PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1693928

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1693928
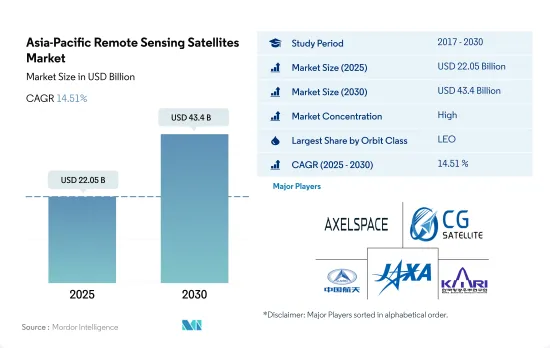
Asia-Pacific Remote Sensing Satellites - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Asia-Pacific Remote Sensing Satellites Market size is estimated at 22.05 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 43.4 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 14.51% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
LEO satellites are significantly driving market demand
- The Asia-Pacific region has seen a significant increase in the demand for satellite buses to accommodate a wide range of satellite orbits, including low Earth orbit (LEO), medium Earth orbit (MEO), and geostationary orbit (GEO).
- LEO satellites have become increasingly popular for various applications, including Earth observation, weather forecasting, and communication. The demand for LEO satellites has been particularly strong in China, where companies such as Spacety and Chang Guang Satellite Technology Co. Ltd are offering satellite buses for LEO missions. China has been active in this market with the launch of its Gaofen series satellites.
- MEO satellites have become increasingly important for global navigation and positioning services such as GPS and Galileo. In the Asia-Pacific region, Japan has been a leader in this field, with the launch of the Michibiki series of MEO navigation satellites. China has also been investing in MEO satellites with the launch of the Beidou system.
- GEO satellites are particularly important for communication and broadcasting services, such as television and the Internet. The demand for GEO satellites has been particularly strong in India, where companies such as ISRO and Antrix Corporation Ltd have been developing advanced satellite buses for communication missions. China has also been investing heavily in GEO satellites, with the launch of the Zhongxing series of satellites.
Asia-Pacific Remote Sensing Satellites Market Trends
Rising demand for satellite miniaturization is driving the market
- Miniature satellites leverage advances in computation, miniaturized electronics, and packaging to produce sophisticated mission capabilities. As microsatellites can share the ride to space with other missions, they offer a considerable reduction in launch costs.
- The demand from Asia-Pacific is primarily driven by China, Japan, and India, which manufacture the largest number of small satellites annually. Though the launches have decreased over the last three years, the satellite market in these countries continues to hold huge potential. Ongoing investments in startups and nano and microsatellite development projects are expected to boost the revenue growth of the region. From 2017 to 2022, more than 550 nano and microsatellites were placed into orbit by various players in the region.
- China is investing significant resources toward augmenting its space-based capabilities. The country has launched the largest number of nano and microsatellites in the Asia-Pacific region. In April 2022, Chinese startup SpaceWish's nanosatellite was launched into LEO aboard the CZ-2C (3) rocket. XINGYUAN-2 is a 6U remote sensing CubeSat that weighs approximately 7.5 kg.
- Singapore has become a pioneer in the fabrication of nanosatellites, with several models being designed each year for scientific missions. The SpooQy-1 NanoSat, which was launched by JAXA in 2019, is the brainchild of the Centre for Quantum Technologies (CQT) at the National University of Singapore. The 3,000 cm3 satellite weighs just 2.6 kg and is designed to demonstrate the physical phenomenon of quantum entanglement in space, which, if proven, may unlock quantum communications in space and attract investments worth USD 20 billion by 2030.
Rising investment opportunities in the market are driving spending on space programs
- Considering the increase in space-related activities in the Asia-Pacific region, satellite manufacturers are enhancing their production capabilities to tap into the rapidly emerging market potential. The prominent countries in Asia-Pacific that possess a robust space infrastructure are China, India, Japan, and South Korea. China National Space Administration announced space exploration priorities for the 2021-2025 period, including enhancing national civil space infrastructure and ground facilities. As a part of this plan, the Chinese government established China Satellite Network Group Co. Ltd for the development of a 13,000-satellite constellation for providing satellite internet services.
- In 2022, according to the draft budget of Japan, the space budget of the country was over USD 1.4 billion, which included investment for space activities of 11 government ministries. These activities include the development of the H3 rocket, Engineering Test Satellite-9, and the nation's Information Gathering Satellite (IGS) program. India has become a global leader in third-party launch services and has several ongoing R&D programs for new launch platforms. The proposed budget for India's space programs for FY22 was USD 1.83 billion.
- South Korea's space program has seen slow progress as other countries are reluctant to transfer core technologies. In 2022, the Ministry of Science and ICT announced a space budget of USD 619 million for manufacturing satellites, rockets, and other key space equipment. Many Southeast Asian countries have also recently started investing in space technology. As of March 2021, the Indonesian government had secured USD 545 million to continue the fabrication of the Very High Throughput Satellite (SATRIA), using a Public Private Partnership (PPP) scheme.
Asia-Pacific Remote Sensing Satellites Industry Overview
The Asia-Pacific Remote Sensing Satellites Market is fairly consolidated, with the top five companies occupying 96.77%. The major players in this market are Axelspace Corporation, Chang Guang Satellite Technology Co. Ltd, China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI) (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Satellite Mass
- 4.2 Satellite Miniaturization
- 4.3 Spending On Space Programs
- 4.4 Regulatory Framework
- 4.4.1 Australia
- 4.4.2 China
- 4.4.3 India
- 4.4.4 Japan
- 4.4.5 New Zealand
- 4.4.6 Singapore
- 4.4.7 South Korea
- 4.5 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Satellite Mass
- 5.1.1 10-100kg
- 5.1.2 100-500kg
- 5.1.3 500-1000kg
- 5.1.4 Below 10 Kg
- 5.1.5 above 1000kg
- 5.2 Orbit Class
- 5.2.1 GEO
- 5.2.2 LEO
- 5.2.3 MEO
- 5.3 Satellite Subsystem
- 5.3.1 Propulsion Hardware and Propellant
- 5.3.2 Satellite Bus & Subsystems
- 5.3.3 Solar Array & Power Hardware
- 5.3.4 Structures, Harness & Mechanisms
- 5.4 End User
- 5.4.1 Commercial
- 5.4.2 Military & Government
- 5.4.3 Other
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments).
- 6.4.1 Airbus SE
- 6.4.2 Axelspace Corporation
- 6.4.3 Chang Guang Satellite Technology Co. Ltd
- 6.4.4 China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC)
- 6.4.5 Esri
- 6.4.6 GomSpaceApS
- 6.4.7 IHI Corp
- 6.4.8 ImageSat International
- 6.4.9 Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
- 6.4.10 Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA)
- 6.4.11 Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI)
- 6.4.12 Lockheed Martin Corporation
- 6.4.13 Maxar Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.14 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- 6.4.15 Northrop Grumman Corporation
- 6.4.16 Planet Labs Inc.
- 6.4.17 Spire Global, Inc.
- 6.4.18 Thales
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SATELLITE CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms




