PUBLISHER: Coherent Market Insights | PRODUCT CODE: 1705952

PUBLISHER: Coherent Market Insights | PRODUCT CODE: 1705952
Nuclear Waste Management Market, By Waste Type, By Reactor Type, By Disposal Method, By Geography
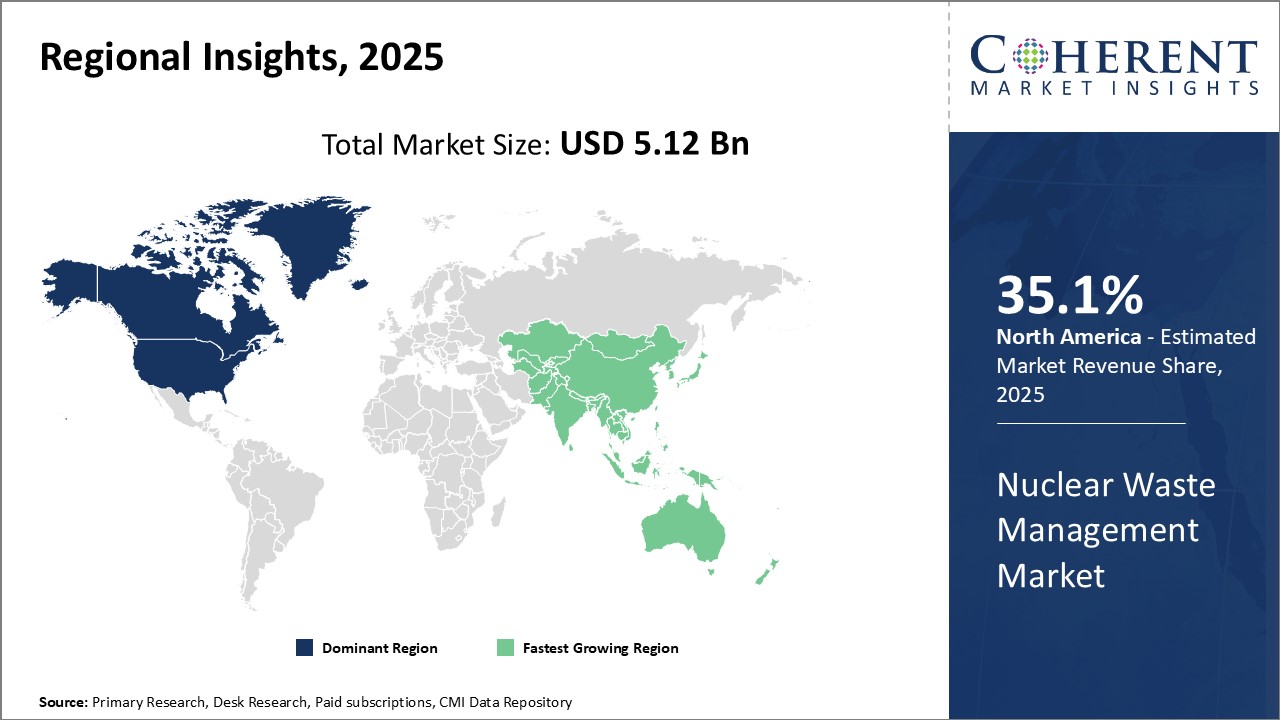
Global Nuclear Waste Management Market is estimated to be valued at USD 5.12 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 6.00 Bn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.3% from 2025 to 2032.
| Report Coverage | Report Details | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Base Year: | 2024 | Market Size in 2025: | USD 5.12 Bn |
| Historical Data for: | 2020 To 2024 | Forecast Period: | 2025 To 2032 |
| Forecast Period 2025 to 2032 CAGR: | 2.30% | 2032 Value Projection: | USD 6.00 Bn |
Nuclear waste management refers to the handling, treatment, and disposal of radioactive materials generated from nuclear power plants, research laboratories, medical usage, and other industrial activities. With the growing adoption of nuclear energy across the world as a viable alternative to fossil fuels, the volumes of nuclear waste being generated have increased substantially over the past few decades. Effective waste management through safe storage, transportation, and disposal has become an important issue to address concerns over potential radioactive contamination of the environment. Governments and nuclear regulatory bodies worldwide have framed stringent regulations and guidelines to ensure radioactive materials are isolated from the environment and human contact for the required amounts of time until they reduce to safe levels of radioactivity. Research is ongoing on methods to reduce the half-lives of radioactive isotopes and convert high-level waste into safer forms.
Market Dynamics:
One of the key drivers propelling the nuclear waste management market is the increasing volumes of spent fuel being generated from the steadily growing number of nuclear reactors. As of now, over 450 nuclear reactors are operating across 30 countries globally. Stricter regulations regarding the handling, treatment, and final disposal of nuclear waste have also boosted investments in relevant infrastructure and services. Technological advancements in areas such as optimized storage containers, encapsulation matrices for containers and underground geological repositories present lucrative growth opportunities. However, public opposition towards nuclear energy and final waste disposal sites pose significant challenges for market participants. High costs associated with construction of geological repositories and transportation logistics also restrict wider adoption. Ongoing R&D in areas of transmutation technology and partitioning-transmutation systems can help reduce volumes of long-lived radionuclides and create new prospects.
