PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1911351

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1911351
India Transportation Infrastructure Construction - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The India Transportation Infrastructure Construction market was valued at USD 74.33 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 80.02 billion in 2026 to reach USD 115.69 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 7.66% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
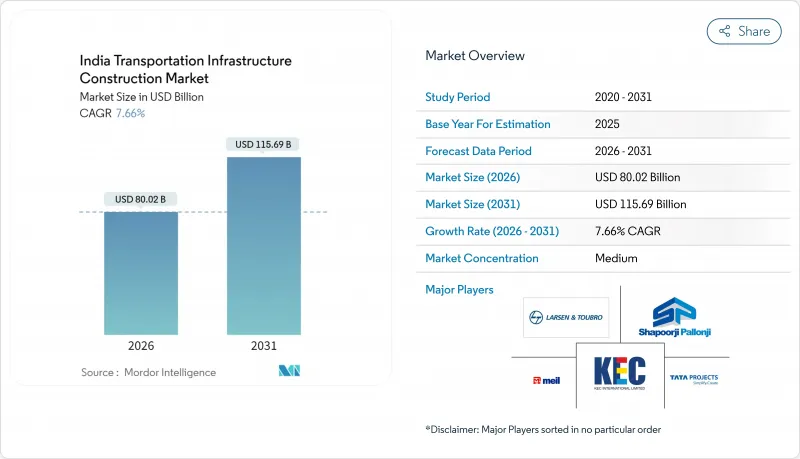
Robust federal outlays of USD 135.1 billion for 2025-26 and a steady pipeline of greenfield corridors, regional rapid transit lines, and multimodal hubs keep the India Transportation Infrastructure Construction market on a predictable growth path. Strong public-sector dominance, rising private capital through asset-monetization trusts, and the rollout of digital project-management tools further underline resilient demand. Intensified competition among EPC majors, a pivot toward high-speed freight routes, and a decisive policy shift aimed at cutting logistics costs form the three most important currents shaping competitive behavior inside the India Transportation Infrastructure Construction market.
India Transportation Infrastructure Construction Market Trends and Insights
Government Flagship Programs Boost Capital Mobilization
Bharatmala and PM Gati Shakti replace siloed execution with an integrated digital planning stack that already covers 115 national highways totaling 13,500 km. The emphasis on 6,669 km of high-speed corridors, 4,610 km of which are finished, signals a long-term freight-efficiency agenda. Although Phase I completion moved to 2027-28 as the cabinet vets rising costs, embedded AI-based monitoring and LiDAR surveys underpin better risk control. Inclusive routing through tribal and aspirational districts ensures the multiplier effect spreads beyond major metros, further anchoring the India Transportation Infrastructure Construction market.
Rapid Urbanization Accelerates Metro & RRTS Roll-outs
Operationalization of the Delhi-Meerut Regional Rapid Transit System trims end-to-end travel to one hour and sets a regulatory template for city clusters eyeing 100-120 km/h regional links. Upcoming RRTS corridors to Gurugram-Jaipur and Chennai-Parandur airport illustrate how ballooning metropolitan footprints push planners to leapfrog conventional metro designs. However, land procurement hurdles, Mumbai Metro 5 has secured only 40% of its parcels, continue to slow commissioning schedules. On balance, the urban-mobility push expands addressable opportunity for four-track viaducts, signaling, and depot works inside the India Transportation Infrastructure Construction market.
Land-acquisition Complexity Remains the Largest Structural Drag
A single 1,600 m2 dispute halted the USD 1.2 billion Delhi-Dehradun Expressway even after 78% physical progress, underscoring how individual parcels can stall corridor economics. More stringent environmental assessment norms extend approval cycles for ecologically sensitive alignments. Successful closures, such as the 100% land handover for the Mumbai-Ahmedabad high-speed rail after 5.5 years, prove that sustained stakeholder engagement works, but the additional time erodes the headline CAGR of the India Transportation Infrastructure Construction market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- National Infrastructure Pipeline Channels Long-term Funding
- Logistics-cost-reduction Mandate Reshapes Freight Corridors
- Material Cost Inflation Squeezes Margins
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Railways posted the quickest 8.05% CAGR and enlarge their slice of the India Transportation Infrastructure Construction market size through 2031 as the 1,506 km Western Dedicated Freight Corridor nears full operation. The corridor allows 25-ton axle loads at 100 km/h, an uplift that de-risks truck-based long-haul logistic. Meanwhile, roadways still held a commanding 58.10% India Transportation Infrastructure Construction market share in 2025, fueled by the 1,386 km Delhi-Mumbai Expressway running 82% complete. Greenfield bullet-train and metro-grade rail viaducts deepen the order book of specialized viaduct and track-laying contractors, signaling sustained multi-modal opportunity across the India Transportation Infrastructure Construction market.
