PUBLISHER: Aviation & Defense Market Reports (A&D) | PRODUCT CODE: 1858534

PUBLISHER: Aviation & Defense Market Reports (A&D) | PRODUCT CODE: 1858534
Global Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market 2025-2035
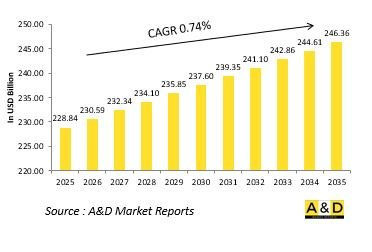
The Global Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles market is estimated at USD 228.84 billion in 2025, projected to grow to USD 246.36 billion by 2035 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 0.74% over the forecast period 2025-2035.
Introduction to Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market:
The defense Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBM) market represents the core of strategic deterrence capabilities, underpinning global security architectures and military balance among major powers. ICBMs are long-range delivery systems capable of carrying conventional or nuclear warheads, designed to ensure credible retaliation and deterrence in the event of aggression. Their speed, reach, and precision make them critical elements of national defense strategies and nuclear triads. The market is characterized by ongoing modernization efforts aimed at improving reliability, accuracy, and survivability against emerging missile defense systems. As nations focus on maintaining credible deterrent postures, investments in advanced propulsion, guidance, and reentry vehicle technologies are accelerating. The development of mobile launch platforms and hardened silos further strengthens strategic readiness. Overall, the ICBM market remains a cornerstone of global defense strategy, balancing power projection with deterrence stability.
Technology Impact in Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market:
Technological advancements have profoundly shaped the capabilities and effectiveness of intercontinental ballistic missiles. Improvements in propulsion systems, particularly solid-fuel technology, have enabled faster launch readiness and longer operational life. Enhanced guidance and navigation systems, integrating inertial navigation, satellite-based correction, and AI-assisted trajectory optimization, have greatly improved targeting precision. Developments in reentry vehicle technology, including multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), allow a single missile to strike multiple targets simultaneously. Stealth coatings, decoys, and maneuverable warheads are being introduced to overcome advanced missile defense systems. Digital command and control integration ensures secure and rapid communication between strategic units and national defense networks. Furthermore, modernization programs increasingly incorporate cyber-resilient architectures to safeguard against electronic interference. Collectively, these innovations are transforming ICBMs into more accurate, survivable, and strategically flexible deterrent systems.
Key Drivers in Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market:
The key forces driving the ICBM market stem from evolving security threats, strategic deterrence needs, and modernization imperatives. Rising geopolitical tensions and renewed emphasis on nuclear deterrence have led major powers to enhance or expand their missile arsenals. The need to maintain second-strike capability and ensure credible deterrence against adversaries with comparable strategic assets fuels continuous technological advancement. Upgrading aging missile systems to enhance reliability and counter modern missile defense networks is another major driver. Defense organizations are also prioritizing mobile and concealed launch platforms to enhance survivability and operational flexibility. The integration of digital technologies and automation in launch systems improves readiness and reduces human error. Collectively, these factors are reinforcing the role of ICBMs as essential components of strategic defense postures and deterrence frameworks.
Regional Trends in Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market:
Regional developments in the ICBM market reflect distinct strategic ambitions and defense doctrines. In North America, modernization programs emphasize enhanced accuracy, secure communication, and life extension of existing missile systems. European defense strategies remain closely tied to alliance-based deterrence frameworks, focusing on integration with broader strategic defense networks. The Asia-Pacific region is witnessing increased activity as regional powers develop or upgrade their ICBM capabilities to bolster strategic autonomy and counterbalance rival nations. In the Middle East, interest in long-range missile technology is growing, though development remains limited due to geopolitical and regulatory constraints. Emerging defense industries in other regions are monitoring advancements for potential collaboration or technology transfer opportunities. Across all regions, ICBM programs continue to symbolize technological strength and strategic independence, reinforcing national defense and global power dynamics.
Key Defense Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Program:
The land-based component of the U.S. nuclear triad currently consists of 400 deployed Minuteman III Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs) housed in underground silos located across Montana, North Dakota, Wyoming, Nebraska, and Colorado, and operated from the Malmstrom, Minot, and Warren Air Force Bases. Each missile is equipped with a single nuclear warhead - either the W87 or W78 - though in theory, each could accommodate two or three warheads.
The U.S. Air Force concluded a $7 billion modernization effort that spanned several decades, extending the operational life of the Minuteman III fleet through at least 2030. Following the upgrades, the Air Force described the renewed missiles as "essentially new systems, apart from the outer shell."
Table of Contents
Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market - Table of Contents
Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market Report Definition
Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market Segmentation
By Region
By Propulsion
By Range
Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market Analysis for next 10 Years
The 10-year Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market analysis would give a detailed overview of Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
Market Technologies of Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
Global Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market Forecast
The 10-year Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
Regional Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market Trends & Forecast
The regional Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
Country Analysis of Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
Opportunity Matrix for Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Expert Opinions on Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market Report
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.
Conclusions
About Aviation and Defense Market Reports
List of Tables
- Table 1: 10 Year Market Outlook, 2025-2035
- Table 2: Drivers, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 3: Restraints, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 4: Challenges, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 5: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 6: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 7: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 8: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 9: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 10: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 11: Drivers, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 12: Restraints, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 13: Challenges, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 14: Drivers, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 15: Restraints, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 16: Challenges, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 17: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Region, 2025-2035
- Table 18: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Propulsion, 2025-2035
- Table 19: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Range, 2025-2035
- Table 20: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Region, 2025-2035
- Table 21: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Propulsion, 2025-2035
- Table 22: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Range, 2025-2035
List of Figures
- Figure 1: Global Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 2: Global Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market Forecast, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 3: Global Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market Forecast, By Propulsion, 2025-2035
- Figure 4: Global Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market Forecast, By Range, 2025-2035
- Figure 5: North America, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 6: Europe, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 7: Middle East, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 8: APAC, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 9: South America, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 10: United States, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 11: United States, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 12: Canada, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 13: Canada, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 14: Italy, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 15: Italy, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 16: France, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 17: France, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 18: Germany, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 19: Germany, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 20: Netherlands, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 21: Netherlands, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 22: Belgium, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 23: Belgium, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 24: Spain, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 25: Spain, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 26: Sweden, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 27: Sweden, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 28: Brazil, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 29: Brazil, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 30: Australia, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 31: Australia, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 32: India, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 33: India, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 34: China, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 35: China, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 36: Saudi Arabia, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 37: Saudi Arabia, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 38: South Korea, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 39: South Korea, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 40: Japan, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 41: Japan, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 42: Malaysia, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 43: Malaysia, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 44: Singapore, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 45: Singapore, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 46: United Kingdom, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 47: United Kingdom, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 48: Opportunity Analysis, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, By Region (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 49: Opportunity Analysis, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, By Region (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 50: Opportunity Analysis, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, By Propulsion (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 51: Opportunity Analysis, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, By Propulsion (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 52: Opportunity Analysis, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, By Range (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 53: Opportunity Analysis, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, By Range (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 54: Scenario Analysis, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Cumulative Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 55: Scenario Analysis, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Global Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 56: Scenario 1, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Total Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 57: Scenario 1, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 58: Scenario 1, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, By Propulsion, 2025-2035
- Figure 59: Scenario 1, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, By Range, 2025-2035
- Figure 60: Scenario 2, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, Total Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 61: Scenario 2, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 62: Scenario 2, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, By Propulsion, 2025-2035
- Figure 63: Scenario 2, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, By Range, 2025-2035
- Figure 64: Company Benchmark, Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market, 2025-2035




