PUBLISHER: IoT Analytics GmbH | PRODUCT CODE: 1520984

PUBLISHER: IoT Analytics GmbH | PRODUCT CODE: 1520984
IoT Use Case Adoption Report 2024
The "IoT Use Case Adoption Report 2024" is part of IoT Analytics' ongoing coverage of the IoT in general . The information presented in this report is based on an extensive survey of IoT end-users in manufacturing, healthcare, retail, and other industries. The purpose is to inform other market participants about the current state of adoption of IoT use cases across companies.
SAMPLE VIEW

How IoT use cases have evolved since 2021
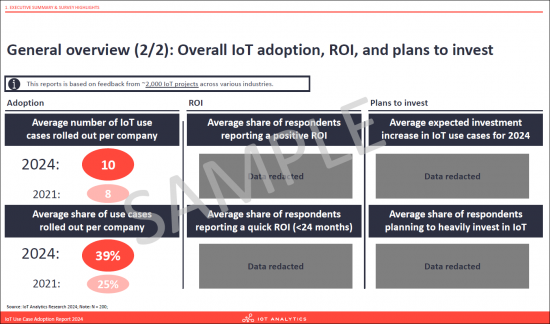
IoT initiatives are even more successful, but payback takes time. Currently a majority of IoT projects have a positive ROI, a 13-percentage point increase compared to 2021. However, the share of projects that amortize in 2 years have declined.
SAMPLE VIEW

APAC is steadily ahead; North America is catching up. In 2024, APAC companies are still at ~11 use cases rolled out on average (+0.9 increase since 2021). North America and Europe have each rolled out ~10 use cases (+3.5 and +1.7 since 2021, respectively).
SAMPLE VIEW
This report includes 27 IoT use cases across smart operations, smart supply chain, and connected products
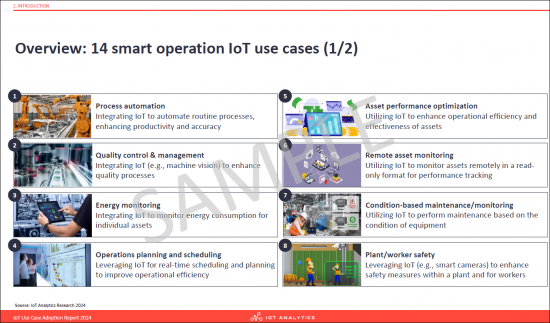
- Process automation. Integrating IoT to automate routine processes, enhancing productivity and accuracy.
- Quality control & management. Integrating IoT (e.g., machine vision) to enhance quality processes.
- Energy monitoring. Integrating IoT to monitor energy consumption for individual assets.
- Operations planning and scheduling. Leveraging IoT for real-time scheduling and planning to improve operational efficiency.
- Asset performance optimization. Utilizing IoT to enhance operational efficiency and effectiveness of assets.
- Remote asset monitoring. Utilizing IoT to monitor assets remotely in a read-only format for performance tracking.
- Condition-based maintenance/monitoring. Utilizing IoT to perform maintenance based on the condition of equipment.
- Plant/worker safety. Leveraging IoT (e.g., smart cameras) to enhance safety measures within a plant and for workers.
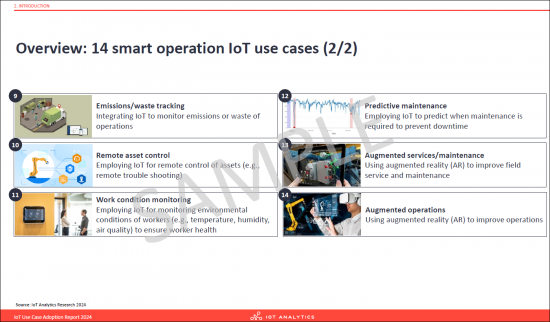
- Emissions/waste tracking. Integrating IoT to monitor emissions or waste of operations.
- Remote asset control. Employing IoT for remote control of assets (e.g., remote trouble shooting).
- Work condition monitoring. Employing IoT for monitoring environmental conditions of workers (e.g., temperature, humidity, air quality) to ensure worker health.
- Predictive maintenance. Employing IoT to predict when maintenance is required to prevent downtime.
- Augmented services/maintenance. Using augmented reality (AR) to improve field service and maintenance.
- Augmented operations. Using augmented reality (AR) to improve operations.
- Real-time inventory management. Utilizing IoT for tracking inventory levels in real-time to optimize stock and reduce shortages or excesses.
- Supply chain track & trace. Employing IoT for monitoring the location, condition and/or status of products and materials along the supply chain.
- On-site facility track & trace. Employing IoT for real-time tracking and tracing of assets on a site (e.g., in a factory or warehouse).
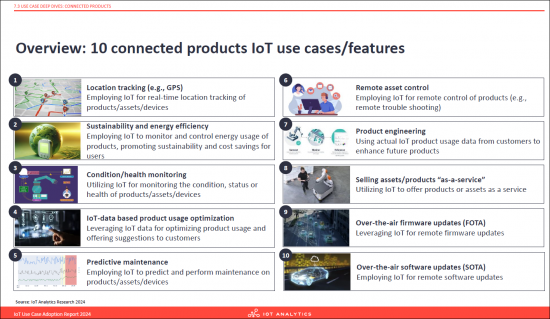
- Location tracking (e.g., GPS). Employing IoT for real-time location tracking of products/assets/devices.
- Sustainability and energy efficiency. Employing IoT to monitor and control energy usage of products, promoting sustainability and cost savings for users.
- Condition/health monitoring. Utilizing IoT for monitoring the condition, status or health of products/assets/devices.
- IoT-data based product usage optimization. Leveraging IoT data for optimizing product usage and offering suggestions to customers.
- Predictive maintenance. Employing IoT to predict and perform maintenance on products/assets/devices.
- Remote asset control. Employing IoT for remote control of products (e.g., remote troubleshooting).
- Product engineering. Using actual IoT product usage data from customers to enhance future products.
- Selling assets/products "as-a-service". Utilizing IoT to offer products or assets as a service.
- Over-the-air firmware updates (FOTA). Leveraging IoT for remote firmware updates.
- Over-the-air software updates (SOTA). Employing IoT for remote software updates.
SAMPLE VIEW
Analyses in the report includes:
- IoT use case adoption (by region, by industry, by use case group)
- Detailed breakdown of IoT use case spending (upfront, recurring, hardware, software, services)
- Return on investment (by region, by industry, amortization by use case)
- Use case investment priorities (by region, by industry, change by use case)
- Impact of IoT implementation on company KPIs (e.g., Overall equipment efficiency, revenue, quality)
- Challenges faced when implementing IoT use cases
- Methods of ensuring a skilled workforce
- Impact of IoT strategy on company's sustainability goals
- Key vendors for IoT use cases and vendor satisfaction with deep dives on strengths and weaknesses of most used vendors and most used vendors by tech stack
- Detailed case studies for every use case
- Deep dives for each of the 27 use cases (adoption, spending, ROI, planned investment, impact on company KPIs)
SAMPLE VIEW

Questions answered:
- What are the most adopted IoT use cases (out of a list of 27)?
- Which IoT use cases have the highest return on investment (ROI)?
- Which KPIs are most important for a company's IoT strategy, and how are the KPIs affected by implementing IoT use cases?
- How much do companies spend on hardware, software, and services for individual IoT use cases?
- Which IoT use cases do companies plan to invest in the most in 2024?
- Who are the leading vendors for IoT use cases, how satisfied are end users, and what are the strengths and weaknesses of the top vendors?
- What challenges do IoT end users face when implementing use cases?
- How do companies ensure their workforce has the necessary IoT skills?
- How much are companies' IoT strategies impacting their sustainability goals?
Companies mentioned:
A selection of companies mentioned in the report.
|
|
Table of Contents
1. Executive summary and survey highlights
- General overview (1/2): How things evolved since our 2021 use case report
- General overview (2/2): Overall IoT adoption, ROI, and plans to invest
- Regional overview: IoT use case adoption 2024 vs. 2021 and spending plan
- Industry overview: IoT use case adoption, investment, KPIs, and challenges
- Use case overview (1/2): Use cases ranked by adoption, ROI, and investment plans
- Use case overview (2/2): Impact of individual IoT use cases
- Executive summary
2. Introduction
- Reminder: How IoT Analytics defines IoT
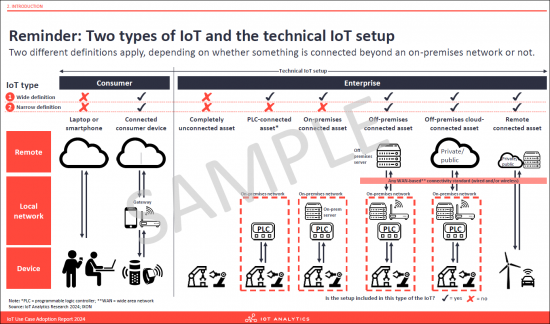
- Reminder: Two types of IoT and the technical IoT setup
- Starting point: IoT is now a top 5 corporate technology priority
- Our view: Many companies are on or moving to stage 4 of their IoT journey
- Some major tech trends are currently affecting IoT growth
- Our view: The market for independent IoT applications reached $45 billion in 2023
- IoT applications can have many benefits and interest is at high levels
- There are several ways to classify IoT use cases
- Search interest is also growing for popular IoT use cases ...
- ... and with good reason, as companies are realizing their value
- This report looks at 27 IoT use cases from 3 different groups
- Examples of IoT initiatives in each use case group
- Overview: 14 smart operation IoT use cases (1/2)
- Overview: 14 smart operation IoT use cases (2/2)
- Overview: 3 smart supply IoT chain use cases
- Overview: 10 connected products IoT use cases/features
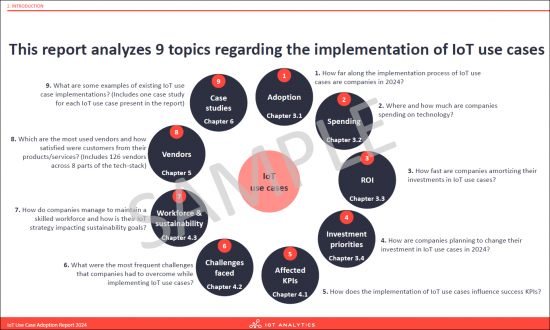
- This report analyzes 9 topics regarding the implementation of IoT use cases
3. Global results
- Chapter 3.1: Adoption - Overview and key takeaways
- IoT use case adoption (1/3): By region
- IoT use case adoption (2/3): By industry
- IoT use case adoption (3/3): By detailed industry
- Comparison 2024 vs. 2021: Adoption growth by region and industry
- Global adoption of use cases
- Global adoption of use cases by group
- Comparison 2024 vs. 2021: Adoption by use case
- Chapter 3.2: Spending - Overview and key takeaways
- Tech spend (1/4): Definitions
- Tech spend (2/4): Overview
- Tech spend (3/4): By segment
- Tech spend (4/4): Breakdown and detailed IoT spending
- Deep dive: Non-use case-specific IoT budget
- Upfront/recurring and tech stack IoT spending
- Distribution of IoT spending on upfront/recurring by use case
- Distribution of IoT spending on hardware/software/services by use case
- Chapter 3.3: ROI - Overview and key takeaways
- Positive ROI (1/2): By region
- Positive ROI (2/2): By industry
- Quick ROI (1/3): By region
- Quick ROI (2/3): By industry
- Comparison 2024 vs. 2021: Positive ROI growth by region and industry
- Quick ROI (3/3): Detailed view
- Amortization by use case (1/2): Quick ROI
- Amortization by use case (2/2): Positive ROI
- Comparison 2024 vs. 2021: Quick ROI by use case
- Comparison 2024 vs. 2021: Positive ROI by use case
- Chapter 3.4: Investment priorities - Overview and key takeaways
- Average investment change (1/2): By region
- Average investment change (2/2): By industry
- Strong investment (1/2): By region
- Strong investment (2/2): By industry
- Comparison 2024 vs. 2021: Investment plans growth by region and industry
- Strong investment: Detailed view
- Investment change by use case
- Comparison 2024 vs. 2021: Investment plans by use case
4. Impact of IoT implementation
- Chapter 4.1: Impact of IoT implementation Affected KPIs - Overview and key takeaways
- List of KPIs analyzed in this chapter
- Importance of KPIs for IoT strategy (1/4): Group overview
- Importance of KPIs for IoT strategy (2/4): Detailed overview
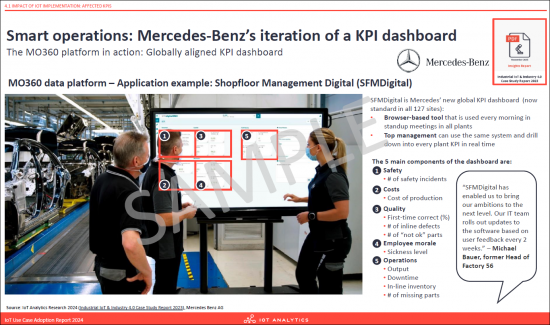
- Smart operations: Mercedes-Benz's iteration of a KPI dashboard
- Connected products: Konig & Bauer's iteration of a KPI dashboard
- Importance of KPIs for IoT strategy (3/4): By industry
- Three most important KPIs for each industry
- Deep dive: Why cybersecurity KPIs are more important in the energy sector
- Importance of KPIs for IoT strategy (4/4): By region and size
- Impact of IoT implementation on KPIs (1/7): Overview
- Impact of IoT implementation on KPIs (2/7): By use case
- Impact of IoT implementation on KPIs (3/7): Top 3 by use case (1/3): Smart operations
- Impact of IoT implementation on KPIs (4/7): Top 3 by use case (2/3): Smart supply chain
- Impact of IoT implementation on KPIs (5/7): Top 3 by use case (3/3): Connected products
- Impact of IoT implementation on KPIs (6/7): By use case detailed (1/2): Smart operations
- Impact of IoT implementation on KPIs (7/7): By use case detailed (2/2): Smart supply chain/con. prods.
- Chapter 4.2: Impact of IoT implementation Challenges faced - Overview and key takeaways
- Challenges faced when implementing IoT use cases (1/4): Overview
- Deep dive: Legacy systems (1/4) - Organizational challenges arise
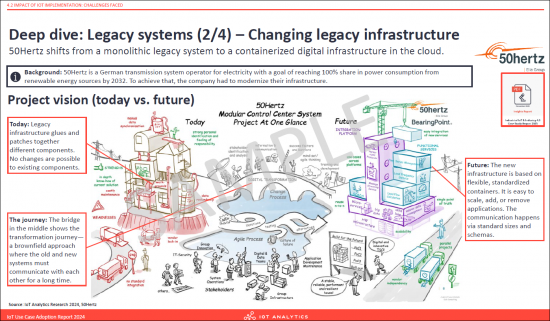
- Deep dive: Legacy systems (2/4) - Changing legacy infrastructure
- Deep dive: Legacy systems (3/4) - Difficult to replace them in operations
- Deep dive: Legacy systems (4/4) - Insights from the Hannover Messe
- Deep dive: IT & data security - IoT is a growing target for cyberattacks
- Deep dive: Missing talent/skill gaps - Corporate earnings calls
- Challenges faced when implementing IoT use cases (2/4): By industry
- Challenges faced when implementing IoT use cases (3/4): By region and size
- Challenges faced when implementing IoT use cases (4/4): By department
- Chapter 4.3: Impact of IoT implementation Workforce & sustainability - Overview and key takeaways
- Ensuring a skilled workforce (1/5): Overview
- Ensuring a skilled workforce (2/5): Training deep dive
- Ensuring a skilled workforce (3/5): Hiring, third-parties, internal communication, and collaborations
- Ensuring a skilled workforce (4/5): Obstacles faced by respondents
- Ensuring a skilled workforce (5/5): Additional tips from respondents
- Deep dive: Examples of company training programs
- Tech expertise in demand in Q1 2024: IoT (1/2)
- Tech expertise in demand in Q1 2024: IoT (2/2)
- IoT strategy and sustainability (1/4): Overview
- IoT strategy and sustainability (2/4): Sustainability goals being impacted
- IoT strategy and sustainability (3/4): Deep dive on how IoT helps with sustainability goals
- IoT strategy and sustainability (4/4):Future planned impact on sustainability/no impact planned
- How an IoT implementation improves sustainability
- How CEOs think about their sustainability goals
5. Key vendors & vendor satisfaction
- The 20 most used IoT vendors and their satisfaction ratings
- 20 most used vendors for IoT use case projects
- Comparison 2024 vs. 2021: Unique vendors used
- Comparison 2024 vs. 2021: Most used vendors and their satisfaction
- Most used vendors by region and industry (1/2)
- Most used vendors by region and industry (2/2)
- Extensive list with all vendors that respondents have worked with
- Key IoT vendor deep dives (1/7): Microsoft (1/2)
- Key IoT vendor deep dives (1/7): Microsoft (2/2)
- Key IoT vendor deep dives (2/7): Cisco (1/2)
- Key IoT vendor deep dives (2/7): Cisco (2/2)
- Key IoT vendor deep dives (3/7): AWS (1/2)
- Key IoT vendor deep dives (3/7): AWS (2/2)
- Key IoT vendor deep dives (4/7): Honeywell (1/2)
- Key IoT vendor deep dives (4/7): Honeywell (2/2)
- Key IoT vendor deep dives (5/7): Google
- Key IoT vendor deep dives (6/7): Siemens
- Key IoT vendor deep dives (7/7): IBM
- Most used vendors by tech stack (1/7): Hardware - Computers, controllers, and gateways
- Most used vendors by tech stack (2/7): Hardware - Sensors/semiconductors
- Most used vendors by tech stack (3/7): Software - Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
- Most used vendors by tech stack (4/7): Software - IoT platforms/PaaS
