PUBLISHER: Coherent Market Insights | PRODUCT CODE: 1705991

PUBLISHER: Coherent Market Insights | PRODUCT CODE: 1705991
Parenteral Nutrition Market, By Nutrition Type, By Patient Type, By Application, By Distribution Channel, By Geography
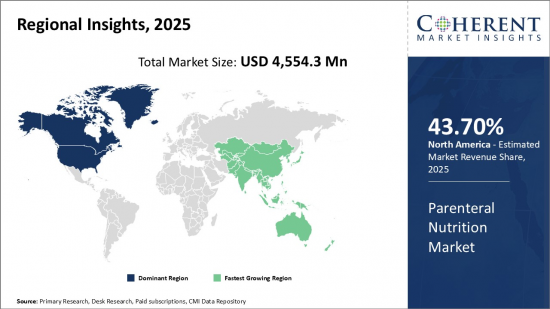
Global Parenteral Nutrition Market is estimated to be valued at USD 4,554.3 Mn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 6,939. Mn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% from 2025 to 2032.
| Report Coverage | Report Details | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Base Year: | 2024 | Market Size in 2025: | USD 4,554.3 Mn |
| Historical Data for: | 2020 To 2024 | Forecast Period: | 2025 To 2032 |
| Forecast Period 2025 to 2032 CAGR: | 6.20% | 2032 Value Projection: | USD 6,939. Mn |
Parenteral nutrition, often called total parenteral nutrition, is the medical term for infusing a specialized form of food through a vein (intravenously). The goal of the treatment is to correct or prevent malnutrition. Parenteral nutrition provides liquid nutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals and electrolytes. Some people use parenteral nutrition to supplement feeding through a tube placed into the stomach or small bowel (enteral nutrition), and others use it by itself. People whose digestive systems either can't absorb or can't tolerate adequate food eaten by mouth use parenteral nutrition. When used outside the hospital, intravenous feeding is called home parenteral nutrition. Using home parenteral nutrition may be necessary for weeks or months, or in some cases for life. Catheter infection is a common and serious complication of parenteral nutrition. Other potential short-term complications of parenteral nutrition include blood clots, fluid and mineral imbalances, and problems with blood sugar metabolism.
Market Dynamics:
The global parenteral nutrition market has been witnessing significant growth in the recent past owing to the rising prevalence of chronic diseases inducing malnutrition. Parenteral nutrition entails delivering nutrients directly into the bloodstream through an intravenous catheter when oral or enteral routes are not feasible. It finds wide application in treating malnourished patients suffering from cancer, gastrointestinal disorders, liver diseases, and other chronic conditions. Furthermore, the growing geriatric population who are more susceptible to malnutrition due to weak digestive system has also contributed to the rising demand for parenteral formulations. Various market players are engaged in developing innovative parenteral nutrition solutions to meet the treatment demands of such patient groups. However, high costs associated with parenteral feeding remains a major challenge for widespread adoption.
Key features of the study:
- This report provides an in-depth analysis of the global parenteral nutrition market and provides market size (US$ Mn) and compound annual growth rate (CAGR %) for the forecast period (2025-2032), considering 2024 as the base year
- It elucidates potential revenue opportunities across different segments and explains attractive investment proposition matrices for this market.
- This study also provides key insights about market drivers, restraints, opportunities, new product launches or approval, market trends, regional outlook, and competitive strategies adopted by key players.
- It profiles key players in the global parenteral nutrition market based on the following parameters - company highlights, products portfolio, key highlights, financial performance, and strategies.
- Key companies covered as a part of this study include global parenteral nutrition market include AbbVie Inc., Danone, Fresenius Kabi AG, GENTAG, Inc., GSK plc., Nestle SA, Nutricia, Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd, Pfizer Inc., Sanofi, Otsuka Holdings Co., Ltd., and Otsuka Holdings Co., Ltd.
- Insights from this report would allow marketers and the management authorities of the companies to make informed decisions regarding their future product launches, type up-gradation, market expansion, and marketing tactics.
- The global parenteral nutrition market report caters to various stakeholders in this industry including investors, suppliers, product manufacturers, distributors, new entrants, and financial analysts.
- Stakeholders would have ease in decision-making through various strategy matrices used in analyzing the global parenteral nutrition market.
Detailed Segmentation:
- Global Parenteral Nutrition Market, By Nutrition Type
- Carbohydrates
- Lipid Emulsion
- Vitamins and Trace Minerals
- Proteins
- Others (Amino acids, etc.)
- Global Parenteral Nutrition Market, By Patient Type
- Infants
- Adults
- Geriatric
- Global Parenteral Nutrition Market, By Application
- Diabetes
- Renal Failures
- Obesity
- Sarcopenia
- Cancer
- Others (Digestive disorders, Metabolic Syndromes, etc.)
- Global Parenteral Nutrition Market, By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
- Global Parenteral Nutrition Market, By Region
- North America
- Latin America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- Africa
- Company Profiles
- AbbVie Inc.
- Danone
- Fresenius Kabi AG
- GENTAG, Inc.
- GSK plc.
- Nestle SA
- Nutricia
- Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- Pfizer Inc.
- Sanofi
- VIRIDIAN SA
Table of Contents
1. Research Objectives and Assumptions
- Research Objectives
- Assumptions
- Abbreviations
2. Market Purview
- Report Description
- Market Definition and Scope
- Executive Summary
- Market Snippet, By Nutrition Type
- Market Snippet, By Patient Type
- Market Snippet, By Application
- Market Snippet, By Distribution Channel
- Market Snippet, By Region
- Coherent Opportunity Map (COM)
3. Market Dynamics, Regulations, and Trends Analysis
- Market Dynamics
- Increasing collaborations by key market players
- Lack of awareness regarding healthcare, diet, and proper nutrition
- Emergence of enhanced parenteral nutrition solutions
- Key Highlights
- Regulatory Scenario
- Market Trends
- Product Launch/Approval
- PEST Analysis
- PORTER's Analysis
- Epidemiology
- New Investments by Major Market Players
- Pricing Analysis
- Mergers, Acquisitions, and Collaborations
4. Global Parenteral Nutrition Market - Impact of Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pandemic
- COVID-19 Epidemiology
- Supply Side and Demand Side Analysis
- Economic Impact
5. Global Parenteral Nutrition Market, By Nutrition Type, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Introduction
- Market Share Analysis, 2025 and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2021 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Carbohydrates
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Lipid Emulsion
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Vitamins and Trace Minerals
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Proteins
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Others (Amino acids, etc.)
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
6. Global Parenteral Nutrition Market, By Patient Type, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Introduction
- Market Share Analysis, 2025 and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2021 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Infants
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Adults
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Geriatric
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
7. Global Parenteral Nutrition Market, By Application, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Introduction
- Market Share Analysis, 2025 and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2021 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Diabetes
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Renal Failures
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Sarcopenia
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Cancer
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Others (Digestive disorders, Metabolic Syndromes, etc.)
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
8. Global Parenteral Nutrition Market, By Distribution Channel, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Introduction
- Market Share Analysis, 2025 and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, 2021 - 2032
- Segment Trends
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Retail Pharmacies
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Online Pharmacies
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
9. Global Parenteral Nutrition Market, By Region, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Introduction
- Market Share Analysis, By Region, 2025 and 2032 (%)
- Y-o-Y Growth Analysis, For Region, 2021 -2032
- Country Trends
- North America
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Nutrition Type, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Patient Type, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Application, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Distribution Channel, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Country, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Nutrition Type, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Patient Type, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Application, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Distribution Channel, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Country, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Germany
- U.K.
- Spain
- France
- Italy
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Nutrition Type, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Patient Type, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Application, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Distribution Channel, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Country, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia
- South Korea
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Nutrition Type, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Patient Type, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Application, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Distribution Channel, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Country, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Nutrition Type, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Patient Type, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Application, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Distribution Channel, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Country, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- GCC Countries
- Israel
- Rest of Middle East
- Africa
- Introduction
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Nutrition Type, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Patient Type, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Application, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Distribution Channel, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- Market Size and Forecast, and Y-o-Y Growth, By Country/Region, 2020-2032, (US$ Mn)
- North Africa
- Central Africa
- South Africa
10. Competitive Landscape
- Company Profile
- AbbVie Inc.
- Company Highlights
- Product Portfolio
- Key Highlights
- Financial Performance
- Strategies
- Danone
- Company Highlights
- Product Portfolio
- Key Highlights
- Financial Performance
- Strategies
- Fresenius Kabi AG
- Company Highlights
- Product Portfolio
- Key Highlights
- Financial Performance
- Strategies
- GENTAG, Inc.
- Company Highlights
- Product Portfolio
- Key Highlights
- Financial Performance
- Strategies
- GSK plc.
- Nestle SA
- Nutricia
- Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- Pfizer Inc.
- Sanofi
- VIRIDIAN SA
- Analyst Views
11. Section
- References
- Research Methodology
- About us