Key Features of the Study:
- This report provides in-depth analysis of the global nuclear waste management market, and provides market size (US$ Bn) and compound annual growth rate (CAGR%) for the forecast period (2025-2032), considering 2024 as the base year
- It elucidates potential revenue opportunities across different segments and explains attractive investment proposition matrices for this market
- This study also provides key insights about market drivers, restraints, opportunities, new product launches or approval, market trends, regional outlook, and competitive strategies adopted by key players
- It profiles key players in the global nuclear waste management market based on the following parameters - company highlights, products portfolio, key highlights, financial performance, and strategies
- Key companies covered as a part of this study include Veolia, Enercon, TUV SUD, Orano Group, SKB International, Fortum, US Ecology Inc., Posiva Oy, Stericycle Inc., John Wood Group PLC, Perma-Fix, Bechtel Corporation, Fluor Corporation, BHI Energy, Waste Control Specialists LLC, Augean PLC, Chase Environmental Group Inc., DMT, Holtec International, Westinghouse Electric Company LLC
- Insights from this report would allow marketers and the management authorities of the companies to make informed decisions regarding their future product launches, type up-gradation, market expansion, and marketing tactics
- The global nuclear waste management market report caters to various stakeholders in this industry including investors, suppliers, product manufacturers, distributors, new entrants, and financial analysts
- Stakeholders would have ease in decision-making through various strategy matrices used in analyzing the global nuclear waste management market.
Detailed Segmentation-
- By Waste Type:
- Low-Level Radioactive Waste
- Intermediate-Level Radioactive Waste
- High-Level Radioactive Waste
- By Reactor Type:
- Pressurized Water Reactor
- Boiling Water Reactor
- Gas Cooled Reactor
- Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor
- By Disposal Method:
- Incineration
- Storage
- Deep Geological Disposal
- Others
- By Region:
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- Company Profiles:
- Veolia
- Enercon
- TUV SUD
- Orano Group
- SKB International
- Fortum
- US Ecology Inc.
- Posiva Oy
- Stericycle Inc.
- John Wood Group PLC
- Perma-Fix
- Bechtel Corporation
- Fluor Corporation
- BHI Energy
- Waste Control Specialists LLC
- Augean PLC
- Chase Environmental Group Inc.
- DMT
- Holtec International
- Westinghouse Electric Company LLC
Table of Contents
1. Research Objectives and Assumptions
- Research Objectives
- Assumptions
- Abbreviations
2. Market Purview
- Report Description
- Market Definition and Scope
- Executive Summary
- Market Snippet, By Waste Type
- Market Snippet, By Reactor Type
- Market Snippet, By Disposal Method
- Market Snippet, By Region
- Coherent Opportunity Map (COM)
3. Market Dynamics, Regulations, and Trends Analysis
- Market Dynamics
- Drivers
- Restraints
- PEST Analysis
- PORTER's Five Forces Analysis
- Market Opportunities
- Regulatory Scenario
- Industry Trend
- Mergers and Acquisitions
4. Global Nuclear Waste Management Market - Impact of Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pandemic
- Overview
- Factors Affecting the Global Nuclear Waste Management Market
- Impact Analysis
5. Global Nuclear Waste Management Market, By Waste Type, 2020-2032, (US$ Bn)
- Introduction
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028 and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2021 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Low-Level Radioactive Waste
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Segment Trends
- Intermediate-Level Radioactive Waste
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Segment Trends
- High-Level Radioactive Waste
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Segment Trends
6. Global Nuclear Waste Management Market, By Reactor Type, 2020-2032, (US$ Bn)
- Introduction
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028 and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2021 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Pressurized Water Reactor
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Segment Trends
- Boiling Water Reactor
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Segment Trends
- Gas Cooled Reactor
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Segment Trends
- Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Segment Trends
7. Global Nuclear Waste Management Market, By Disposal Method, 2020-2032, (US$ Bn)
- Introduction
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028 and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2021 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Incineration
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Segment Trends
- Storage
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Segment Trends
- Deep Geological Disposal
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Segment Trends
- Others
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Segment Trends
8. Global Nuclear Waste Management Market, By Region, 2020-2032, (US$ Bn)
- Introduction
- Market Share Analysis, By Region, 2025, 2028 and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, For Region, 2021-2032
- North America
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, By Waste Type, 2021 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Reactor Type, 2021 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Disposal Method, 2021 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Country, 2021 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- U.S.
- Canada
- Latin America
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, By Waste Type, 2021 - 2032, (US$ Bn))
- Market Size and Forecast, By Reactor Type, 2021 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Disposal Method, 2021 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Country, 2021 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Europe
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, By Waste Type, 2021 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Reactor Type, 2021 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Disposal Method, 2021 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Country, 2021 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- U.K.
- Germany
- Italy
- France
- Spain
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, By Waste Type, 2021 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Reactor Type, 2021 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Disposal Method, 2021 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Country, 2021 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- China
- India
- Japan
- ASEAN
- Australia
- South Korea
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, By Waste Type, 2021 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Reactor Type, 2020 - 2032 (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Disposal Method, 2021 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, By Country, 2021 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- GCC Countries
- Israel
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
9. Competitive Landscape
- Market Share Analysis
- Company Profiles
- Veolia
- Company Overview
- Waste Type Portfolio
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Enercon
- TUV SUD
- Orano Group
- SKB International
- Fortum
- US Ecology Inc.
- Posiva Oy
- Stericycle Inc.
- John Wood Group PLC
- Perma-Fix
- Bechtel Corporation
- Fluor Corporation
- BHI Energy
- Waste Control Specialists LLC
- Augean PLC
- Chase Environmental Group Inc.
- DMT
- Holtec International
- Westinghouse Electric Company LLC
- Veolia
10. Analyst Recommendations
- Wheel of Fortune
- Analyst View
- Coherent Opportunity Map
11. Section
- References
- Research Methodology
- About Us and Sales Contact