- Most used vendors by tech stack (5/7): Services - Wireless connectivity
- Most used vendors by tech stack (6/7): Services - Professional services
- Most used vendors by tech stack (7/7): Security
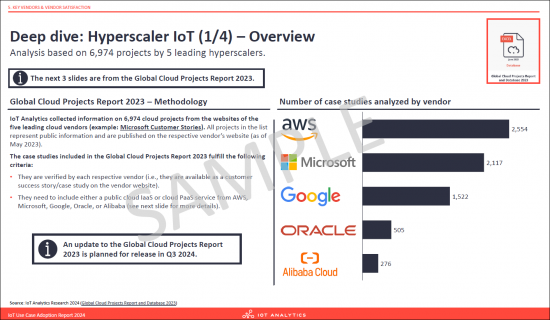
- Deep dive: Hyperscaler IoT (1/4) - Overview
- Deep dive: Hyperscaler IoT (2/4) - Relevance of IoT
- Deep dive: Hyperscaler IoT (3/4) - Relevance of IoT by industry
- Deep dive: Hyperscaler IoT (4/4) - Products vs. operations*
6. Case studies
- List of included smart operations case studies
- Smart operations case study 1/14: Eldorado Brasil
- Smart operations case study 2/14: Schneider Electric
- Smart operations case study 3/14: Greggs
- Smart operations case study 4/14: Somfy
- Smart operations case study 5/14: Longroad Energy
- Smart operations case study 6/14: ONGC
- Smart operations case study 7/14: ArcelorMittal
- Smart operations case study 8/14: Swire Coca-Cola
- Smart operations case study 9/14: Roeslein Alternative Energy
- Smart operations case study 10/14: framas
- Smart operations case study 11/14: Silotank
- Smart operations case study 12/14: Aquafin
- Smart operations case study 13/14: MAN
- Smart operations case study 14/14: Volvo Group
- List of included smart supply chain case studies
- Smart supply chain case study 1/3: Tyson Foods
- Smart supply chain case study 2/3: Konvoy
- Smart supply chain case study 3/3: Salco
- List of included connected products case studies
- Connected products case study 1/10: John Deere
- Connected products case study 2/10: Alfa Laval
- Connected products case study 3/10: Trumpf
- Connected products case study 4/10: Vossloh Rail Services
- Connected products case study 5/10: Middle Atlantic
- Connected products case study 6/10: Unox
- Connected products case study 7/10: Dyson
- Connected products case study 8/10: Carrier
- Connected products case study 9-10/10: Volkswagen
7. Use case deep dives
- Chapter 7.1: Smart operations use cases
- Smart operations use cases (1/5): Adoption
- Smart operations use cases (2/5): Spending hardware, software, services
- Smart operations use cases (3/5): Spending CAPEX vs. OPEX
- Smart operations use cases (4/5): Planned investment
- Smart operations use cases (5/5): ROI
- Deep dives for all 14 smart operations use cases
- Chapter 7.2: Smart supply chain use cases
- Smart supply chain use cases (1/5): Adoption
- Smart supply chain use cases (2/5): Spending hardware, software, services
- Smart supply chain use cases (3/5): Spending CAPEX vs. OPEX
- Smart supply chain use cases (4/5): Planned investment
- Smart supply chain use cases (5/5): ROI
- Deep dives for all 3 smart supply chain use cases
- Chapter 7.3: Smart products use cases
- Connected products use cases (1/5): Adoption
- Connected products use cases (2/5): Spending hardware, software, services
- Connected products use cases (3/5): Spending CAPEX vs. OPEX
- Connected products use cases (4/5): Planned investment
- Connected products use cases (5/5): ROI
- Deep dives for all 10 connected products use cases
8. Methodology
9. Appendix
10. About IoT Analytics




