PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851037

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851037
Autonomous Aircraft - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
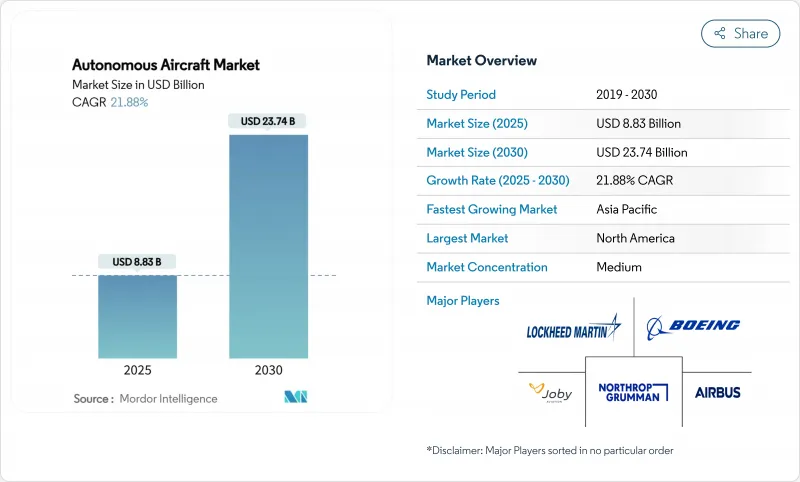
The autonomous aircraft market size stands at USD 8.83 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 23.74 billion by 2030, equating to a vigorous 21.88% CAGR.
A wave of defense modernization, urban mobility plans, and logistics automation is reshaping aviation economics and elevating demand for progressively self-directed platforms. Fixed-wing configurations command present dominance, yet hybrid fixed-wing VTOL aircraft lead the growth curve, reflecting airlines' and militaries' preference for versatile mid-range solutions. Rapid investments by defense agencies in collaborative combat aircraft and ISR drones accelerate technology readiness. At the same time, urban air mobility (UAM) programs foster beyond-visual-line-of-sight corridors and vertiport construction. Deepening AI integration helps unlock fully autonomous operations and widens the addressable envelope across cargo, passenger, and special-mission use cases. Conventional turbine engines remain the primary propulsion base, but hydrogen fuel-cell and advanced electric systems draw rising capital as sustainability mandates tighten.
Global Autonomous Aircraft Market Trends and Insights
Advancements in AI-Driven Flight Control Systems
Real-time machine-learning algorithms guide tactical maneuvers, obstacle avoidance, and route optimization without pilot intervention. Saab's autonomous Gripen E trials illustrate fighter-grade AI executing split-second decisions, validating moves from rule-based automation to adaptive cognition. The FAA's AI Safety Assurance Roadmap, released in June 2024, outlines certification tiers for statically trained and continuously learning AI, clearing a progression path for civil fleets. Combat programs demanding millisecond decision loops, such as the US Air Force's collaborative combat aircraft, spill proven architectures into commercial systems, enabling cargo operators and emerging air-taxi fleets to inherit hardened AI stacks for navigation, sense-and-avoid, and health-monitoring functions.
Rapid Growth in Urban Air Mobility and eVTOL Adoption
Metropolitan planners increasingly view three-dimensional mobility as a lever for congestion relief and regional connectivity. Vertical Aerospace committed USD 1 billion of Honeywell avionics orders to certify the VX4 by 2028, a signal of supply-chain confidence. Japan's first eVTOL routes target the 2028 Osaka Expo, with SkyDrive capturing over 300 provisional orders, aligning national priorities for advanced air mobility. Network effects amplify as vertiport developers such as Urban-Air Port plan 200 sites that bundle energy, maintenance, and air-traffic services. Regulatory hurdles ease: EASA released its VTOL package, and the FAA's powered-lift final rule clarifies pilot licensing, paving the runway-free aircraft toward scaled service. Improved batteries and certified autonomy underpin business cases for 20-100-mile urban hops where time savings justify premium fares.
Regulatory Complexity in Certification and Airspace Integration
Legacy aviation rules struggle to fit aircraft with no onboard crew. The FAA aims to publish comprehensive BVLOS regulations by 2026, extending present waiver-based operations into routine commercial lanes. EASA's certified category demands type certificates and air operator approvals similar to manned fleets, stretching autonomous programs to multi-year timelines. Cross-border routes magnify complexity because harmonization remains partial, pushing manufacturers to chase parallel approvals. Air-traffic integration further hinges on unmanned-traffic-management systems that must interface seamlessly with conventional ATC. Resource-constrained startups often struggle to fund long certification paths, tilting competitive advantage toward incumbent aerospace primes.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Cost Reduction Incentives for Logistics via Autonomous Cargo Drones
- Increased Military Investments in ISR and Combat Autonomy
- Limitations in Battery Technology and High Capital Costs
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Fixed-wing models accounted for 51.08% of the autonomous aircraft market 2024, underscoring their aerodynamic efficiency and range advantages for long-haul ISR and cargo missions. General Atomics' MQ-20 Avenger upgrade proves that legacy airframes can be retrofitted with full autonomy, keeping lifecycle costs low while enhancing capability. Hybrid fixed-wing VTOL systems, however, register a 26.89% CAGR, indicating fleet planners' appetite for runway-independent operations that preserve cruise performance. The autonomous aircraft market size attached to hybrid VTOL platforms will broaden sharply as urban networks demand aircraft that lift vertically yet sustain 200-knot cruise.
Hybrid VTOL growth also springs from defense refueling concepts such as Boeing's MQ-25 Stingray, which proves carrier compatibility without deck-space penalties. Rotary-wing craft hold niche roles for hover-intensive tasks like medevac and firefighting, but tilt-rotor and tilt-wing architectures now offer similar vertical dexterity with extended reach. Combining designs bridges the gap between sprawling runways and tightly packed city cores, easing infrastructure constraints and expanding mission sets.
In 2024, platforms classed as increasingly autonomous made up 68.45% of active deliveries, reflecting regulators' and operators' preference for step-wise feature upgrades over radical leaps. Retrofittable kits such as AeroVironment's ARK add advanced autonomy to existing fleets, enabling operators to harvest benefits without new-type certification. Fully autonomous systems-still a smaller slice-are growing at 27.75% CAGR as AI reliability, sensor fusion, and cloud connectivity converge.
The autonomous aircraft market size for fully autonomous craft will expand as regulatory confidence builds through supervised operations data. Military programs embracing optionally crewed designs provide real-world stress tests for perception stacks, accelerating tech maturity. On the civil side, Joby Aviation's takeover of Xwing's autonomy division highlights capital gravitating toward turnkey AI flight decks aimed at passenger services. Over the forecast period, human-on-the-loop governance will gradually yield to exception-only intervention, cutting operating costs and extending 24/7 utilization.
The Autonomous Aircraft Market Report is Segmented by Aircraft Type (Fixed-Wing, Rotary-Wing, and Hybrid (VTOL)), Autonomy Level (Increasingly Autonomous, and Fully Autonomous), Application (Cargo Aircraft, and More), Propulsion Type (Conventional Turbine, Electric, and More), Component (Flight Control Computers, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America accounted for 37.23% of global revenue in 2024. Pentagon funding for collaborative combat aircraft and high-altitude ISR drones underpins domestic demand, while the FAA's regulatory leadership shapes global certification pathways. Major primes-Boeing, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman-pair with AI start-ups to field pilotless fighters and delivery drones, enriching a talent pipeline spanning universities to Silicon Valley labs. Canada bolsters supply with avionics and composite manufacturing, and Mexico hosts cost-effective assembly lines that feed cross-border programs. The autonomous aircraft market size will continue to compound as defense appropriations and urban mobility pilots mature under clarified BVLOS frameworks.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing arena at 24.37% CAGR through 2030. China's low-altitude economy plan, which targets 1.5 trillion yuan aviation output by 2025, funnels subsidies into eVTOL production bases such as EHang's Hefei plant. Japan aims for commercial air-taxi launches coinciding with the 2028 Osaka Expo, spotlighting public-private coordination on vertiport zoning and autonomous flight-testing. South Korea's Incheon-centered vertiport grid and Australia's electric air-taxi feasibility studies widen regional experimentation. India's defense R&D incentives and increasing satellite connectivity open opportunities for autonomous ISR and cargo operations in remote terrain, while Southeast Asia eyes drones for medical resupply amid archipelagic geography.
Europe maintains a strategic foothold, balancing a stringent safety culture with sustainability imperatives. EASA's phased VTOL regulations define global benchmarks and anchor confidence for city planners across Germany, France, and the United Kingdom, each hosting eVTOL prototypes from Volocopter and Vertical Aerospace. Regional funds target hydrogen propulsion and recyclable structures, giving European OEMs an edge in eco-centric tenders. Italy's plan for nationwide vertiport corridors and Sweden's autonomous swarm trials echo the continent's dual civilian-military thrust. Although the continent grows more slowly than APAC, its policy influence and carbon targets position it as a key reference market.
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- The Boeing Company
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- RTX Corporation
- Elbit Systems Ltd.
- AeroVironment, Inc.
- Saab AB
- BAE Systems plc
- Airbus SE
- Textron Inc.
- Israel Aerospace Industries Ltd.
- General Atomics
- Joby Aviation, Inc.
- Volocopter Technologies GmbH
- Guangzhou EHang Intelligent Technology Co. Ltd.
- Archer Aviation Inc.
- Wisk Aero LLC
- Kratos Defense & Security Solutions Inc.
- Kaman Corporation
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Advancements in AI-driven flight control systems
- 4.2.2 Rapid growth in Urban Air Mobility (UAM) and eVTOL adoption
- 4.2.3 Cost reduction incentives for logistics via autonomous cargo drones
- 4.2.4 Increased military investments in ISR and combat autonomy
- 4.2.5 Deployment of BVLOS air corridors and Unmanned Traffic Management (UTM)
- 4.2.6 Increased availability of flight-certified autonomous avionics and sensor suites
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Regulatory complexity in certification and airspace integration
- 4.3.2 Limitations in battery technology and high capital costs
- 4.3.3 Heightened vulnerability to cyber threats and system hijacking
- 4.3.4 Semiconductor supply disruptions affecting AI processing units
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Aircraft Type
- 5.1.1 Fixed-wing
- 5.1.2 Rotary-wing
- 5.1.3 Hybrid (Fixed-Wing VTOL)
- 5.2 By Autonomy Level
- 5.2.1 Increasingly Autonomous
- 5.2.2 Fully Autonomous
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Cargo Aircraft
- 5.3.2 Passenger Aircraft
- 5.3.3 Special Mission/ISR
- 5.3.4 Air Taxi/UAM
- 5.4 By Propulsion Type
- 5.4.1 Conventional Turbine
- 5.4.2 Electric
- 5.4.3 Hybrid-Electric
- 5.4.4 Hydrogen Fuel-cell
- 5.5 By Component
- 5.5.1 Flight Control Computers
- 5.5.2 Sensors and Navigation
- 5.5.3 Communication and Data Links
- 5.5.4 Software and AI Algorithms
- 5.5.5 Propulsion Systems
- 5.5.6 Airframe and Structure
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 Europe
- 5.6.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.6.2.2 France
- 5.6.2.3 Germany
- 5.6.2.4 Italy
- 5.6.2.5 Russia
- 5.6.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.3.1 China
- 5.6.3.2 India
- 5.6.3.3 Japan
- 5.6.3.4 South Korea
- 5.6.3.5 Australia
- 5.6.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4 South America
- 5.6.4.1 Brazil
- 5.6.4.2 Rest of South America
- 5.6.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5.1 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.1.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.5.2 Africa
- 5.6.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.6.5.2.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Northrop Grumman Corporation
- 6.4.2 The Boeing Company
- 6.4.3 Lockheed Martin Corporation
- 6.4.4 RTX Corporation
- 6.4.5 Elbit Systems Ltd.
- 6.4.6 AeroVironment, Inc.
- 6.4.7 Saab AB
- 6.4.8 BAE Systems plc
- 6.4.9 Airbus SE
- 6.4.10 Textron Inc.
- 6.4.11 Israel Aerospace Industries Ltd.
- 6.4.12 General Atomics
- 6.4.13 Joby Aviation, Inc.
- 6.4.14 Volocopter Technologies GmbH
- 6.4.15 Guangzhou EHang Intelligent Technology Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.16 Archer Aviation Inc.
- 6.4.17 Wisk Aero LLC
- 6.4.18 Kratos Defense & Security Solutions Inc.
- 6.4.19 Kaman Corporation
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




