expanding fastest on the back of public investment in biomedical innovation. Kits & Reagents hold the lion's share because they simplify isolation, yet Services & Software are growing quicker as users outsource complex analytics. Diagnostics currently represent the largest application, although therapeutic programs are accelerating as clinical evidence mounts.
Global Exosomes Market Trends and Insights
Escalating Oncology Burden Boosting Liquid Biopsy & Therapeutics
Global cancer incidence is climbing, spurring demand for minimally invasive tests that track tumor biology in real time. Exosome-based liquid biopsies harbor tumor-specific nucleic acids and proteins that enable earlier detection and dynamic monitoring. A 2024 study presented at the American Association for Cancer Research showed that an exosome assay detected 97% of stage 1-2 pancreatic cancers when paired with CA 19-9. Concurrently, research groups are engineering tumor-derived vesicles for precision drug payloads, reducing off-target toxicities and opening new therapeutic avenues. Oncology thus remains the single largest driver for the exosomes market, catalyzing platform evolution and clinical acceptance.
Clarity on CMC Guidelines For Exosome Products
The U.S. FDA evaluates vesicles based on physiological activity, whereas the European Medicines Agency frames them under Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products. Draft guidance now specifies critical-quality-attribute testing and release criteria. Japan's expedited pathway for regenerative products provides further momentum. Clearer regulations reduce approval risk and attract late-stage capital, a modest but meaningful tailwind for the exosomes market over the long term.
Lack of Standardized Characterization Protocols Undermining Reproducibility
Heterogeneous isolation methods generate vesicle preparations with divergent particle counts, size distributions, and bioactivity. A 2024 review in Journal of Nanobiotechnology documented wide variability even when laboratories used nominally similar kits. Without agreed-upon standards, cross-study comparisons suffer, slowing translational progress. Ongoing efforts by the International Society for Cell & Gene Therapy are encouraging, but widespread adoption remains a mid-term challenge that may temper the exosomes market trajectory.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Venture-Capital & Big-Pharma Funding of Extracellular-Vesicle Pipelines
- Rising Academic-Industry Consortia Accelerating Biomarker Validation
- Stringent GMP Demands Elevating Manufacturing Complexity & Cost
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Kits & Reagents generated 47% of 2024 revenue in the exosomes market, reflecting their role in simplifying isolation and reducing operator variability. Off-the-shelf products such as the ExoEasy Maxi Kit deliver consistent vesicle yields across plasma, serum, and urine. The segment benefits from recurring consumable demand and entrenched user familiarity. Services & Software, while representing a smaller base, are scaling at a 39.7% CAGR as laboratories outsource multi-omics profiling and bioinformatics. Contract research organizations now bundle sample processing with AI-driven analytics, positioning themselves as indispensable partners for biomarker discovery. Instruments occupy the third-largest slice, buoyed by automated bead-based pull-down platforms and benchtop nano-flow cytometers that offer higher throughput. As integration deepens, vendors increasingly release hardware-consumable-software bundles, strengthening stickiness in the exosomes market.
A parallel dynamic is reshaping competitive priorities: consumables secure stable margins, instruments command one-time capex, and software unlocks data-centric recurring revenue. The interplay is encouraging partnerships between toolmakers and analytics specialists to offer end-to-end workflows. Vendors able to tie reagents, automation, and cloud pipelines into a seamless user experience will capture incremental exosomes market share during the forecast period.
Isolation Methods accounted for 55% of workflow revenue in 2024, underscoring their centrality to reproducible experimentation. Ultracentrifugation remains widely adopted despite scale limitations, while polymer precipitation kits gain traction for rapid small-volume processing. Proprietary solutions such as Biological Dynamics' ExoVerita Pro integrate alternating current fields to enrich vesicles from plasma with high purity. Downstream Analysis, expanding at a 38.5% CAGR, exemplifies the field's analytical pivot. Single-vesicle nano-flow cytometry now profiles surface antigens at near-virus resolution, and tandem mass spectrometry identifies thousands of protein cargo species per run. AI models link multi-omic signatures to disease phenotypes, converting raw readouts into clinically actionable indices. As isolation workflow matures, competitive differentiation is shifting to data richness and interpretation speed, an opportunity for tech-enabled service providers within the exosomes market.
The long-term outlook favors integrated isolation-to-analysis pipelines that compress turnaround time from days to hours. Vendors embedding on-chip fractionation with embedded sensors could eventually render bench-top centrifugation obsolete, further redefining best-practice workflows and unlocking new revenue layers across the exosomes market.
The Exosomes Market Report is Segmented by Product (Kits and Reagents, and More), Workflow (Isolation Methods [Ultracentrifugation, and More] and Downstream Analysis), Biomolecule Type (Proteins & Peptides, and More), Application (Diagnostics and Therapeutics), End-User (Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America anchors the exosomes market with a 53% revenue share in 2024. The United States hosts the majority of clinical trials and venture-backed start-ups, aided by NIH grants and FDA draft guidance that clarifies manufacturing expectations. Leading academic hubs such as Harvard, MIT, and MD Anderson operate specialized extracellular-vesicle centers that foster technology spin-outs. Exosomes market size in the region is projected to climb sharply through 2030 as liquid biopsy reimbursement codes roll out and therapeutic assets enter late-stage studies. Diagnostics dominate current uptake, while engineered vesicle therapeutics for neuro-oncology and cardiometabolic diseases approach pivotal trials.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-expanding territory, with a forecast 39.0% CAGR. China, Japan, and South Korea fund dedicated translational programs and offer tax incentives for biotech manufacturing. South Korea's Brexogen licensing deal marked the region's first exosome therapeutic out-licensing milestone, underscoring commercial maturation. Regional regulators are drafting harmonized guidelines patterned after ATMP frameworks, which will ease cross-border trial execution. While diagnostics currently headline revenue, therapeutic programs are poised to gain share as local CDMOs scale GMP suites and clinical data emerge.
Europe ranks third, supported by Germany, the United Kingdom, and France. The European Medicines Agency's ATMP pathway guides vesicle drugs, yet diverging emphasis on potency assays versus U.S. functional metrics can complicate global trial alignment. Horizon Europe funds multinational consortia that bridge bench to bedside, accelerating technology validation. Pharmaceutical companies increasingly leverage continental research strength for co-development, particularly in neurodegenerative and rare-disease indications. Middle East & Africa and South America form nascent markets centered on academic centers of excellence. Targeted public-health initiatives and rising chronic-disease prevalence should kindle gradual uptake of exosome diagnostics and, longer term, locally manufactured therapeutics, expanding the global footprint of the exosomes market.
- Danaher Corp. (Beckman Coulter)
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Fujifilm Holdings Corp.
- QIAGEN
- Lonza Group
- Miltenyi Biotec
- Illumina
- Hologic
- JSR Corp. (MBL International)
- Bio-Techne Corp. (Novus Biologicals)
- Takara Bio
- Malvern Instruments
- Abcam
- Capricor Therapeutics
- Evox Therapeutics Ltd
- Aethlon Medical Inc.
- Aegle Therapeutics
- Mursla Ltd
- Aruna Bio
- NanoSomix Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Escalating Oncology Burden Fueling Demand for Exosome-based Liquid Biopsy & Therapeutics
- 4.2.2 Rapid Advancements in High-Yield Exosome Isolation Technologies Lowering Cost of Goods
- 4.2.3 Growing VC & Big-Pharma Investments in Extracellular Vesicle Drug-Delivery Pipelines
- 4.2.4 Expansion of Companion Diagnostics Partnerships in Precision Medicine
- 4.2.5 Rising Academic Industry Consortia Accelerating Biomarker Discovery & Validation
- 4.2.6 Favorable Regulatory Initiatives Defining CMC Guidelines for Exosome Products
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Lack of Standardized Characterization Protocols Undermining Reproducibility
- 4.3.2 Stringent GMP Compliance Requirements Elevating Manufacturing Complexity & Cost
- 4.3.3 Limited Long-Term Safety Data Slowing Large-Scale Therapeutic Approvals
- 4.3.4 Fragmented Intellectual-Property Landscape Creating Freedom-to-Operate Uncertainty
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Product
- 5.1.1 Kits & Reagents
- 5.1.2 Instruments
- 5.1.3 Services & Software
- 5.2 By Workflow
- 5.2.1 Isolation Methods
- 5.2.1.1 Ultracentrifugation
- 5.2.1.2 Immuno-affinity Capture
- 5.2.1.3 Polymer-based Precipitation
- 5.2.1.4 Microfluidic Isolation
- 5.2.2 Downstream Analysis
- 5.2.2.1 Nano-flow Cytometry
- 5.2.2.2 Electron Microscopy
- 5.2.2.3 Mass Spectrometry
- 5.2.1 Isolation Methods
- 5.3 By Biomolecule Type
- 5.3.1 Non-coding RNA (miRNA, lncRNA)
- 5.3.2 Proteins & Peptides
- 5.3.3 Lipids
- 5.3.4 mRNA
- 5.3.5 DNA Fragments
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Diagnostics
- 5.4.1.1 Cancer
- 5.4.1.2 Neuro-degenerative Diseases
- 5.4.1.3 Cardiovascular Diseases
- 5.4.1.4 Infectious Diseases
- 5.4.2 Therapeutics
- 5.4.2.1 Oncology
- 5.4.2.2 Regenerative Medicine
- 5.4.2.3 Drug Delivery Platforms
- 5.4.1 Diagnostics
- 5.5 By End-user
- 5.5.1 Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies
- 5.5.2 Academic & Research Institutes
- 5.5.3 Hospitals & Clinics
- 5.5.4 Diagnostic Centers
- 5.6 Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 Europe
- 5.6.2.1 Germany
- 5.6.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.2.3 France
- 5.6.2.4 Italy
- 5.6.2.5 Spain
- 5.6.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.3.1 China
- 5.6.3.2 Japan
- 5.6.3.3 India
- 5.6.3.4 Australia
- 5.6.3.5 South Korea
- 5.6.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.4.1 GCC
- 5.6.4.2 South Africa
- 5.6.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5 South America
- 5.6.5.1 Brazil
- 5.6.5.2 Argentina
- 5.6.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and analysis of Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Danaher Corp. (Beckman Coulter)
- 6.3.2 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- 6.3.3 Fujifilm Holdings Corp.
- 6.3.4 Qiagen N.V.
- 6.3.5 Lonza Group Ltd
- 6.3.6 Miltenyi Biotec
- 6.3.7 Illumina Inc.
- 6.3.8 Hologic Inc.
- 6.3.9 JSR Corp. (MBL International)
- 6.3.10 Bio-Techne Corp. (Novus Biologicals)
- 6.3.11 Takara Bio Inc.
- 6.3.12 Malvern Instruments Ltd
- 6.3.13 Abcam plc
- 6.3.14 Capricor Therapeutics Inc.
- 6.3.15 Evox Therapeutics Ltd
- 6.3.16 Aethlon Medical Inc.
- 6.3.17 Aegle Therapeutics
- 6.3.18 Mursla Ltd
- 6.3.19 Aruna Bio
- 6.3.20 NanoSomix Inc.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment




