PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1690134

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1690134
Floating LNG Power Plant - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
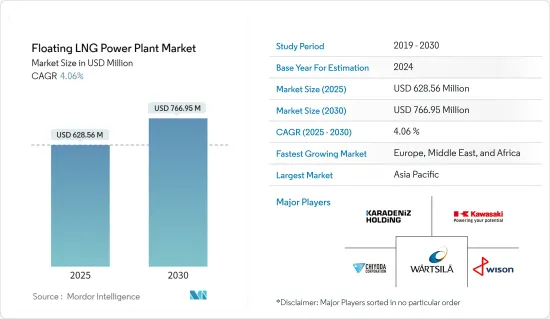
The Floating LNG Power Plant Market size is estimated at USD 628.56 million in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 766.95 million by 2030, at a CAGR of 4.06% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Over the long term, factors such as increasing demand for power due to increasing population and the lack of proper power infrastructures in developing countries are expected to drive the floating LNG power plant market.
On the other hand, high volatility and uneven LNG prices are expected to restrain the floating LNG power plant market.
Nevertheless, LNG adoption is expected to increase in the future owing to global emission norms. LNG, being a comparatively cleaner fuel, fulfills emission regulations. In 2020, IMO's reduced sulfur content in maritime fuel came into force, which is likely to result in the adoption of LNG as a bunker fuel. Offshore West Africa is also seeing increased oil and gas activity that, in turn, will present opportunities in the FLNG power plant market as well.
Asia-Pacific held a significant market share recently, and it is expected to be the largest and fastest market during the forecast period.
Floating LNG Power Plant Market Trends
Power Barge Segment Expected to Dominate the Market
- A power barge is a power plant facility installed on flat floating structures. Unlike power ships, a barge doesn't have a self-propelled system for moving from one location to the other, which cuts the cost of production for barges.
- As these power barges do not have any self-propelled moving systems, they are moved by other small boats or ships. The space saved from the propulsion engines in barges is used for more usable space in the vessel.
- The market for power barge is estimated to grow significantly in upcoming years due to the increasing installation of floating LNG-based power plants in countries with lower CAPEX for power generation or by countries having lower infrastructure availability.
- Moreover, as per the Statistical Review of World Energy 2023, the electricity generation from natural gas reached 6631.39 TWh in 2022 from around 4883.80 TWh in 2010 and 5635.95 TWh in 2015.
- Power barges have several advantages that fuel their adoption across the FLNG power generation segment. These are used to transport bulk with lower transportation costs, and they are available in different sizes. These barges can travel in low-tide water, and they can facilitate successful transportation of any sort of cargo while producing energy and floating.
- The barge is designed to carry out for a specific water body, and that barge can only run in that water body throughout its life. If that barge is used in some different water body, then it needs to be properly tugged or assisted by a tugboat.
- In June 2022, ExcelerateEnergy Inc. announced to supply power barge for floating power plants that will generate electricity and buoy the grid in the European nation. The company is also developing an LNG-to-Power project together with Exxon Mobil Corp. in the Albanian port of Vlora.
- Hence, owing to the above points, the power barge segment is expected to dominate the floating LNG power plant market during the forecast period.
Asia-Pacific Expected to Dominate the Market
- In the Asia-Pacific region, the supply-demand energy gap is often mitigated by sources such as coal, hydro, natural gas, nuclear, and renewable energy technologies. A significant rate of electricity access has been achieved in most of the economies. On the other hand, renewable energy sources have eradicated power reliability issues to the maximum extent, which indicates low chances for the development of a floating LNG power plants market in the region.
- However, few countries in Southeast Asia have adopted floating power plants to secure energy supplies. According to Malaysia's energy authority, the electricity demand is expected to reach about 24 GW in 2039. To cater to the growing demand, the government has taken measures to scale up energy systems, such as floating LNG power plants, to fulfill the same.
- In 2023, Petronas contracted Kejuruteraan Asastera(KAB) to develop and commission a 52MW floating LNG power plant worth USD 52.2 million. The floating LNG power plant would be located at Sabah. The development work is expected to start in the second quarter of 2023. Also, the Sri Lankan government, in association with the Asian Development Bank, agreed to conduct a feasibility study in 2022 on a floating LNG power plant, which could help the country diversify its energy mix.
- Further, in 2022, Indonesia received a floating power barge designed to run on LNG, which is likely to bridge the power generation requirements in the country. BMPP Nusantara-1 holds the potential to fulfill the electricity demand of far-flung areas of the country, which would help businesses and residents minimize their dependence on rented power generation barges.
- Hence, owing to the above points, Asia-Pacific is expected to dominate the floating LNG power plant market during the forecast period.
Floating LNG Power Plant Industry Overview
The floating LNG power plant market is moderately consolidated. Some of the key players in the market (in no particular order) include Wison Group, Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd, Wartsila Oyj Abp, Chiyoda Corp, and Karadeniz Holding., among others.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Scope of the Study
- 1.2 Market Definition
- 1.3 Study Assumptions
2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
4 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Market Size and Demand Forecast in USD, till 2029
- 4.3 Recent Trends and Developments
- 4.4 Government Policies and Regulations
- 4.5 Market Dynamics
- 4.5.1 Drivers
- 4.5.1.1 An Increase in the Use of LNG as an Energy Source
- 4.5.2 Restraints
- 4.5.2.1 Increasing Adoption of Solar and Wind Energy
- 4.5.1 Drivers
- 4.6 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes Products and Services
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Component Type
- 5.1.1 Gas Engines or Gas Turbines
- 5.1.2 IC Engines
- 5.1.3 Steam Turbines & Generators
- 5.2 Vessel Type
- 5.2.1 Power Ship
- 5.2.2 Power Barge
- 5.3 Geography
- 5.3.1 North America
- 5.3.1.1 United States
- 5.3.1.2 Canada
- 5.3.1.3 Rest of North America
- 5.3.2 Europe
- 5.3.2.1 Germany
- 5.3.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.3.2.3 France
- 5.3.2.4 Spain
- 5.3.2.5 Italy
- 5.3.2.6 Nordic Countries
- 5.3.2.7 Turkey
- 5.3.2.8 Russia
- 5.3.2.9 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.3.1 China
- 5.3.3.2 India
- 5.3.3.3 Japan
- 5.3.3.4 South Korea
- 5.3.3.5 Malaysis
- 5.3.3.6 Thailand
- 5.3.3.7 Indonesia
- 5.3.3.8 Vietnam
- 5.3.3.9 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.4 South America
- 5.3.4.1 Brazil
- 5.3.4.2 Argentina
- 5.3.4.3 Colombia
- 5.3.4.4 Rest of South America
- 5.3.5 Middle East & Africa
- 5.3.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.3.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.3.5.3 South Africa
- 5.3.5.4 Nigeria
- 5.3.5.5 Qatar
- 5.3.5.6 Egypt
- 5.3.5.7 Rest of Middle East & Africa
- 5.3.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Mergers, Acquisitions, Collaboration and Joint Ventures
- 6.2 Strategies Adopted by Key Players
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd.
- 6.3.2 Wartsila Oyj Abp
- 6.3.3 Siemens Energy AG
- 6.3.4 Waller Marine Inc.
- 6.3.5 Wison Group
- 6.3.6 Chiyoda Corporation
- 6.3.7 Karadeniz Holding
- 6.4 Market Ranking/Share Analysis
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS
- 7.1 Usage Of Hybrid Gensets Provides A Significant Opportunity for the Floating LNG Power Market




