PUBLISHER: Coherent Market Insights | PRODUCT CODE: 1707517

PUBLISHER: Coherent Market Insights | PRODUCT CODE: 1707517
Precision Fermentation Market, By Ingredient, By Microbe, By Application, By Geography
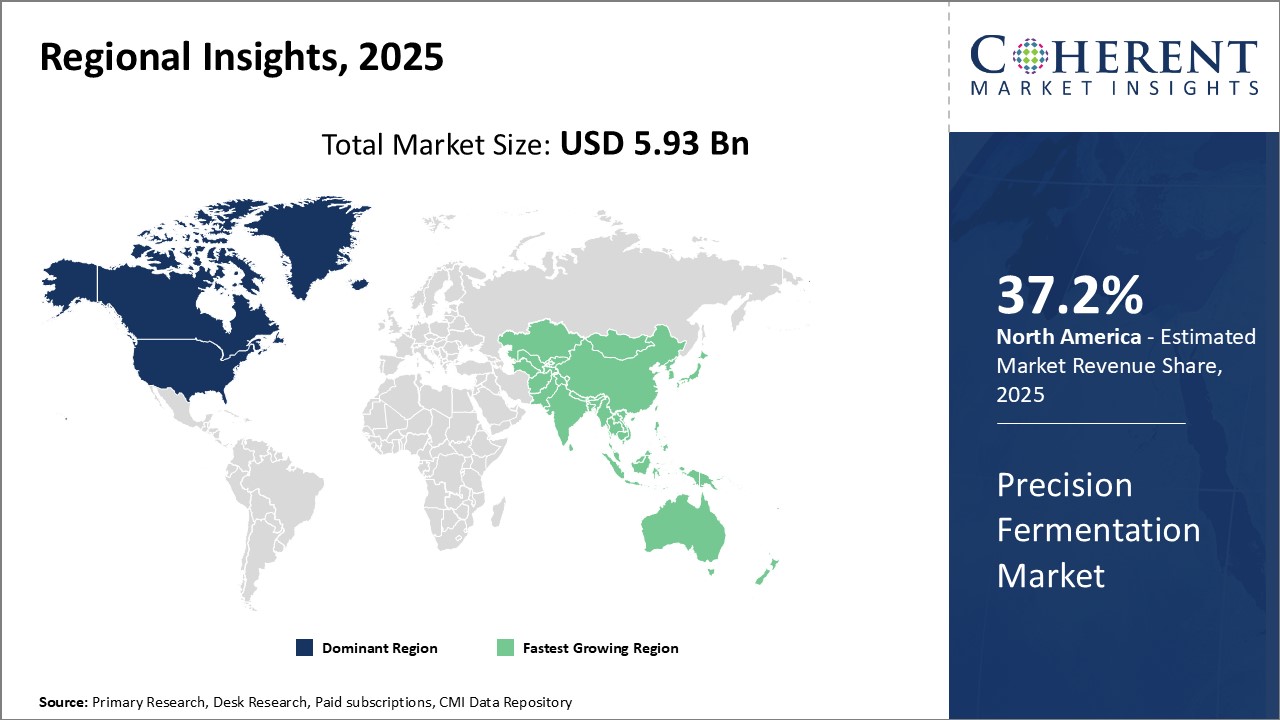
Global Precision Fermentation Market is estimated to be valued at USD 5.93 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 65.07 Bn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 40.8% from 2025 to 2032.
| Report Coverage | Report Details | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Base Year: | 2024 | Market Size in 2025: | USD 5.93 Bn |
| Historical Data for: | 2020 To 2024 | Forecast Period: | 2025 To 2032 |
| Forecast Period 2025 to 2032 CAGR: | 40.80% | 2032 Value Projection: | USD 65.07 Bn |
Precision fermentation is a form of cellular agriculture that utilizes fermentation processes to produce foods, ingredients, and materials in a sustainable way. It involves the cultivation of microorganisms like yeast and bacteria in bioreactors to synthesize proteins, fats, flavors, and other compounds. By leveraging advanced molecular biology techniques, precision fermentation allows manufacturing desired compounds with enhanced nutritional profiles, lowered environmental impacts and reduced costs compared to traditional agriculture. Several startups are developing technologies to produce seafood, dairy, and egg alternatives using precision fermentation that mimics the taste, texture, and other attributes of animal-based products. This evolving field promises to revolutionize the future of foods.
