PUBLISHER: Coherent Market Insights | PRODUCT CODE: 1699576

PUBLISHER: Coherent Market Insights | PRODUCT CODE: 1699576
Global Ethylene Market, By Feedstock (Naphtha, Ethane, Butane, Propane, Coal), By Derivative (Polyethylene, Ethylene Oxide, Ethylene Dichloride), By Geography (North America, Latin America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa)
Global Ethylene Market is estimated to be valued at USD 220.36 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 329.16 Bn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.9% from 2025 to 2032.
| Report Coverage | Report Details | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Base Year: | 2024 | Market Size in 2025: | USD 220.36 Bn |
| Historical Data for: | 2020 To 2024 | Forecast Period: | 2025 To 2032 |
| Forecast Period 2025 to 2032 CAGR: | 5.90% | 2032 Value Projection: | USD 329.16 Bn |
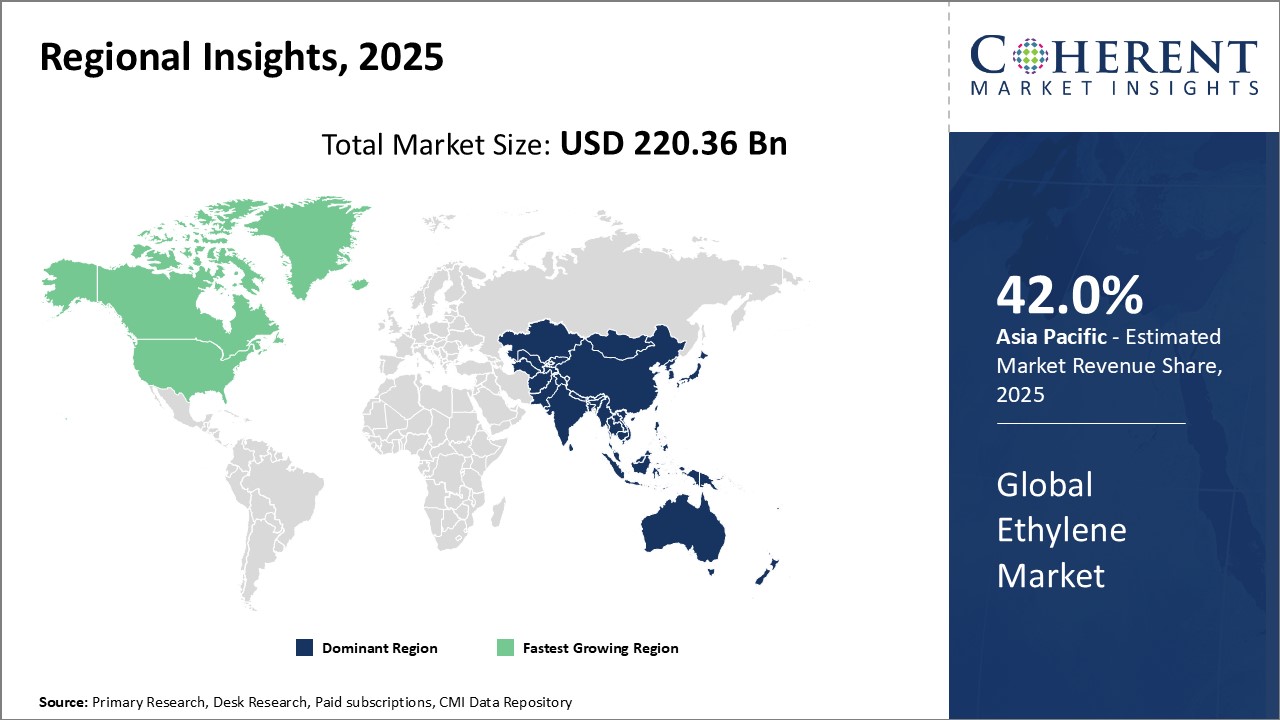
Ethylene is an important basic petrochemical product and building block primarily used in the production of polyethylene. The growing demand for polyethylene from end-use industries, such as packaging, construction, automotive, and electrical and electronics, has been a key driver of the global ethylene market. According to recent projections, the polyethylene demand alone is expected to increase by over 5% per year through 2030. With limited substitutes available, rising polyethylene consumption directly correlates to increased ethylene production. Ethylene is the lightest olefinic hydrocarbon or organic hydrocarbon, and it is the basic raw material generally derived from various hydrocarbons which are largely used in the manufacturing of polymers such as fibers, polymer plastics, and other organic chemicals. Naphtha and ethane are the major feedstock used to produce ethylene globally. The other feedstock used in manufacturing ethylene are butane, propane, coal, methanol to olefins (MTO), and gas oil.
Market Dynamics:
The global ethylene market is driven by the robust demand from polyethylene manufacturers. Expanding applications of polyethylene in the packaging, consumer goods, and construction sectors continue to support market volume gains. However, fluctuating feedstock prices present a challenge as ethylene production is heavily reliant on crude oil and natural gas liquids. Volatility in energy markets can squeeze producer margins. Additionally, stringent environmental regulations regarding volatile organic compound (VOC) and hazardous emissions constrain capacity expansion plans. On the positive side, ongoing capacity ramp-ups in key manufacturing hubs, such as the U.S., provide new opportunities for market participants. Furthermore, the development of more efficient production technologies helps reduce costs and greenhouse gas emissions.
Key Features of the Study:
- This report provides an in-depth analysis of the global ethylene market, and provides market size (US$ Bn) and compound annual growth rate (CAGR%) for the forecast period (2025-2032), considering 2024 as the base year.
- It elucidates potential revenue growth opportunities across different segments and explains attractive investment proposition matrices for this market.
- This study also provides key insights about market drivers, restraints, opportunities, new product launches or approvals, market trends, regional outlook, and competitive strategies adopted by key players.
- It profiles key players in the global ethylene market based on the following parameters - company highlights, products portfolio, key highlights, financial performance, and strategies.
- Key companies covered as a part of this study include Saudi Basic Industries Corporation (SABIC), Exxon Mobil Corporation, The Dow Chemical Company, Royal Dutch Shell plc, China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation (Sinopec Corporation), Chevron Phillips Chemical Company LLC, LyondellBasell Industries, National Petrochemical Company (NPC), and INEOS Group AG.
- Insights from this report would allow marketers and the management authorities of the companies to make informed decisions regarding their future product launches, type up-gradation, market expansion, and marketing tactics.
- The global ethylene market report caters to various stakeholders in this industry including investors, suppliers, product manufacturers, distributors, new entrants, and financial analysts.
- Stakeholders would have ease in decision-making through various strategy matrices used in analyzing the global ethylene market.
Detailed Segmentation:
- By Feedstock
- Naphtha
- Ethane
- Butane
- Propane
- Coal
- By Derivative
- Polyethylene
- Ethylene Oxide
- Ethylene Dichloride
- By Region
- North America
- Latin America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Company Profiles
- Saudi Basic Industries Corporation (SABIC)
- Exxon Mobil Corporation
- The Dow Chemical Company
- Royal Dutch Shell plc
- China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation (Sinopec Corporation)
- Chevron Phillips Chemical Company LLC
- LyondellBasell Industries
- National Petrochemical Company (NPC)
- INEOS Group AG.
Table of Contents
1. Research Objectives and Assumptions
- Research Objectives
- Assumptions
- Abbreviations
2. Market Purview
- Report Description
- Market Definition and Scope
- Executive Summary
- Global Ethylene Market, By Feedstock
- Global Ethylene Market, By Derivative
- Global Ethylene Market, By Region
- Coherent Opportunity Map (COM)
3. Market Dynamics, Regulations, and Trends Analysis
- Market Dynamics
- Drivers
- Growing demand for renewable ethylene
- Restraints
- Fluctuations in crude oil prices
- Opportunities
- Growing demand from emerging economies
- Key Highlights
- Regulatory Scenario
- Recent Trends
- Product Launches/Approvals
- PEST Analysis
- PORTER's Analysis
- Mergers, Acquisitions, and Collaborations
4. Global Ethylene Market - Impact of Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pandemic
- COVID-19 Epidemiology
- Supply Side and Demand Side Analysis
- Economic Impact
5. Global Ethylene Market, By Feedstock, 2020-2032, (US$ Bn)
- Introduction
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028, and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2020 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Naphtha
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Ethane
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Butane
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Propane
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Coal
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
6. Global Ethylene Market, By Derivative, 2020 - 2032 (US$ Bn)
- Introduction
- Market Share Analysis, 2025, 2028, and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2020 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Polyethylene
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Ethylene Oxide
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Ethylene Dichloride
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020 - 2032, (US$ Bn)
7. Global Ethylene Market, By Region, 2020-2032, (US$ Bn)
- Introduction
- Market Share Analysis, By Region, 2025 and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, For Region, 2020 - 2032
- Region Trends
- North America
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Feedstock, 2020-2032,(US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Derivative, 2020-2032, (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Country, 2020-2032, (US$ Bn)
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Feedstock, 2020-2032,(US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Derivative, 2020-2032, (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Country, 2020-2032, (US$ Bn)
- Germany
- U.K.
- Spain
- France
- Italy
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Feedstock, 2020-2032,(US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Derivative, 2020-2032, (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Country, 2020-2032, (US$ Bn)
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia
- South Korea
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Feedstock, 2020-2032,(US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Derivative, 2020-2032, (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Country, 2020-2032, (US$ Bn)
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Feedstock, 2020-2032,(US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Derivative, 2020-2032, (US$ Bn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Country, 2020-2032, (US$ Bn)
- GCC Countries
- Israel
- Rest of Middle East
- South Africa
- Central Africa
- North Africa
8. Competitive Landscape
- Company Profile
- Saudi Basic Industries Corporation (SABIC)
- Company Overview
- Product Portfolio
- Financial Performance
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Future Plans
- Exxon Mobil Corporation
- Company Overview
- Product Portfolio
- Financial Performance
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Future Plans
- The Dow Chemical Company
- Company Overview
- Product Portfolio
- Financial Performance
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Future Plans
- Royal Dutch Shell plc
- Company Overview
- Product Portfolio
- Financial Performance
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Future Plans
- China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation (Sinopec Corporation)
- Company Overview
- Product Portfolio
- Financial Performance
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Future Plans
- Chevron Phillips Chemical Company LLC.
- Company Overview
- Product Portfolio
- Financial Performance
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Future Plans
- LyondellBasell Industries
- Company Overview
- Product Portfolio
- Financial Performance
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Future Plans
- National Petrochemical Company (NPC)
- Company Overview
- Product Portfolio
- Financial Performance
- Recent Developments/Updates
- Future Plans
- INEOS Group AG.
- Analyst Views
9. Section
- References
- Research Methodology
- About us




