PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1910588

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1910588
Project Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
Project logistics market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 485.62 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 462.30 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 621.06 billion, growing at 5.04% CAGR over 2026-2031.
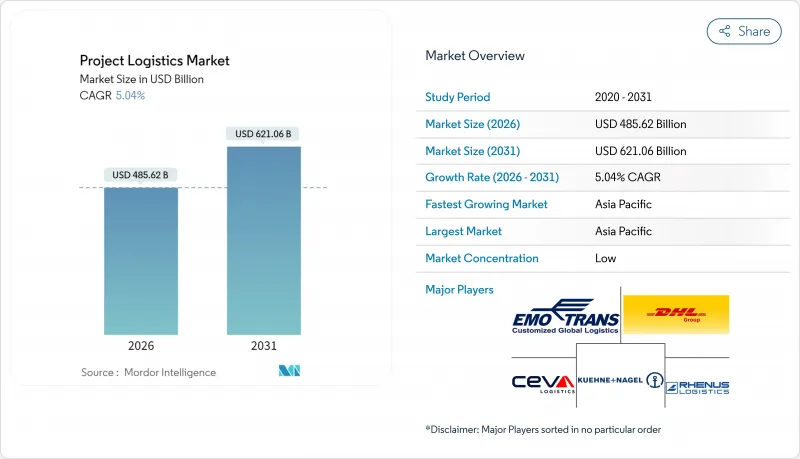
Capacity additions in renewable energy, synchronized infrastructure super-cycles in emerging economies, and the maturation of trans-Eurasian rail corridors are broadening service scope while lifting value per shipment. Mid-scale LNG terminals, hydrogen pipeline conversions, and modular construction projects are enlarging average component dimensions, boosting demand for specialized vessels, self-propelled modular transporters, and climate-controlled storage. In parallel, AI-enabled route-optimization platforms are trimming end-to-end costs by 10-15% and shortening delivery windows, allowing operators to redeploy scarce assets faster. Heightened competition, driven by regional specialists and technology-first entrants, is accelerating consolidation among mid-tier firms, yet market concentration remains low because no single provider exceeds 8% share. Persistent headwinds volatile freight rates, certified heavy-lift labor shortages, and chronic port congestion are pushing carriers to invest in digital visibility tools, multi-modal hubs, and simulation-based training programs.
Global Project Logistics Market Trends and Insights
Renewable-Energy Mega-Projects Drive Specialized Logistics Demand
Offshore wind farms and green-hydrogen corridors are rewriting transport blueprints. Turbine blades now surpass 100 meters, necessitating jack-up vessels designed for 15-20 MW turbines. Venture Global's USD 18 billion phase-three expansion at Plaquemines LNG embodies the boom in component scale, while Germany's conversion of 400 kilometers of natural-gas pipeline to hydrogen service signals a new class of cryogenic cargo that must be kept below -253 °C. These shifts require operators to recalibrate route planning, vessel selection, and inventory staging.
Infrastructure Super-Cycles in Emerging Economies Sustain Long-Term Growth
China's Belt and Road Initiative has spawned a USD 10 billion East-African port program and rail links that cut transit times by up to 50%. Simultaneously, the Trans-Caspian International Transport Route moved 27,000 TEU in 2024, a 25-fold jump over the prior year. The project logistics market benefits from this predictable, multi-decade capital pipeline that justifies fleet expansion and regional depot build-outs.
High Upfront Capital Requirements Constrain Market Entry
A 1,000-tonne crawler crane can cost USD 50-100 million, and wind-installation vessels exceed USD 200 million. These sums deter new entrants and force regional specialists to lease gear at premiums, curbing margin upside even as project volumes rise.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Modular Construction Transforms Project Delivery Models
- Mid-Scale LNG Export Terminals Create Regional Hubs
- Volatile Freight and Fuel Costs Pressure Operating Margins
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Transportation captured 60.45% of the project logistics market in 2025, reflecting the indispensable role of route engineering, heavy-lift vessels, and escorts for oversized cargo. Warehousing, distribution, and inventory management, though smaller, is the fastest-expanding slice at a 5.18% CAGR. The uptick mirrors modular builds that need climate-controlled laydown yards and synchronized staging. The project logistics market size for warehousing services is set to climb as integrated providers bundle storage with last-mile assembly. Operators deploying automated inventory systems gain visibility over component dwell times, curbing idle capital and penalties.
A wider service mix also elevates demand for on-site logistics coordination, customs brokerage, and risk advisory. Highland Fairview's logistics megacenter embodies this one-stop model, offering 40 million square feet tailored for complex cargo streams. As asset owners outsource cradle-to-installation responsibility, the project logistics industry pivots from move-centric contracts to outcome-driven partnerships, raising stickiness and fee potential.
The Project Logistics Market Report is Segmented by Service (Transportation, Warehousing, Distribution & Inventory Management, Other Services), Cargo Type (Oversized, Heavy-Lift, Breakbulk, Others), End-User (Oil & Gas, Energy Generation/Transmission, Construction and Infrastructure, and More), and Geography (North America, South America, Asia-Pacific, Europe, Middle East and Africa). Market Forecasts are Provided in Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific contributes 38.60% of global revenue, supported by China's Belt and Road ports, India's highways, and Australia's renewable-minerals surge. The Trans-Caspian route's 25-fold volume jump to 27 000 TEU in 2024 underscores alternate corridors that reduce reliance on Suez passages. Regional governments fund inland depots and digital customs windows, enabling carriers to rotate assets faster and clip demurrage fees.
North America ranks second, driven by LNG build-outs along the Gulf, 40-GW renewable-energy pipelines, and corridor upgrades such as the USD 6.4 billion Gordie Howe International Bridge that will open in late 2025. Canada's Arctic Trade Corridor advances through Hudson Bay Railway refurbishments that shave transit times and unlock critical-mineral exports. Favorable permitting reforms bolster schedule certainty, encouraging logistics firms to lock in long-term charter commitments.
Europe, the Middle East, and Africa compose a mosaic of mature and emerging lanes. Germany's 400-kilometer hydrogen-pipeline conversion pioneers a new cargo category, while Egypt's port expansions and Saudi Arabia's Landbridge escalate demand for coastal heavy-lift cranes. China-backed East-African ports, including Bagamoyo in Tanzania, redirect trade loops and invite regional specialists to establish feeder services. South America's mining corridor and renewable plans open frontier opportunities that reward risk-ready operators.
- Deutsche Post DHL
- Rhenus Logistics
- CEVA Logistics
- Kuehne + Nagel
- EMO Trans
- Hellmann Worldwide Logistics
- C.H. Robinson
- NMT Global Project Logistics
- Rohlig Logistics
- Expeditors International
- Kerry Logistics
- DSV A/S
- Fagioli group
- FLS Transportation
- Megalift
- Express Global Logistics (EXG)
- Yusen Logistics
- Geodis
- Crane Worldwide Logistics
- Transworld
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Renewable-energy mega-projects (offshore wind, green-hydrogen corridors)
- 4.2.2 Infrastructure super-cycles in emerging economies
- 4.2.3 Up-scaling of modular construction and prefabricated plants
- 4.2.4 Surge in mid-scale LNG export terminals (U.S. Gulf, West Africa)
- 4.2.5 Belt-and-Road trans-Eurasian rail corridors maturing
- 4.2.6 AI-enabled route and risk optimization platforms
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High upfront capex for heavy-lift assets
- 4.3.2 Volatile freight and fuel costs eroding margins
- 4.3.3 Acute shortage of certified heavy-lift operators
- 4.3.4 Port-side permit and congestion delays
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Impact of COVID-19 and Geo-Political Events
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Service
- 5.1.1 Transportation
- 5.1.1.1 Road
- 5.1.1.2 Rail
- 5.1.1.3 Air
- 5.1.1.4 Sea
- 5.1.2 Warehousing, Distribution and Inventory Management
- 5.1.3 Value-added Services and Others
- 5.1.1 Transportation
- 5.2 By Cargo Type
- 5.2.1 Oversized (Out-of-Gauge) Cargo
- 5.2.2 Heavy-Lift Cargo
- 5.2.3 Breakbulk Cargo
- 5.2.4 Others
- 5.3 By End-User Industry
- 5.3.1 Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying
- 5.3.2 Energy Generation and Transmission (Includes Renewable Energy)
- 5.3.3 Construction and Infrastructure
- 5.3.4 Manufacturing and Industrial Plants
- 5.3.5 Aerospace and Defense
- 5.3.6 Others (Maritime and Shipbuilding, Telecommunications, etc.)
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 South America
- 5.4.2.1 Brazil
- 5.4.2.2 Peru
- 5.4.2.3 Chile
- 5.4.2.4 Argentina
- 5.4.2.5 Rest of South America
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 India
- 5.4.3.2 China
- 5.4.3.3 Japan
- 5.4.3.4 Australia
- 5.4.3.5 South Korea
- 5.4.3.6 South East Asia (Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, Vietnam, and Philippines)
- 5.4.3.7 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 Europe
- 5.4.4.1 United Kingdom
- 5.4.4.2 Germany
- 5.4.4.3 France
- 5.4.4.4 Spain
- 5.4.4.5 Italy
- 5.4.4.6 BENELUX (Belgium, Netherlands, and Luxembourg)
- 5.4.4.7 NORDICS (Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden)
- 5.4.4.8 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 United Arab of Emirates
- 5.4.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.3 South Africa
- 5.4.5.4 Nigeria
- 5.4.5.5 Rest of Middle East And Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Deutsche Post DHL
- 6.4.2 Rhenus Logistics
- 6.4.3 CEVA Logistics
- 6.4.4 Kuehne + Nagel
- 6.4.5 EMO Trans
- 6.4.6 Hellmann Worldwide Logistics
- 6.4.7 C.H. Robinson
- 6.4.8 NMT Global Project Logistics
- 6.4.9 Rohlig Logistics
- 6.4.10 Expeditors International
- 6.4.11 Kerry Logistics
- 6.4.12 DSV A/S
- 6.4.13 Fagioli group
- 6.4.14 FLS Transportation
- 6.4.15 Megalift
- 6.4.16 Express Global Logistics (EXG)
- 6.4.17 Yusen Logistics
- 6.4.18 Geodis
- 6.4.19 Crane Worldwide Logistics
- 6.4.20 Transworld
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