Market Dynamics:
The precision fermentation market growth is driven by the growing demand for sustainable and alternative protein sources. Conventional meat and dairy production places considerable strain on land and water resources. Precision fermentation helps address these challenges by producing products in controlled industrial fermenters using fewer natural resources. For example, brewer's yeast can be engineered to secrete cow's milk proteins instead of alcohol. The market also benefits from favorable regulations supporting cellular agriculture innovations. However, high capital costs and the need for larger production volumes to achieve economies of scale remain key restraints. Meanwhile, continuous R&D expanding the range of fermented ingredients offers new opportunities.
Key Features of the Study:
- This report provides an in-depth analysis of the global precision fermentation market, and provides market size (US$ Bn) and compound annual growth rate (CAGR%) for the forecast period (2025-2032), considering 2024 as the base year.
- It elucidates potential revenue opportunities across different segments and explains attractive investment proposition matrices for this market.
- This study also provides key insights about market drivers, restraints, opportunities, new product launches or approval, market trends, regional outlook, and competitive strategies adopted by key players.
- It profiles key players in the global precision fermentation market based on the following parameters - company highlights, products portfolio, key highlights, financial performance, and strategies.
- Key companies covered as a part of this study include Change Foods, Geltor, Helania Inc, Formo, FUMI Ingredients, Fybraworks Foods, Imagindairy Ltd, Eden Brew, Impossible Foods Inc, Melt & Marble, Motif Foodworks, Inc, Mycorena, Myco Technology, New Culture, Nourish Ingredients, Perfect Day Inc, Remilk Ltd, Shiru Inc, The Every Co., Triton Algae Innovations.
- Insights from this report would allow marketers and the management authorities of the companies to make informed decisions regarding their future product launches, type up-gradation, market expansion, and marketing tactics.
- The global precision fermentation market report caters to various stakeholders in this industry including investors, suppliers, product manufacturers, distributors, new entrants, and financial analysts.
Market Segmentation
- Ingredient:
- Whey & Casein Protein
- Egg White
- Collagen Protein
- Heme Protein
- Enzymes
- Others
- Microbe:
- Yeast
- Algae
- Fungi
- Bacteria
- Others
- Application:
- Meat & Seafood
- Dairy Alternatives
- Egg Alternatives
- Others
- Regional:
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- Company Profiles:
- Change Foods
- Geltor
- Helania Inc
- Formo
- FUMI Ingredients
- Fybraworks Foods
- Imagindairy Ltd
- Eden Brew
- Impossible Foods Inc
- Melt & Marble
- Motif Foodworks, Inc
- Mycorena
- Myco Technology
- New Culture
- Nourish Ingredients
- Perfect Day Inc
- Remilk Ltd
- Shiru Inc
- The Every Co.
- Triton Algae Innovations
Table of Contents
1. Research Objectives and Assumptions
- Research Objectives
- Assumptions
- Abbreviations
2. Market Purview
- Report Description
- Market Definition and Scope
- Executive Summary
- Market Snippet, By Ingredient
- Market Snippet, By Microbe
- Market Snippet, By Application
- Market Snippet, By Region
- Coherent Opportunity Map (COM)
3. Market Dynamics, Regulations, and Trends Analysis
- Market Dynamics
- Drivers
- Restraints
- PEST Analysis
- PORTER's Five Forces Analysis
- Market Opportunities
- Regulatory Scenario
- Key Developments
- Industry Trend
4. Global Precision Fermentation Market - Impact of Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pandemic
- Overview
- Factors Affecting Global Precision Fermentation Market - COVID-19
- Impact Analysis
5. Global Precision Fermentation Market, By Ingredient, 2020-2032 (US$ Bn)
- Introduction
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028, and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2020 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Whey & Casein Protein
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028, and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2020 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Egg White
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028, and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2020 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Collagen Protein
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028, and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2020 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Heme Protein
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028, and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2020 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Enzymes
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028, and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2020 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Others
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028, and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2020 - 2032
- Segment Trends
6. Global Precision Fermentation Market, By Microbe, 2020-2032 (US$ Bn)
- Introduction
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028, and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2020 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Yeast
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028, and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2020 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Algae
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028, and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2020 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Fungi
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028, and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2020 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Bacteria
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028, and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2020 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Others
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028, and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2020 - 2032
- Segment Trends
7. Global Precision Fermentation Market, By Application, 2020-2032 (US$ Bn)
- Introduction
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028, and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2020 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Meat & Seafood
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028, and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2020 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Dairy Alternatives
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028, and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2020 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Egg Alternatives
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028, and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2020 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Others
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028, and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2020 - 2032
- Segment Trends
8. Global Precision Fermentation Market, By Region, 2020-2032 (US$ Bn)
- Introduction
- Market Share Analysis, By Region, 2025, 2028, and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, For Region, 2020 - 2032
- North America
- Market Share Analysis, By Country, 2025, 2028 and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, For Region, 2020 - 2032
- Market Size and Forecast, By Ingredient, 2020- 2032 (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Microbe, 2020- 2032 (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Application, 2020- 2032 (US$ Bn)
- Countries
- U.S.
- Canada
- Latin America
- Market Share Analysis, By Country, 2025, 2028 and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, For Region, 2020 - 2032
- Market Size and Forecast, By Ingredient, 2020- 2032 (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Microbe, 2020- 2032 (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Application, 2020- 2032 (US$ Bn)
- Countries
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Europe
- Market Share Analysis, By Country, 2025, 2028 and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, For Region, 2020 - 2032
- Market Size and Forecast, By Ingredient, 2020- 2032 (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Microbe, 2020- 2032 (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Application, 2020- 2032 (US$ Bn)
- Countries
- U.K.
- Germany
- Italy
- France
- Spain
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Market Share Analysis, By Country, 2025, 2028 and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, For Region, 2020 - 2032
- Market Size and Forecast, By Ingredient, 2020- 2032 (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Microbe, 2020- 2032 (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Application, 2020- 2032 (US$ Bn)
- Countries
- China
- India
- Japan
- ASEAN
- Australia
- South Korea
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Market Share Analysis, By Country, 2025, 2028 and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, For Region, 2020 - 2032
- Market Size and Forecast, By Ingredient, 2020- 2032 (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Microbe, 2020- 2032 (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Application, 2020- 2032 (US$ Bn)
- Sub-regions/Countries
- GCC Countries
- Israel
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
9. Competitive Landscape
- Heat Map Analysis
- Market Share Analysis (3x3 Matrix)
- Company Profiles
- Change Foods
- Company Overview
- Ingredient Portfolio
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Geltor
- Company Overview
- Ingredient Portfolio
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Helania Inc
- Company Overview
- Ingredient Portfolio
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Formo
- Company Overview
- Ingredient Portfolio
- Recent Developments/Updates
- FUMI Ingredients
- Company Overview
- Ingredient Portfolio
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Fybraworks Foods
- Company Overview
- Ingredient Portfolio
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Imagindairy Ltd
- Company Overview
- Ingredient Portfolio
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Eden Brew
- Company Overview
- Ingredient Portfolio
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Impossible Foods Inc
- Company Overview
- Ingredient Portfolio
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Melt & Marble
- Company Overview
- Ingredient Portfolio
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Motif Foodworks, Inc
- Company Overview
- Ingredient Portfolio
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Mycorena
- Company Overview
- Ingredient Portfolio
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Myco Technology
- Company Overview
- Ingredient Portfolio
- Recent Developments/Updates
- New Culture
- Company Overview
- Ingredient Portfolio
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Nourish Ingredients
- Company Overview
- Ingredient Portfolio
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Perfect Day Inc
- Company Overview
- Ingredient Portfolio
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Remilk Ltd
- Company Overview
- Ingredient Portfolio
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Shiru Inc
- The Every Co.
- Triton Algae Innovations
- Change Foods
10. Analyst Recommendation
- Wheel of Fortune
- Analyst View
- Coherent Opportunity Map
11. Section
- References
- Research Methodology
- About Us and Sales Contact




