PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1852111

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1852111
Insulin Pens - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The insulin pens market size is valued at USD 8.39 billion in 2025 and will climb to USD 12.57 billion by 2030, advancing at an 8.42% CAGR.
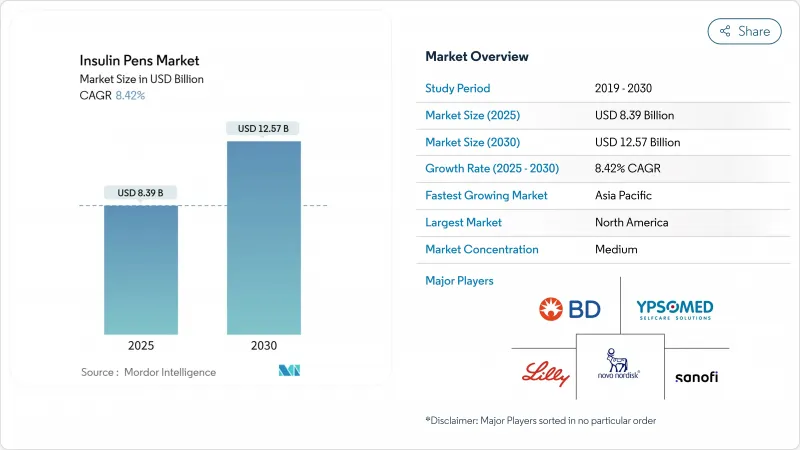
Strong momentum originates from the climbing global diabetes burden, the rapid normalization of smart-connectivity features, and the steady shift from hospital-centric to home-based diabetes care. Manufacturers are injecting capital into capacity scale-ups-Novo Nordisk is spending USD 4.1 billion on new capacity in North Carolina, while Eli Lilly is allocating USD 5.3 billion in Indiana-as they juggle insulin pen demand with parallel GLP-1 production priorities. Supply tightness, visible through Tresiba FlexTouch shortages that persist until January 2026, has nudged prescribers toward reusable and smart alternatives. In parallel, the diabetes population is projected to rise from 529 million in 2021 to 1.31 billion by 2050, a trend that hardwires structural volume growth into the insulin pens market.
Global Insulin Pens Market Trends and Insights
Increasing Diabetes Prevalence
Global diabetes prevalence continues to swell, with type 2 diabetes comprising 96% of total cases and prompting sustained demand for reliable insulin delivery. The International Diabetes Federation projects 783.2 million cases by 2045, and middle-income nations are set to shoulder a 21.1% relative jump that magnifies insulin pens market demand. Emerging economies wrestle with resource constraints even as their patient pools expand, compelling manufacturers to balance volume with affordability. Brazil typifies the surge, where type 2 prevalence could rise from 9.2% to 27.0% by 2036 amid obesity rates that doubled between 2003 and 2019. Such epidemiological patterns lock-in baseline growth for the insulin pens market, regardless of technology cycles or competitive moves.
Rising Adoption of User-Friendly Insulin Delivery Devices
Close to 60% of global insulin users favor pens over syringes because pens offer consistent dosing, portability, and lower injection anxiety. Uptake accelerates where health-literacy programs and supply chains expand together, especially across Latin America and Southeast Asia. Clinical studies show measurable adherence gains when patients switch to pens, with fewer missed bolus doses and improved time-in-range glucose metrics. Device makers that refine ergonomic design and needle micro-sharpness boost competitive stickiness, as shorter 4-5 mm needles reduce pain while sustaining accuracy. Such human-factor improvements reinforce patient loyalty and secure recurring cartridge revenue.
High Cost of Advanced Pen Technologies
Smart pens bundle sensors, processors, and connectivity modules that inflate bill-of-materials costs, limiting affordability in price-sensitive countries despite clinical gains. Asia-Pacific studies highlight that upfront device prices remain the chief hurdle to insulin adoption among uninsured urban populations. Manufacturers are piloting subscription models that amortize device costs over cartridge purchases and exploring outcome-based discounts that hinge on real-world glycemic improvements. Continued silicon cost declines and design for manufacturability efforts should ease this restraint over the medium term.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Technological Advancements in Smart Pen Connectivity
- Growing Preference for Home-Based Diabetes Management
- Stringent Regulatory Approval Processes
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Disposable pens retained 55.67% of 2024 revenue as their one-piece format remains the default prescription starting point in most formularies. Familiar design lowers training costs and underpins the insulin pens market size leadership at the entry price tier. Reusable models deliver cartridge savings for high-volume users yet still hinge on manual record keeping. Smart Bluetooth/NFC pens, expanding at a 10.34% CAGR, embed memory chips and wireless radios that auto-log every bolus; this feature shortens clinic consultations by replacing paper diaries with objective data streams. As insurers reimburse the added value, experts expect connectivity to become table stakes by 2028, positioning smart pens to capture progressively larger slices of incremental growth within the insulin pens market.
Manufacturers are re-platforming entire portfolios to ensure feature parity. Sanofi's AllStar Connect demonstrates how incremental electronics can coexist with established mechanical architecture, minimizing retraining hurdles. Dose-capture dashboards give clinicians line-of-sight to time-in-range metrics, reinforcing pay-for-performance models. The competitive spotlight thus shifts from hardware to analytics, prompting device makers to partner with algorithm specialists and cloud-hosting providers for holistic care offerings.
Type 2 patients generated 60.34% demand in 2024, reflecting epidemiological reality rather than product preference. Later-stage progression to insulin therapy, plus higher volumes per patient, propels this cohort's share of the insulin pens market size. Automated insulin dosing clearances for adults with type 2 diabetes extend the addressable market for connected pens that feed data to closed-loop algorithms. Type 1 users, though fewer, adopt premium devices earlier because they manage glycemia from diagnosis onward, making them critical early adopters of smart features.
Specialty categories-gestational and other atypical forms-grow at 9.65% CAGR as testing protocols improve and therapy guidelines recommend precise basal-bolus titration. Weekly insulin icodec trials promise lower injection burdens, yet clinicians still prescribe pens for prandial spikes, maintaining relevance across diabetes sub-types. For type 2, lifestyle comorbidities like obesity ensure a stable influx of new insulin initiations, solidifying volume prospects for the insulin pens market.
The Insulin Pens Market Report is Segmented by Product Type (Disposable Insulin Pens, and More), Diabetes Type (Type 1 Diabetes, and More), End User (Hospitals & Clinics, and More), Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacy, and More), Technology (Mechanical Spring-Loaded, and More), Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America commanded 41.45% revenue in 2024, buoyed by comprehensive insurance coverage, strong clinician adoption of smart pens, and policy caps on insulin co-pays that expand patient access. Advanced interoperability standards facilitate rapid EHR integration, making connected pens attractive for hospital systems pursuing value-based contracts. Supply constraints stemming from GLP-1 line prioritization have nudged prescribers to trial alternative pen SKUs, preserving unit demand despite brand-level shortages.
Europe, characterized by centralized tendering and a high biosimilar uptake rate, maintains robust volume but exerts price pressure on brand leaders. Environmental legislation is steering procurement toward recyclable or reusable formats, prompting lifecycle assessments that feed into tender scoring. Segment-specific reimbursement for connectivity, already active in Germany's DiGA framework, paves a path for subscription reimbursement attached to digital therapeutic companions.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest climber at 9.65% CAGR through 2030. Rising middle-class disposable income, state insurance rollouts, and urban diabetes hotspots converge to accelerate pen penetration. China's National Volume-Based Procurement initiative cut insulin list prices yet also stipulates tighter quality and supply guarantees, rewarding companies with local production footprints. India's National Digital Health Mission fosters electronic prescription uptake, laying groundwork for smart pen data-sharing uptake once device ASPs align with market affordability. Southeast-Asian private insurers bundle mobile coaching with connected pens, compressing the adoption curve often seen in Western markets.
Latin America and the Middle East post mid-single-digit CAGRs; government-funded chronic-disease programs drive pen purchases yet still emphasize low unit cost. Smart connectivity remains niche but is gaining traction in private clinics catering to affluent urban populations. Africa remains the smallest region by value; global foundations focus on basal insulin vial access, but pilot smart-pen donations in South Africa's private sector hint at future beachheads.
- Novo Nordisk
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Sanofi
- Ypsomed
- Beckton Dickinson
- Terumo
- Owen Mumford
- Biocon
- Julphar
- Medtronic
- Roche
- Haselmeier
- Companion Medical / Medtronic (InPen)
- Emperra
- Dongbao
- Wockhardt
- HTL-Strefa
- Sun Pharmaceuticals Industries
- Lupin
- Bigfoot Biomedical
- Cambridge Consultants
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope Of The Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increasing Diabetes Prevalence
- 4.2.2 Rising Adoption of User-Friendly Insulin Delivery Devices
- 4.2.3 Technological Advancements in Smart Pen Connectivity
- 4.2.4 Growing Preference for Home-Based Diabetes Management
- 4.2.5 Expansion of Reimbursement Coverage for Pen Devices
- 4.2.6 Ecosystem Partnerships Integrating Pens with Digital Therapeutics
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Cost of Advanced Pen Technologies
- 4.3.2 Stringent Regulatory Approval Processes
- 4.3.3 Environmental Concerns Over Disposable Plastic Waste
- 4.3.4 Competitive Threat from Alternate Insulin Delivery Systems
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Threat Of New Entrants
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power Of Buyers / Consumers
- 4.5.3 Bargaining Power Of Suppliers
- 4.5.4 Threat Of Substitute Products
- 4.5.5 Intensity Of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Disposable Insulin Pens
- 5.1.2 Reusable Insulin Pens
- 5.1.3 Smart / Connected Insulin Pens
- 5.2 By Diabetes Type
- 5.2.1 Type 1 Diabetes
- 5.2.2 Type 2 Diabetes
- 5.2.3 Gestational / Other
- 5.3 By End User
- 5.3.1 Hospitals & Clinics
- 5.3.2 Home-Care Settings
- 5.3.3 Other End Users
- 5.4 By Distribution Channel
- 5.4.1 Hospital Pharmacy
- 5.4.2 Retail Pharmacy
- 5.4.3 Online Sales
- 5.4.4 Diabetes Clinics
- 5.5 By Technology
- 5.5.1 Mechanical Spring-Loaded
- 5.5.2 Smart (Bluetooth / NFC)
- 5.5.3 Embedded Dose-Tracking Cap
- 5.6 Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 Europe
- 5.6.2.1 Germany
- 5.6.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.2.3 France
- 5.6.2.4 Italy
- 5.6.2.5 Spain
- 5.6.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.3.1 China
- 5.6.3.2 Japan
- 5.6.3.3 India
- 5.6.3.4 Australia
- 5.6.3.5 South Korea
- 5.6.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4 Middle East & Africa
- 5.6.4.1 GCC
- 5.6.4.2 South Africa
- 5.6.4.3 Rest of Middle East & Africa
- 5.6.5 South America
- 5.6.5.1 Brazil
- 5.6.5.2 Argentina
- 5.6.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and analysis of Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Novo Nordisk A/S
- 6.3.2 Eli Lilly
- 6.3.3 Sanofi
- 6.3.4 Ypsomed
- 6.3.5 BD (Becton, Dickinson and Company)
- 6.3.6 Terumo
- 6.3.7 Owen Mumford
- 6.3.8 Biocon
- 6.3.9 Julphar
- 6.3.10 Medtronic
- 6.3.11 Roche Diabetes Care
- 6.3.12 Haselmeier
- 6.3.13 Companion Medical / Medtronic (InPen)
- 6.3.14 Emperra
- 6.3.15 Dongbao
- 6.3.16 Wockhardt
- 6.3.17 HTL-Strefa
- 6.3.18 Sun Pharma
- 6.3.19 Lupin
- 6.3.20 Bigfoot Biomedical
- 6.3.21 Cambridge Consultants
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space & Unmet-Need Assessment




