PUBLISHER: Aviation & Defense Market Reports (A&D) | PRODUCT CODE: 1927668

PUBLISHER: Aviation & Defense Market Reports (A&D) | PRODUCT CODE: 1927668
Global Close In Weapon System (CIWS) Market 2026-2036
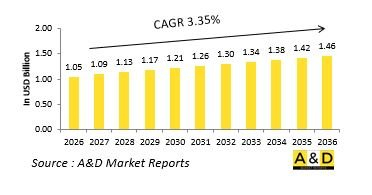
The Global Close in Weapon System market is estimated at USD 1.05 billion in 2026, projected to grow to USD 1.46 billion by 2036 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 3.35% over the forecast period 2026-2036.
Introduction to Global Close In Weapon System (CIWS)
Close In Weapon Systems are defensive platforms designed to detect, track, and neutralize short-range threats such as missiles, aircraft, and small surface targets, protecting naval vessels from imminent attacks. CIWS integrate rapid-fire guns or missile interceptors with advanced radar and tracking systems to provide automated, immediate response against fast-moving threats. These systems serve as the final protective layer in layered defense architectures, complementing long-range missile systems and shipboard countermeasures. Modern CIWS platforms emphasize speed, accuracy, and automation, allowing minimal human intervention while ensuring high engagement success rates. Integration with ship combat management systems facilitates coordinated defense and optimized target prioritization. Technological developments in radar, sensor fusion, projectile design, and fire control algorithms have enhanced reaction time, targeting precision, and survivability. Nations invest in CIWS to strengthen naval defense against asymmetric threats, including anti-ship missiles, small boats, and low-flying aircraft. Continuous upgrades, modular configurations, and interoperability with broader naval networks ensure operational readiness. CIWS platforms are integral to modern naval strategy, providing reliable last-line defense, protecting critical assets, and maintaining maritime operational security against diverse short-range threats.
Technology Impact in Global Close In Weapon System (CIWS)
Technological innovation has significantly improved the capabilities of CIWS, enhancing accuracy, reaction speed, and defensive effectiveness. Radar and optical sensors provide rapid threat detection and tracking, while advanced fire control algorithms prioritize targets and optimize engagement. High-rate-of-fire guns and missile interceptors enable timely neutralization of incoming threats. Automation reduces operator workload and ensures consistent performance during high-pressure engagements. Integration with shipboard combat systems and networked defense architectures improves situational awareness and coordinated responses across multiple vessels. Stealth-resistant radar, multi-spectral sensors, and adaptive targeting enhance survivability against modern anti-ship threats. Materials innovation, including heat-resistant alloys and lightweight composites, supports high-speed operation and extended durability. Software-defined control systems allow upgrades and adaptability to evolving threats without extensive hardware modifications. The combination of sensor fusion, precision targeting, and rapid response ensures CIWS remain effective against missiles, aircraft, and fast-approaching surface vessels. Technology continues to drive improvements in reaction time, reliability, and operational integration, solidifying CIWS as a critical component of layered naval defense and modern maritime security strategies.
Key Drivers in Global Close In Weapon System (CIWS)
Global CIWS demand is driven by increasing naval threats, including advanced anti-ship missiles, fast attack craft, and low-altitude aerial attacks. Modern naval strategies emphasize layered defense, making CIWS essential for last-line protection of high-value assets. Technological progress in sensor systems, fire control, automation, and targeting accuracy enhances system effectiveness and supports fleet modernization. Naval fleet expansion, coastal defense priorities, and strategic maritime security initiatives encourage procurement and upgrades of CIWS platforms. Integration with combat management systems, networked operations, and multi-vessel coordination increases operational efficiency and situational awareness. Geopolitical tensions, asymmetric threats, and the need for rapid response capabilities reinforce demand for automated, high-speed defense systems. Budget allocation toward defense modernization, international collaboration, and indigenous production programs further drives adoption. Operational experience demonstrates the necessity of reliable last-resort defenses to safeguard vessels and critical maritime infrastructure. Collectively, threat evolution, technological advancement, strategic priorities, and operational requirements form the key drivers of CIWS growth worldwide.
Regional Trends in Global Close In Weapon System (CIWS)
Regional adoption of CIWS reflects naval priorities, threat perceptions, and technological capabilities. North America emphasizes highly automated, network-integrated systems designed for multi-domain fleet protection and high survivability. Europe focuses on modular, interoperable platforms compatible with allied naval forces, emphasizing precision, reliability, and adaptability. Asia-Pacific growth is driven by regional maritime disputes, fleet expansion, and modernization programs requiring last-line defensive solutions. Middle Eastern nations prioritize coastal protection, strategic asset defense, and rapid threat response, often acquiring CIWS through international partnerships. African and South American regions adopt cost-effective platforms to enhance coastal security, counter asymmetric threats, and protect vital infrastructure. Across regions, trends include integration with radar and sensor networks, software-driven upgrades, and enhanced reaction time against emerging threats. Regional differences in naval budgets, technological infrastructure, and threat perception shape procurement and deployment strategies. CIWS platforms remain a central component of modern naval defense, providing reliable last-resort protection for vessels and supporting global maritime security.