Air transport and port infrastructure provide secondary demand streams. The UDAN program pushed the operational airport count to 157 and enlarged the runway EPC pipeline for tier-2 clusters. At the coast, the USD 9.2 billion Vadhavan Port targets top-10 global container status, promising bundled contracts for breakwaters, container berths, and rail sidings under the Sagarmala roadmap.
The India Transportation Infrastructure Construction Market Report is Segmented by Type (Roadways, Railways, Airways, Ports, and Inland Waterways), by Construction Type (New Construction, Renovation), by Investment Source (Public, Private), and by Geography (North India, South India, East India, West India). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Larsen & Toubro Limited
- TATA Projects
- KEC International Limited
- Shapoorji Pallonji
- Megha Engineering & Infrastructures Limited
- IRB Infrastructure Developers Ltd
- Eagle Infra India Ltd
- Reliance Infrastructure Limited
- Dilip Buildcon Limited
- Hindustan Construction Company Limited
- GMR Infrastructure Limited
- Adani Ports & Special Economic Zone Limited
- Afcons Infrastructure Limited
- NCC Limited
- Ashoka Buildcon Limited
- Gayatri Projects Limited
- JMC Projects (India) Ltd
- IRCON International Limited
- Simplex Infrastructures Limited
- PNC Infratech Limited
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Government flagship programs (Bharatmala, PM Gati Shakti) boosting capex
- 4.2.2 Rapid urbanisation fuelling metro & RRTS expansion
- 4.2.3 National Infrastructure Pipeline's dedicated funding commitments
- 4.2.4 Logistics-cost-reduction imperative under National Logistics Policy
- 4.2.5 Adoption of digital construction tech (BIM, drones) improving efficiency
- 4.2.6 Surge in ESG-linked financing & green bonds for sustainable infra
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Land acquisition & environmental clearance delays
- 4.3.2 Fiscal constraints amid high public debt levels
- 4.3.3 Rising material-cost volatility impacting budgets
- 4.3.4 Contractor liquidity crunch due to delayed payments
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.4.1 Overview
- 4.4.2 Real Estate Developers and Contractors - Key Quantitative and Qualitative Insights
- 4.4.3 Architectural and Engineering Companies - Key Quantitative and Qualitative Insights
- 4.4.4 Building Material and Equipment Companies - Key Quantitative and Qualitative Insights
- 4.5 Government Initiatives & Vision
- 4.6 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.7 Technological Outlook
- 4.8 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Force Analysis
- 4.8.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.8.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.8.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.8.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.8.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.9 Pricing (Construction Materials) and Construction Cost (Materials, Labour, Equipment) Analysis
- 4.10 Comparison of Key Industry Metrics of India with Other Countries
- 4.11 Key Upcoming/Ongoing Projects (with a focus on Mega Projects)
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts(Value, In USD Billion)
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 Roadways
- 5.1.2 Railways
- 5.1.3 Airways
- 5.1.4 Ports and Inland Waterways
- 5.2 By Construction Type
- 5.2.1 New Construction
- 5.2.2 Renovation
- 5.3 By Investment Source
- 5.3.1 Public
- 5.3.2 Private
- 5.4 By Region
- 5.4.1 North India
- 5.4.2 South India
- 5.4.3 East India
- 5.4.4 West India
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Larsen & Toubro Limited
- 6.4.2 TATA Projects
- 6.4.3 KEC International Limited
- 6.4.4 Shapoorji Pallonji
- 6.4.5 Megha Engineering & Infrastructures Limited
- 6.4.6 IRB Infrastructure Developers Ltd
- 6.4.7 Eagle Infra India Ltd
- 6.4.8 Reliance Infrastructure Limited
- 6.4.9 Dilip Buildcon Limited
- 6.4.10 Hindustan Construction Company Limited
- 6.4.11 GMR Infrastructure Limited
- 6.4.12 Adani Ports & Special Economic Zone Limited
- 6.4.13 Afcons Infrastructure Limited
- 6.4.14 NCC Limited
- 6.4.15 Ashoka Buildcon Limited
- 6.4.16 Gayatri Projects Limited
- 6.4.17 JMC Projects (India) Ltd
- 6.4.18 IRCON International Limited
- 6.4.19 Simplex Infrastructures Limited
- 6.4.20 PNC Infratech Limited
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment




