PUBLISHER: Aviation & Defense Market Reports (A&D) | PRODUCT CODE: 1896742

PUBLISHER: Aviation & Defense Market Reports (A&D) | PRODUCT CODE: 1896742
Global Electromagnetic Weapons Market 2026-2036
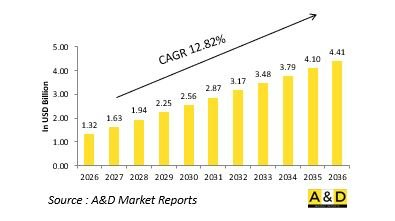
The Global Electromagnetic Weapons market is estimated at USD 1.32 billion in 2026, projected to grow to USD 4.41 billion by 2036 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 12.82% over the forecast period 2026-2036.
Introduction to Electromagnetic Weapons Market:
The defense electromagnetic weapons market represents a transformative shift in modern warfare, focusing on systems that use electromagnetic energy to disable, damage, or destroy enemy targets without relying on conventional explosives. These weapons operate through mechanisms such as high-powered microwaves, electromagnetic pulses, and railguns, offering rapid engagement, deep magazine capacity, and reduced logistical constraints. Their ability to neutralize electronics, communication systems, and guided munitions makes them particularly valuable in electronic warfare and counter-drone operations. As militaries seek more efficient, precise, and cost-effective deterrence tools, electromagnetic weapons are emerging as a key component of next-generation defense strategies. They provide a non-kinetic, scalable means of targeting that aligns with the growing focus on minimizing collateral damage while maintaining decisive tactical superiority in increasingly electronic and data-centric battlefields.
Technology Impact in Electromagnetic Weapons Market:
Technological advancements are redefining the potential and practicality of electromagnetic weapons. Breakthroughs in pulsed power systems, superconducting materials, and compact energy storage have significantly improved energy density and weapon efficiency. These innovations allow electromagnetic systems to deliver high levels of directed energy with increased precision and reduced size. The integration of advanced targeting algorithms, artificial intelligence, and adaptive control systems enhances weapon responsiveness against fast-moving or stealth targets. Improvements in cooling systems and energy recovery have further enabled sustained operation and mobility across land, sea, and air platforms. Additionally, advancements in electromagnetic shielding and hardening are driving parallel innovation in countermeasure technologies. Overall, the synergy of power electronics, materials science, and AI-driven control has accelerated the transition of electromagnetic weapons from conceptual prototypes to deployable battlefield assets.
Key Drivers in Electromagnetic Weapons Market:
The growing need for rapid, cost-effective, and precise engagement capabilities is a major driver of the defense electromagnetic weapons market. As modern warfare becomes increasingly electronic, the ability to disable enemy systems without physical destruction offers strategic advantages. Rising concerns over drone swarms, missile saturation attacks, and electronic interference have intensified the demand for electromagnetic solutions capable of neutralizing multiple threats simultaneously. The global focus on energy-based weapon systems stems from their low cost per shot, reduced logistical burden, and near-instantaneous strike potential. Defense modernization programs are prioritizing directed-energy technologies to enhance both offensive and defensive capabilities. Additionally, the push for greater survivability and adaptability in contested environments drives research into portable, scalable electromagnetic systems. These factors collectively position electromagnetic weapons as a cornerstone of future combat operations, complementing conventional kinetic arsenals.
Regional Trends in Electromagnetic Weapons Market:
Regional dynamics in the defense electromagnetic weapons market are shaped by differing strategic priorities, research capabilities, and threat landscapes. North America leads in development and testing, supported by strong defense research institutions and large-scale energy weapon programs. Europe focuses on integrating electromagnetic technologies into naval and air defense applications, emphasizing interoperability and sustainability. In the Asia-Pacific region, rising geopolitical tensions and modernization efforts are driving indigenous research into compact and mobile electromagnetic solutions. The Middle East is increasingly exploring directed-energy systems for counter-drone and border defense roles, seeking to strengthen asymmetric deterrence. Latin America and Africa are engaging through defense collaborations and technology partnerships to explore future adoption. Across all regions, the emphasis is shifting toward deployable, multi-platform electromagnetic weapons that can complement traditional defense systems while addressing evolving threats in electronic and cyber warfare domains.
Key Defense Electromagnetic Weapons Program:
Leidos has received a $38 million contract from the U.S. Air Force to advance electromagnetic weapons development. Under the IDIQ agreement awarded by the Air Force Research Laboratory, the company will focus on developing next-generation High Power Electromagnetic (HPEM) sources and components, as stated in the Department of Defense announcement. HPEM technologies have applications across multiple defense domains, including directed-energy weapons, counter-IED systems, and electronic warfare.
Table of Contents
Electromagnetic Weapons Market - Table of Contents
Electromagnetic Weapons Market Report Definition
Electromagnetic Weapons Market Segmentation
By Range
By Region
By End User
Electromagnetic Weapons Market Analysis for next 10 Years
The 10-year Electromagnetic Weapons Market analysis would give a detailed overview of Electromagnetic Weapons Market growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
Market Technologies of Electromagnetic Weapons Market
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
Global Electromagnetic Weapons Market Forecast
The 10-year Electromagnetic Weapons Market forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
Regional Electromagnetic Weapons Market Trends & Forecast
The regional Electromagnetic Weapons Market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
Country Analysis of Electromagnetic Weapons Market
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
Opportunity Matrix for Electromagnetic Weapons Market
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Expert Opinions on Electromagnetic Weapons Market Report
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.
Conclusions
About Aviation and Defense Market Reports
List of Tables
- Table 1: 10 Year Market Outlook, 2025-2035
- Table 2: Drivers, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 3: Restraints, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 4: Challenges, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 5: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 6: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 7: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 8: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 9: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 10: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 11: Drivers, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 12: Restraints, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 13: Challenges, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 14: Drivers, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 15: Restraints, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 16: Challenges, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 17: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Region, 2025-2035
- Table 18: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Product, 2025-2035
- Table 19: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By End User, 2025-2035
- Table 20: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Region, 2025-2035
- Table 21: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Product, 2025-2035
- Table 22: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By End User, 2025-2035
List of Figures
- Figure 1: Global Electromagnetic Weapons Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 2: Global Electromagnetic Weapons Market Forecast, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 3: Global Electromagnetic Weapons Market Forecast, By Product, 2025-2035
- Figure 4: Global Electromagnetic Weapons Market Forecast, By End User, 2025-2035
- Figure 5: North America, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 6: Europe, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 7: Middle East, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 8: APAC, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 9: South America, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 10: United States, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 11: United States, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 12: Canada, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 13: Canada, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 14: Italy, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 15: Italy, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 16: France, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 17: France, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 18: Germany, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 19: Germany, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 20: Netherlands, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 21: Netherlands, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 22: Belgium, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 23: Belgium, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 24: Spain, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 25: Spain, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 26: Sweden, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 27: Sweden, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 28: Brazil, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 29: Brazil, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 30: Australia, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 31: Australia, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 32: India, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 33: India, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 34: China, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 35: China, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 36: Saudi Arabia, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 37: Saudi Arabia, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 38: South Korea, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 39: South Korea, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 40: Japan, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 41: Japan, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 42: Malaysia, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 43: Malaysia, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 44: Singapore, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 45: Singapore, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 46: United Kingdom, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 47: United Kingdom, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 48: Opportunity Analysis, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, By Region (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 49: Opportunity Analysis, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, By Region (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 50: Opportunity Analysis, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, By Product (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 51: Opportunity Analysis, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, By Product (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 52: Opportunity Analysis, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, By End User (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 53: Opportunity Analysis, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, By End User (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 54: Scenario Analysis, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Cumulative Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 55: Scenario Analysis, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Global Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 56: Scenario 1, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Total Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 57: Scenario 1, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 58: Scenario 1, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, By Product, 2025-2035
- Figure 59: Scenario 1, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, By End User, 2025-2035
- Figure 60: Scenario 2, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, Total Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 61: Scenario 2, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 62: Scenario 2, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, By Product, 2025-2035
- Figure 63: Scenario 2, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, By End User, 2025-2035
- Figure 64: Company Benchmark, Electromagnetic Weapons Market, 2025-2035