Key Close in Weapon System Program:
Raytheon, an RTX business, has secured a $205 million contract from the U.S. Navy to support the continued production of the Phalanx Close-In Weapon System. The agreement includes the delivery of system upgrades, conversions, overhauls, and associated equipment. Phalanx serves as the Navy's final layer of ship self-defense, providing critical protection for sailors against immediate threats. The award reflects the U.S. Navy's continued confidence in the system's effectiveness and reliability. The Phalanx CIWS is a high-rate, radar-guided, computer-controlled gun system designed to counter anti-ship missiles and other close-range threats that penetrate outer defense layers. It is deployed across all classes of U.S. Navy surface combatants and is also in service with the navies of 24 allied countries. The system's operational value was demonstrated in January 2024, when USS Gravely successfully intercepted a Houthi missile in the Red Sea moments before impact, safeguarding more than 300 crew members. Contract work will be performed in Louisville, Kentucky, and at other U.S. facilities through 2029.
Table of Contents
Close In Weapon System Market - Table of Contents
Close In Weapon System Market Report Definition
Close In Weapon System Market Segmentation
By Platform
By Region
By Type
Close In Weapon System Market Analysis for next 10 years
The 10-year close in weapon system market analysis would give a detailed overview of close in weapon system market growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
Market Technologies of Close In Weapon System Market
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
Global Close In Weapon System Market Forecast
The 10-year close in weapon system forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
Regional Close In Weapon System Market Trends & Forecast
The regional close in weapon system market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
Country Analysis of Close In Weapon System Market
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
Opportunity Matrix of Close In Weapon System Market
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Expert Opinions on Close In Weapon System Market Report
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible outlook for this market.
Conclusions
About Aviation and Defense Market Report
List of Tables
- Table 1: 10 Year Market Outlook, 2026-2036
- Table 2: Drivers, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 3: Restraints, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 4: Challenges, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 5: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 6: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 7: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 8: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 9: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 10: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 11: Drivers, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 12: Restraints, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 13: Challenges, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 14: Drivers, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 15: Restraints, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 16: Challenges, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 17: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Region, 2026-2036
- Table 18: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Platform, 2026-2036
- Table 19: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Type, 2026-2036
- Table 20: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Region, 2026-2036
- Table 21: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Platform, 2026-2036
- Table 22: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Type, 2026-2036
List of Figures
- Figure 1: Global CIWS Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 2: Global CIWS Market Forecast, By Region, 2026-2036
- Figure 3: Global CIWS Market Forecast, By Platform, 2026-2036
- Figure 4: Global CIWS Market Forecast, By Type, 2026-2036
- Figure 5: North America, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 6: Europe, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 7: Middle East, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 8: APAC, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 9: South America, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 10: United States, CIWS Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 11: United States, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 12: Canada, CIWS Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 13: Canada, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 14: Italy, CIWS Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 15: Italy, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 16: France, CIWS Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 17: France, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 18: Germany, CIWS Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 19: Germany, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 20: Netherlands, CIWS Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 21: Netherlands, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 22: Belgium, CIWS Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 23: Belgium, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 24: Spain, CIWS Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 25: Spain, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 26: Sweden, CIWS Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 27: Sweden, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 28: Brazil, CIWS Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 29: Brazil, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 30: Australia, CIWS Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 31: Australia, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 32: India, CIWS Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 33: India, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 34: China, CIWS Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 35: China, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 36: Saudi Arabia, CIWS Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 37: Saudi Arabia, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 38: South Korea, CIWS Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 39: South Korea, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 40: Japan, CIWS Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 41: Japan, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 42: Malaysia, CIWS Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 43: Malaysia, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 44: Singapore, CIWS Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 45: Singapore, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 46: United Kingdom, CIWS Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 47: United Kingdom, CIWS Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 48: Opportunity Analysis, CIWS Market, By Region (Cumulative Market), 2026-2036
- Figure 49: Opportunity Analysis, CIWS Market, By Region (CAGR), 2026-2036
- Figure 50: Opportunity Analysis, CIWS Market, By Platform (Cumulative Market), 2026-2036
- Figure 51: Opportunity Analysis, CIWS Market, By Platform (CAGR), 2026-2036
- Figure 52: Opportunity Analysis, CIWS Market, By Type (Cumulative Market), 2026-2036
- Figure 53: Opportunity Analysis, CIWS Market, By Type (CAGR), 2026-2036
- Figure 54: Scenario Analysis, CIWS Market, Cumulative Market, 2026-2036
- Figure 55: Scenario Analysis, CIWS Market, Global Market, 2026-2036
- Figure 56: Scenario 1, CIWS Market, Total Market, 2026-2036
- Figure 57: Scenario 1, CIWS Market, By Region, 2026-2036
- Figure 58: Scenario 1, CIWS Market, By Platform, 2026-2036
- Figure 59: Scenario 1, CIWS Market, By Type, 2026-2036
- Figure 60: Scenario 2, CIWS Market, Total Market, 2026-2036
- Figure 61: Scenario 2, CIWS Market, By Region, 2026-2036
- Figure 62: Scenario 2, CIWS Market, By Platform, 2026-2036
- Figure 63: Scenario 2, CIWS Market, By Type, 2026-2036
- Figure 64: Company Benchmark, CIWS Market, 2026-2036




